Der Beitrag Build vs Buy: E-invoicing Solution Strategy erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- Building your own solution gives you control, but can be risky, and involves significant investment and resources
- Buying an e-invoicing solution offers speed, scalability, and simplicity
- Most enterprises today opt for outsourcing to reduce costs and take the hassle out of complicated compliance processes
Should you build or buy your e-invoicing solution?
If you’re wondering whether to build or buy your e-invoicing solution, the short answer is that for most enterprises, buying is faster, more cost-effective, and less risky – especially as global e-invoicing requirements grow increasingly complex. However, there are specific cases where building in-house may still be worth considering. Ultimately, your decision will depend on many factors, such as your internal capabilities, compliance needs, and strategic priorities.
In-house vs outsourced e-invoicing: what to consider
Deciding between building your own e-invoicing system or purchasing one involves several business-critical factors. What makes most sense for your business will depend largely on the depth of your internal resources and e-invoicing expertise, as well as the strength, flexibility and sustainability of existing technology and processes.
The following chart illustrates the main areas that businesses intending to build an e-invoicing solution will need to ensure they have sufficient capacity to handle internally.
| Capabilities |
Internally built e-invoicing solution | Externally managed e-invoicing solution |
| In-house e-invoicing expertise required |
❌ | ✅ |
| Robust system for tracking ongoing updates |
❌ | ✅ |
| Sufficient resources to handle monitoring and error resolution |
❌ | ✅ |
| Capacity to implement updates |
❌ | ✅ |
| Redundant infrastructure |
❌ | ✅ |
| Redundant staff on duty | ❌ | ✅ |
When does build an e-invoicing solution make sense?
While rare, an in-house approach might work if your organisation:
- Operates in only one or two countries with simple requirements
- Has a large and specialised IT/tax team
- Needs full control over data processing and architecture
- Has long-term budget allocated for ongoing support and compliance
Why most enterprises choose to buy
While many companies still use internally built e-invoicing solutions, externally managed solutions are now by far the more popular choice. Key reasons that businesses opt to buy rather than build an e-invoicing solution include…
1. Insufficient internal tax and IT expertise
E-invoicing compliance demands deep expertise in tax regulations, IT security, and systems integration. Each country enforces unique formats, authentication processes, and reporting obligations, making it challenging for enterprises to maintain in-house knowledge across multiple jurisdictions.
Without dedicated specialists, companies risk compliance failures, fines, and operational inefficiencies. By opting for an external provider, companies can achieve ongoing compliance without internal experts or the need to stay on top of constantly changing regulations.
2. Simpler certification
In many countries, e-invoicing solutions must undergo strict certification processes to gain approval from tax authorities. These certifications often require extensive testing, documentation, and periodic audits to maintain compliance. For enterprises operating across multiple jurisdictions, obtaining and renewing certifications can be resource-intensive. Third-party providers can streamline this process, eliminating this regulatory burden for businesses.
3. More manageable costs
While the up-front costs for some e-invoicing solutions may seem large, they typically are small compared to the cost of building an in-house e-invoicing solution, as this requires substantial investment—not only in initial development and human resources, but also in ongoing maintenance and security. Furthermore, the total cost of an external solution is known and can easily be budgeted for.
4. Reduced risk
Managing e-invoicing in-house exposes businesses to possible compliance failures, penalties, project delays and operational disruptions as regulations evolve. Externally managed solutions eliminate this burden, ensuring seamless updates, regulatory compliance, and security, while allowing internal teams to focus on core business priorities.
5. Increased flexibility
As e-invoicing regulations and company requirements are always evolving, it’s important to have an e-invoicing solution that can adapt and scale accordingly. With in-house solutions, changing requirements can mean time-intensive technical adaptations.
With external solutions, updates – such as expanding compliance to new geographical areas – can typically be implemented extremely fast, as the provider has already done the relevant technical work.
Conclusion
Ultimately, while there may be niche cases where an in-house build makes sense, the vast majority of enterprises find that purchasing an e-invoicing solution delivers faster deployment, greater compliance assurance, and a lower total cost of ownership. Consequently, as regulatory complexity grows, the trend toward external providers is only set to accelerate.
Build vs buy: e-invoicing solution FAQs
What are the hidden costs of building in-house?
Beyond development costs, you’ll need budget for ongoing maintenance, certifications, monitoring, staffing, and upgrades. These costs typically make in-house solutions much more expensive in the long term.
Is buying an e-invoicing solution always faster than building one?
Yes. External solutions are pre-configured for multiple tax authorities and can be implemented rapidly… sometimes in a matter of weeks.
Does outsourcing result in having less control?
Not at all. A good external provider will give you complete visibility into your e-invoicing processes through real-time dashboards, audit trails, and detailed reporting. You retain oversight and control, without the burden of managing compliance and updates in-house.
What happens when regulations change?
With externally managed e-invoicing solutions, updates are automatic. With in-house solutions, your team must continuously monitor and implement changes manually.
Can external solutions be customised to fit specific processes?
Yes. Best-in-class e-invoicing providers offer highly configurable solutions that integrate seamlessly with your ERP and existing workflows. From bespoke routing rules to country-specific compliance logic, a quality provider will tailor the solution to meet your operational, IT, and compliance needs.
Externally managed e-invoicing: see how you could benefit
If managing ever-changing e-invoicing regulations across different countries is eating up your team’s time and energy, it might be time to switch to a smarter approach. At ecosio, we’ve built our Global E-invoicing Compliance solution to remove the headache of fragmented compliance efforts, so your business can stay audit-ready, wherever you operate.
Want to see how it works in action? One of our e-invoicing experts would love to show you.
👉 Get in touch today and discover how easy compliant invoicing can be.
For a deeper dive into our capabilities, check out the full details on our Global E-invoicing Compliance solution page.
Der Beitrag Build vs Buy: E-invoicing Solution Strategy erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Simplifying e-invoicing compliance: a practical approach erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- Manual compliance methods don’t scale and often lead to audits, delays, and IT bottlenecks
- Real-time tax mandates require integrated workflows, connecting ERP data, automation, and technical compliance.
- A scalable setup should enable visibility, repeatable rollouts, and proactive error handling across all countries.
- Fully managed platforms like ecosio’s reduce risk and effort, keeping businesses compliant as mandates evolve.
With e-invoicing mandates accelerating and more and more countries introducing new requirements every year, e-invoicing compliance is becoming a constant challenge.
But the real issue isn’t just the rules, it’s how most businesses try to meet them. Manual workarounds, local tools and support queues may get the job done once, but they don’t scale. They add friction, increase audit stress and inhibit growth.
In this article, we’ll explore:
- Why common approaches to compliance fall short
- What to look for in a scalable e-invoicing setup
- Practical strategies to reduce effort and risk, without starting from scratch every time
- How real-time mandates and tax reporting are reshaping what “compliance” really means
Why traditional compliance setups no longer cut it
E-invoicing compliance sounds simple: understand the rules, send the right format, store the invoice. Done. In practice, it’s anything but.
Most businesses face:
- Constantly evolving local requirements
- Disconnected systems and unclear ownership
- Manual steps and one-off integrations
The result?
- Missed deadlines
- Time-consuming audits
- Reactive rollouts that drain IT and finance teams
And as more governments adopt continuous transaction controls (CTCs), which require invoice data to be sent to tax authorities in real time, legacy systems simply cannot keep up.
E-invoicing, automation and tax reporting are no longer separate
In the past, tax, IT and electronic data interchange functions operated in silos. But those boundaries are disappearing fast.
Today’s compliance requirements go beyond invoicing. Governments increasingly want real-time visibility across entire transactions, from purchase order, to delivery, to invoice. In many countries, mandates already include waybills or purchase orders, and more are coming.
To meet these expectations, businesses need a connected approach that brings together:
- ERP data (e.g. tax rates, line items, delivery terms)
- Workflow automation (e.g. invoice validation and routing)
- Technical compliance (e.g. formats, protocols, audit trails)
That’s why many companies are now rethinking their architecture to reflect the growing convergence of compliance, automation and tax mandates.
Is your e-invoicing setup built to scale?
Before investing in new tools or processes, it’s worth taking a moment to assess how well your current setup is serving you.
Ask yourself:
- Can we track every e-invoice from creation to delivery in one place?
- Are new countries easy to add, or does each rollout feel like a standalone project?
- Is our data stored in an audit-ready format, consistently?
- Do we support both post-audit and real-time (CTC) models?
- How quickly can we adapt if a partner or government changes the rules?
If any of these questions raise doubts, it may be time to rethink your approach. A truly scalable solution should make it easy to stay compliant, no matter how fast mandates evolve.
A practical example: moving from patchwork to platform
Let’s take a fictional but familiar scenario…
The challenge: a European enterprise operates in Germany, Poland and Romania. Each country requires different formats, submission methods and archiving rules. The company uses a mix of manual uploads, local platforms and email-based approvals. Audits are painful, and expanding to new countries feels overwhelming.
A smarter setup would:
- Connect directly to the ERP system
- Route all e-invoices through a central platform
- Automatically apply country-specific validation rules
- Store messages in an audit-ready format
- Allow new countries to be added via configuration, not development
With this approach, compliance becomes part of the process, not a roadblock.
What a scalable e-invoicing setup should look like
Businesses succeeding in this space aren’t doing more; they’re doing things differently. Their setups scale by design and rely on more than just software.
A truly scalable e-invoicing solution should combine powerful automation with ongoing expert support. It’s not enough to have the right tool. You need a partner that monitors, maintains and resolves issues in real time.
Here’s what to aim for:
Centralised visibility
Can you quickly find out where a message is, what rules apply or what was sent last month? A scalable system gives you full access to message flows, compliance data and audit history in one place.
Repeatable rollouts
Each new country shouldn’t feel like a new project. Look for consistent setup flows, predefined country profiles and clear documentation, supported by a team that knows the mandates inside and out.
Built-in flexibility
Can your system adapt to different formats, delivery channels and compliance models without rewriting everything? The ability to handle variability without extra work is key.
Proactive error handling
When something goes wrong, such as invalid formats, failed transmissions or partner mismatches, who fixes it? In a fully managed setup like ecosio’s, errors are caught and resolved before your team even notices. That means fewer tickets, faster resolution and greater peace of mind.
How ecosio enables seamless, future-ready e-invoicing operations
E-invoicing isn’t static, and your solution shouldn’t be either. At ecosio, we continuously adapt our platform in line with emerging mandates and real-world customer needs, so your business stays compliant and efficient without disruption.
Here’s are just some of the ways that commitment has translated into everyday value in the past few months alone:
- You get full control and visibility across your message flows, with real-time access to compliance data, audit-relevant fields and documentation all in one place
- You can expand into new markets faster, thanks to guided, self-service onboarding for countries like Hungary, Poland and Romania that don’t rely on support tickets
- You stay audit-ready without additional prep, as validated invoices are automatically routed to your ERP or archive, already formatted and complete
- You can meet partner-specific requirements with ease, including delivering multiple attachments or handling differing format expectations without manual intervention
- You stay compliant with Germany’s new e-invoicing rules, allowing structured invoices to be sent by email without the need to manually monitor an inbox.
And because ecosio’s Global E-invoicing Compliance solution is fully managed, these capabilities evolve continuously in the background so your teams can focus on growing the business, not chasing compliance.
Final thoughts on turning e-invoicing compliance into a strength
E-invoicing compliance isn’t just a box to tick. It’s a chance to gain control, reduce complexity and move faster across borders.
With the right setup, you can:
- Expand into new markets faster
- Align IT, finance and tax teams
- Stay ready for audits without added effort
- Focus on what drives business, not paperwork
The key is building a system that works for every country, not just the next one. If you’re still getting to grips with real-time mandates, this overview of continuous transaction controls (CTCs) breaks down how they work, what they require and how to prepare for them effectively.
Stay ahead with monthly e-invoicing updates
With international e-invoicing mandates evolving rapidly, staying compliant has never been more important.
To help you stay informed, ecosio’s Product Owner for International E-invoicing, Amy Vahey, hosts a new monthly e-invoicing update video series. Each episode delivers a clear, concise overview of the latest regulatory changes, perfect for businesses expanding into new markets or keeping track of existing requirements.
Watch the latest video now and subscribe to our YouTube channel for instant access to future updates.
Alternatively, if you prefer to stay up-to-date via email, we also run a bi-monthly email “E-invoicing Updates” newsletter!
Der Beitrag Simplifying e-invoicing compliance: a practical approach erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Continuous transaction controls (CTCs) and real-time tax reporting erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- CTCs require invoice data to be shared with tax authorities in real time, shifting compliance from post-audit to live validation
- More countries are adopting CTCs, including for B2C, making technical readiness essential for businesses operating internationally
- Common challenges include system integration, workflow changes, and data security, often requiring cross-department alignment
- CTCs can improve efficiency and audit readiness, especially when supported by scalable solutions and expert guidance
As tax authorities begin to embrace digital tools, the way businesses meet their tax obligations is undergoing a fundamental shift. At the centre of this change is the rise of continuous transaction controls (CTCs).
In this article, we break down what CTCs are, the challenges and benefits they present, and what businesses can do to stay ahead of the curve.
What are CTCs?
Continuous transaction controls (CTCs) are real-time or near-real-time government-imposed mechanisms designed to monitor and regulate business transactions, particularly for VAT compliance. Unlike traditional post-audit models where invoices are reviewed after being issued, CTCs require transactional data, such as e-invoices, to be submitted to or cleared by tax authorities before or during the exchange between buyer and seller.
Why are CTCs growing in popularity?
CTCs are growing in popularity because they allow governments to combat VAT fraud and boost revenue by gaining real-time visibility into business transactions. Traditional tax reporting methods often leave long gaps between invoice issuance and audit, making fraud easier to commit and harder to detect. With continuous transaction controls, tax authorities can validate, approve, or receive transactional data almost instantly, tightening compliance and reducing errors. As digital infrastructure improves and tax gaps remain a priority across regions, more countries are adopting CTC models to modernise their tax systems and ensure better control over domestic and cross-border trade.
How do CTCs work?
Continuous transaction controls (CTCs) change how invoices are processed by requiring businesses to share invoice data with tax authorities in real time, often before sending the invoice to the customer. This contrasts with traditional invoicing, where reporting happens later and in bulk.
Here’s how the CTC process typically works from a technical perspective:
- Invoice creation: A structured e-invoice (in a machine-readable format such as XML or UBL) is generated within the business’s ERP or invoicing system
- Data transmission: The invoice data is sent electronically (often via an API) to a government portal or central tax platform
- Validation by authorities: The tax authority automatically checks the invoice for required fields, accuracy, and compliance with local tax rules
- Clearance or acknowledgment: If the invoice passes validation, the authority either clears it for dispatch or provides a confirmation receipt
- Invoice delivery: The validated invoice is then sent to the buyer, often with an official code or reference attached
This automated process increases transparency and control for tax authorities, while requiring businesses to adopt compliant technical infrastructure.
Why companies can’t ignore CTCs
It’s the law!
More and more countries are implementing CTCs on a mandatory basis. Italy, for example, has been using CTCs across the board since 2019. Meanwhile, France, Poland and Spain are following suit with a staggered introduction.
CTCs are expanding to include B2C transactions too
While the first mandatory CTCs focussed on B2B transactions, the B2C sector is increasingly taking centre stage. Countries such as Romania, Malaysia and Saudi Arabia already require the reporting of B2C transactions, and France will soon too.
Common CTC challenges
Adopting continuous transaction controls (CTCs) can require significant technical and organisational change, with businesses often facing the following hurdles:
- Technical integration: Connecting to government platforms typically involves API-based communication and generating structured e-invoices, which many legacy systems aren’t equipped for.
- Data protection and security: Sensitive invoice data must be transmitted externally, often in real time. Internal teams must ensure systems and processes comply with GDPR and local security laws, without exposing the business to data breaches or non-compliance.
- Process adjustments: In many CTC models, invoices must be validated by authorities before reaching the customer. This demands new workflows, timing, and automation.
- Employee training: Teams across finance, IT, and compliance must understand and implement the new requirements accurately to avoid errors or delays.
Successfully addressing these challenges often involves cross-department collaboration and, in many cases, external support or specialised tools.
How can CTCs benefit companies?
While CTCs are typically seen as a headache by companies due to the effort involved in preparing for them, they do benefit businesses in several ways, including…
- Efficiency gains through expansion of automated processes
- Reduced manual effort relating to tax reporting
- Improved transparency for accounting and auditing
- Fewer queries from authorities
- Faster tax processing
How should you prepare for CTCs?
Being able to comply with CTCs requires strategic preparation – not only technically, but also organisationally. To ensure your business is ready, be sure to follow these steps and ask yourself the accompanying questions:
1. Analyse the status quo
Start by mapping your current invoicing processes and tools to understand your baseline. This helps reveal what already works and what needs updating.
Questions to ask include:
- Which systems are in use (ERP, accounting, archiving)?
- Are invoicing workflows already digital or partly automated?
- Do your current tools support e-invoicing formats?
- What level of integration already exists between systems?
2. Identify technical and personnel gaps
Once your baseline is clear, assess where capability gaps exist, both technical and human.
Questions to ask include:
- Can your system create structured invoices (e.g. XRechnung, ZUGFeRD)?
- Do you support required formats and transmission protocols?
- Does your team have sufficient understanding of API integrations and validation flows?
- Would it be beneficial for representatives from IT, finance, or purchasing to have more involvement moving forward?
3. Consider future requirements
Preparing for CTCs means looking beyond immediate needs. Future mandates may vary by country, customer type, and industry, so maintaining flexibility is key.
Questions to ask include:
- Are CTCs likely to affect any countries in which you operate in the near future?
- What mandatory data is required for compliance?
- How can you prepare this data in your ERP system?
- Which transactions are affected (B2B, B2G, B2C)?
- Do certain customers or industries have extra requirements?
4. Decide whether you want to build or buy
If you have limited internal resources or expect your needs to change in the future, an external solution provider can make life a lot easier.
Questions to ask include:
- Do you have the capacity and expertise to handle CTC compliance in-house?
- Have you fully investigated what external CTC-ready solutions and integrations are available?
- Will your chosen solution scale across markets and evolving rules?
Still have questions?
If you want to know more about continuous transaction controls and what you need to do to achieve compliance with various country-specific regulations, get in touch! Our e-invoicing experts will be more than happy to advise you.
Der Beitrag Continuous transaction controls (CTCs) and real-time tax reporting erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag E-invoicing Tools: How Self-Service Connectors Reduce Setup Struggles erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- Self-service connectors allow suppliers to configure their own e-invoicing connection without relying on technical teams, speeding up onboarding
- These tools reduce setup struggles by automating processes, minimising manual intervention, and providing guided configuration steps
- Benefits include faster supplier activation, fewer errors during setup, and lower demands on internal resources
- Self-service connectors support multiple document formats and transmission protocols, enabling flexible integration with various customer requirements
Many businesses today are prioritising digitisation, driven both by the need to boost internal efficiency and the pressure to comply with a growing number of e-invoicing regulations. Although digitisation offers advantages such as greater accuracy, setting up certain e-invoicing tools – specifically protocol connectors (the digital pipelines that transmit, validate, and deliver invoices across platforms and tax authorities) – can be a complicated process, and one that often results in delays, inefficiencies, and increased operational risk.
Why are protocol connectors crucial e-invoicing tools?
E-invoicing protocol connectors are technical integrations that allow invoice data to be exchanged between systems in a compliant, secure, and automated way. They are the linchpins of the e-invoicing process, especially in countries adopting continuous transaction control (CTC) models, where real-time or near-real-time validation by tax authorities is mandatory.
Without properly configured connectors, the e-invoicing workflow breaks down. These connectors help in tasks such as authenticating credentials and then transmitting data to and from intermediaries or government platforms. They are essential for ensuring that an invoice reaches its destination in a compliant form.
What does a typical e-invoicing flow look like?
To appreciate the critical role of protocol connectors in global e-invoicing, it’s essential to understand how an invoice travels through the system in countries employing a CTC clearance and centralised model, such as Poland, Romania, and Hungary. These frameworks mandate a highly structured, real-time exchange of invoice data between suppliers, intermediaries, tax authorities, and buyers.
- Step 1: Invoice creation in the ERP system
The process begins with the supplier generating an invoice within their ERP or financial software. At this stage, compliance with local tax codes, field-level requirements, and document formatting is essential. While the invoice exists digitally, it is not yet compliant until it has been validated by national authorities – a step that hinges on subsequent data transmission enabled by protocol connectors.
- Step 2: Transmission to the integration platform (via ERP connectors)
Rather than submitting the invoice directly to the government platform, it is passed to an integration layer, such as ecosio’s managed service. Here, protocol connectors perform several critical technical functions:
- Authentication: Confirming the identity and authority of the sending party
- Data transformation: Converting the invoice from ERP-native formats to the schema required by the specific national platform (e.g., XML for KSeF or ANAF)
- Secure transport: Managing communication protocols such as AS4, REST API, or SFTP to ensure encrypted, tamper-proof data exchange
The connector acts as a real-time translator, courier, and gatekeeper, ensuring the invoice is properly prepped and transmitted under the right parameters.
- Step 3: Submission to the government platform via an authorised intermediary
Once formatted and packaged, the invoice is submitted to the centralised tax authority system through an intermediary explicitly authorised by the supplier. This intermediary may be a third party or, in many cases, the integration platform provider itself. The protocol connector remains active in this step, managing session handling, error feedback loops, and ensuring message integrity.
Government systems such as Romania’s ANAF, Poland’s KSeF, and Hungary’s NAV require exacting standards for submission. The protocol connector ensures these standards are met, right down to the required headers, tokens, and cryptographic signatures.
- Step 4: Validation or clearance by the tax authority
Upon successful receipt, the invoice undergoes validation by the tax authority. This may include syntax checks, VAT ID verification, or structural conformity with local compliance rules. Depending on the CTC model, the authority may also assign a clearance ID, signature hash, or digital stamp.
While this validation happens outside the connector, the connector is responsible for relaying clearance statuses and official metadata back to the sender or onward to the buyer. It ensures that the feedback loop is uninterrupted and properly logged—often integrating directly into the ERP to reflect updated document statuses.
- Step 5: Invoice delivery to the buyer
After clearance, the approved invoice is delivered to the buyer. Delivery may be executed by the tax authority or relayed back through the integration platform. In some jurisdictions, the invoice will carry government-issued metadata, such as clearance stamps or timestamps, indicating successful processing.
Once again, the protocol connector ensures the invoice and any additional compliance artifacts (such as clearance codes or timestamps) are securely delivered to the appropriate recipient system – be it another ERP, archive system, or downstream accounting tool.
The strategic role of protocol connectors in CTC compliance
Across every stage of the CTC e-invoicing lifecycle, protocol connectors act as the central nervous system. They do more than just “connect systems”…
- They actively enforce technical compliance, provide traceability, and reduce the risk of failed transactions
- They bridge complex systems and national platforms with real-time adaptability
- They minimise manual intervention, making compliance repeatable and scalable
- They enable auditable, secure communication channels aligned with national and international data security standards
In CTC environments, where delays, rejections, or invalid formats can result in regulatory penalties or revenue disruption, a well-implemented protocol connector isn’t just helpful; it’s essential.
Common connector issues
Delays
For example, a delay in invoice clearance due to improperly mapped XML fields can cause significant disruption to the order-to-cash cycle, particularly in just-in-time supply chains where payment triggers are tightly linked to invoice approval.
Rejections
A rejection stemming from missing authentication tokens can require manual intervention and resubmission, leading to bottlenecks.
Compliance breach
A compliance breach, such as failure to include mandatory tax identification elements, can not only halt invoice processing, but also expose the business to fines, audits, and reputational damage.
Challenges for enterprises
Challenges for business users: lost in translation
For business users, protocol connectors often feel like a technical black box. They know that successful setup is essential to meet compliance requirements and enable invoice automation, yet they rarely understand the technical details.
This lack of visibility leads to a range of challenges, including:
- Knowledge gaps: Most business users aren’t familiar with protocols like AS4, SFTP, or REST APIs, which are often required to establish secure, real-time connections with tax authorities or intermediaries.
- Manual communication: Historically, the exchange of sensitive setup details (like endpoint URLs, certificates, or authentication credentials) has taken place via insecure, manual methods such as email or internal chat. This not only slows down implementation but also increases the risk of errors and data breaches.
- Dependency on IT or external vendors: Without a self-service option, business teams are entirely reliant on technical staff or third-party providers, which can easily lead to delays, miscommunication, and unnecessary costs.
Challenges for technical users: missing the business context
On the other hand, while technical users may be well-versed in API integrations or ERP configuration, that doesn’t mean they’re equipped to handle e-invoicing protocol connectors. For technical users, the challenge lies not in technical execution, but in understanding what needs to be implemented for compliance in each specific country.
Key pain points include:
- Unclear or incomplete requirements: Different countries have vastly different rules and formats for e-invoicing, often buried in hard-to-navigate government websites or fragmented documentation.
- Lack of end-to-end guidance: Without clear, actionable steps tied to each country’s compliance model, IT teams are left piecing together information, risking missteps that can delay or derail deployment.
- Cross-functional bottlenecks: IT often needs input from finance or legal teams to ensure proper invoice content or tax requirements, creating organisational friction and slowing down projects.
Complexity multiplier: navigating CTC model requirements
The global shift towards Continuous Transaction Controls (CTC) is intensifying the pressure created by the surge of e-invoicing mandates. In CTC models, invoice data must be sent to and validated by a tax authority before it reaches the buyer. This introduces a real-time compliance requirement, making robust and accurate protocol integration essential.
Countries such as Romania (RO e-Factura), Poland (KSeF), and Malaysia (MyInvois) already mandate or plan to mandate CTC frameworks. These systems require:
- Precise, secure API connections with central government platforms
- Automated credential handling using government-issued tokens or digital certificates
- Detailed format mapping to ensure the invoice conforms to national standards (often XML-based)
For multinational enterprises, this means managing multiple, often inconsistent connection protocols across countries, which can overwhelm even experienced technical teams.
The ecosio solution: self-service country connectors
To address these issues, ecosio has introduced e-invoicing tools purpose-built for real-world challenges: self-service country connectors. These connectors offer structured, guided support within the ecosio Monitor, making it easier for both technical and business users to establish efficient and reliable e-invoicing connections with selected countries.
What sets ecosio’s approach apart:
- User-friendly design tailored to both tech-savvy users and business stakeholders
- Step-by-step country-specific guidance with screenshots and checklists carefully tailored by our e-invoicing specialist team
- Pre-validated connection points that streamline integration and minimise trial-and-error
Whether you’re onboarding to Romania’s ANAF system, Poland’s KSeF, or Hungary’s NAV (the countries where ecosio’s Self Service connectors are already available), the goal is the same: reduce friction, boost confidence, and accelerate your compliance journey.
ecosio’s self-service country connectors make this possible by replacing manual credential exchange with a guided interface tailored to each country’s regulatory requirements. In Hungary and Poland, this structured approach improves efficiency and reduces errors, while in Romania, it provides added automation to further simplify onboarding and faster integration with ANAF.
Designed to eliminate confusion and manual back-and-forth, these e-invoicing tools empower users to manage complex e-invoicing mandates confidently and independently. By delivering country-specific clarity and streamlined setup processes, ecosio helps businesses minimise risk, adapt quickly to evolving regulations, and focus on what matters most – achieving full e-invoicing compliance with speed and precision.
Why this matters
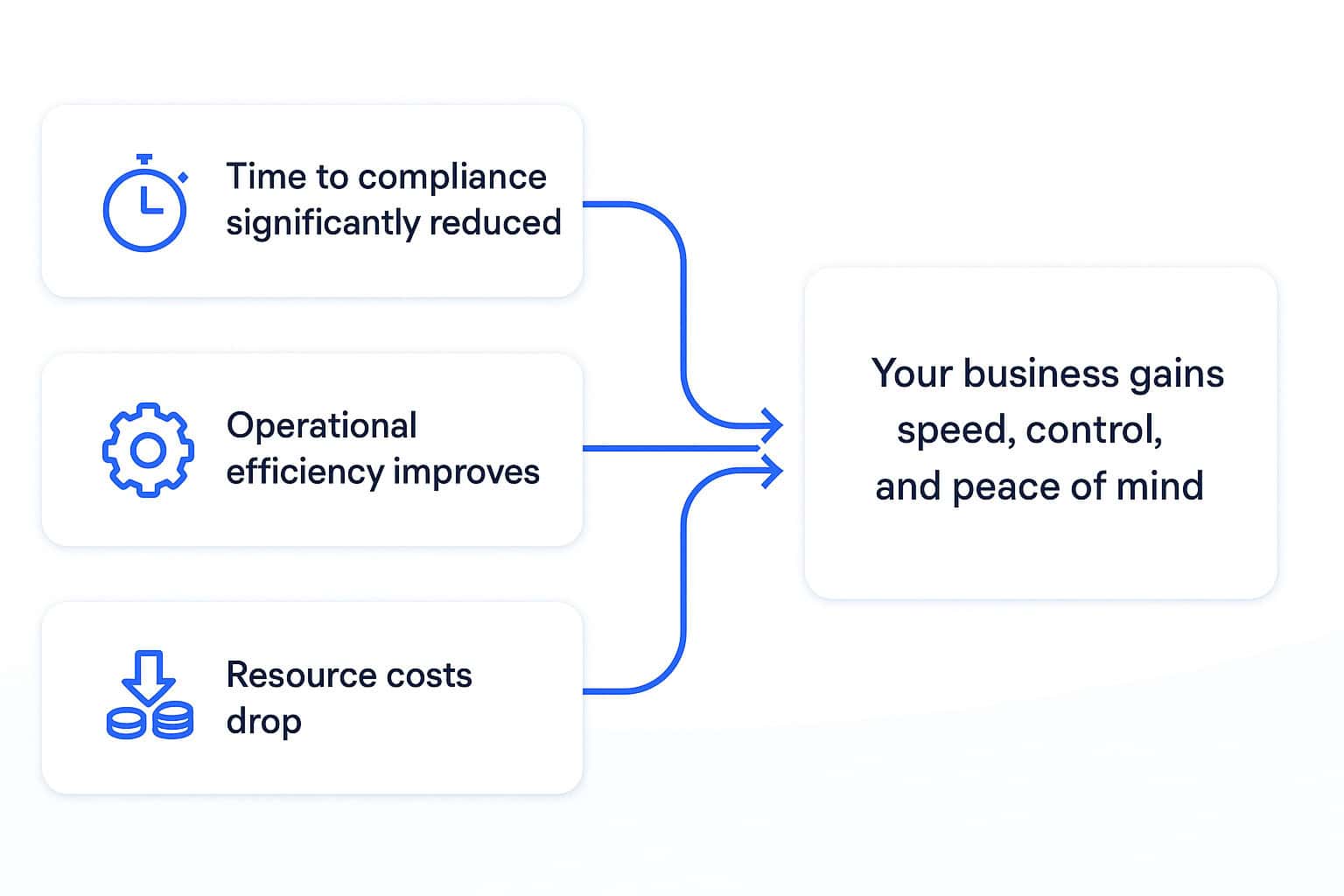
The difference between a well-implemented e-invoicing connector and a flawed one isn’t just technical – it’s strategic.
With ecosio’s approach:
- Time to compliance is shortened, helping you avoid regulatory penalties.
- Operational efficiency improves, as teams waste less time troubleshooting and reworking failed connection implementation.
- Resource costs drop, reducing reliance on external service providers or overburdened internal teams.
Ultimately, your business gains speed, control, and peace of mind.
How to use self-service connectors in the ecosio Monitor
Setting up a supported protocol connector with ecosio Monitor is now a guided, intuitive process. Here’s how it works:
- Request the connector to be added to your ecosio Monitor instance: Contact the ecosio’s Onboarding and Operations team and request the connector to be provisioned for your instance, accessible in the “Connectors” section of the ecosio Monitor, ready for setup.
- Navigate to “Connectors”: Log in to ecosio Monitor and go to the “Connectors” section.
- Choose e-invoicing connectors: Select the appropriate setup option from the dashboard.
- Country-specific guidance: Based on your onboarding flow, the platform presents tailored documentation (e.g. Romania – ANAF guide) with detailed steps.
- Follow the instructions: Utilise the step-by-step comprehensive guidance – including credential requirements, and error handling tips – to complete your connector setup successfully.
Et voilá! Your connection is set up, you’re fully compliant and ready to send e-invoices. Try it yourself with our step-by-step demo:
Limitations to keep in mind
While ecosio’s self-service solution marks a major step forward, it’s important to acknowledge its current limitations:
- Limited country availability: At present, connectors are only available for select CTC-model countries, with more to follow.
- Not universal: Countries using decentralised or post-audit models (e.g. Germany and Belgium) are currently outside the scope of self-service documentation for now.
- Focus on CTC: E-invoicing tools are most valuable where direct API integration with government platforms is required.
Even with these limitations, the solution significantly reduces friction in some of the most complex regulatory environments.
The future of e-invoicing tools and processes: unified and user-centric
ecosio’s vision doesn’t stop at today’s capabilities. The roadmap for self-service country connectors includes:
- Expanded country coverage to match evolving mandates
- Simplified technical documentation to further ease implementation
- A smarter interface that adapts based on your country, business model, and ERP environment
The end goal? A fully unified and intuitive e-invoicing setup process that anyone can navigate, no matter their role or background.
Conclusion
E-invoicing protocol connectors are complex e-invoicing tools, but a critical component of compliance. For too long, they’ve been a source of frustration for both business and technical users. With the rise of CTC models and real-time validation requirements, this challenge will only grow.
Thankfully, it doesn’t have to be this way. With ecosio’s self-service country connectors, what was once a maze of uncertainty can become a fast, guided path to success.
Want more information?
If you’d like to see how protocol connectors could transform the efficiency of your EDI processes, why not speak to one of our EDI experts? We’re always happy to help!
Der Beitrag E-invoicing Tools: How Self-Service Connectors Reduce Setup Struggles erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag ecosio Insights: E-invoicing Mandates and the Growth of B2B Process Automation erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>To explore the latest trends and challenges in this space, we sat down with ecosio ‘s E-invoicing Product Manager, Chris Newman. In this interview, Chris shares his expert insights into the future of e-invoicing, including how businesses can prepare for upcoming e-invoicing mandates, the role of emerging technologies, and the importance of global cooperation in shaping the future of electronic invoicing systems.
————————————————————————
How do you expect e-invoicing to evolve over the next few years?
The global e-invoicing landscape is undergoing significant transformation. In addition to a continued expansion of e-invoicing mandates, one key trend I expect to continue is the adoption of Continuous Transaction Controls (CTCs). These help governments to combat VAT fraud and tax evasion by requiring real-time or near-real-time reporting of the invoice or a subset of transactional data to central platforms.
I also expect interoperability to become a key concern, as more countries mandate electronic invoicing across B2B, B2G, and B2C transactions. This trend is driving the adoption of global standards and frameworks such as Peppol, which facilitates seamless cross-border transactions and ensures compliance with varying national requirements.
Last, but not least, we should see the integration of e-invoicing with broader compliance initiatives, such as e-transport systems, which track the movement of goods to ensure accurate VAT reporting and delivery verification. Countries like Romania, Serbia, and Hungary are already implementing these systems, and I expect others to follow as we move towards more comprehensive compliance frameworks.
Will emerging technologies have a role to play in e-invoicing processes moving forward?
New technologies will undoubtedly play a significant role in enhancing e-invoicing processes moving forward. At ecosio, for example, we are already leveraging AI to enhance our solutions and reduce risk for clients. Meanwhile, governments are also recognising the potential for AI to optimise compliance processes, with some already using AI to identify fraud that would previously have taken weeks to uncover. As is always the case with integration of AI, however, it must be managed carefully if accuracy is to be maintained.
Transitioning to cloud-based solutions is also transforming how businesses handle e-invoicing. Modern cloud architecture offers scalability, instant accessibility and capacity for real-time processing, providing seamless integration between financial systems and enhancing transactional transparency.
Do you anticipate that governments will expand B2B automation requirements beyond invoicing processes?
Yes, I think this is certainly going to happen in many countries moving forward. In fact, several countries have already made progress in this direction. For instance, the United Kingdom, besides e-invoices, also mandates electronic purchase orders and advanced shipping notices for medical suppliers engaging with healthcare providers. Similarly, Italy mandates the use of electronic purchase orders in the public healthcare system.
As already mentioned, e-transportation initiatives are also on the rise, which involves the monitoring and tracking of high fiscal goods during transit. Therefore we can expect to see more countries introducing their own initiatives.
Is there any hope for a universal e-invoicing standard?
It’s certainly true that we’re heading in the right direction. Standards like EN 16931, initially developed for B2G invoicing under EU Directive 2014/55, are now expanding into the B2B sphere across Europe and even countries like Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Singapore and Australia. Similarly, interoperability frameworks such as Peppol are gaining significant traction. However, full global alignment remains highly improbable due to proven, established systems that have been in place for a long time, which is the case in Latin America. While e-invoicing may become more unified in some regions, we won’t see a universal standard emerge any time soon.
What role will global cooperation play in the further development of e-invoicing?
If e-invoicing is to become as simple and efficient as possible, global cooperation is essential. While developing a system specifically to tackle local needs may have seemed logical for the first countries to implement mandatory e-invoicing, this quickly led to fragmentation and overly complicated cross-border transactions.
Thankfully, however, recent years have seen significant steps taken towards international cooperation. In particular, initiatives like the EU’s VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) and the Peppol International Invoice (PINT) exemplify the potential of collaboration. By adopting the EN 16931 standard, ViDA aims to harmonise digital reporting across the EU, facilitating seamless cross-border transactions while enhancing automation and reducing administrative burdens for businesses. Meanwhile, PINT bridges global standards with local requirements, as demonstrated by its adoption in countries such as Japan (PINT-JP), Malaysia (PINT-MY), Singapore (PINT-SG), and Australia & New Zealand (PINT-A-NZ). These efforts not only promote efficiency but also highlight the necessity of international alignment to ensure the sustainable development of e-invoicing systems worldwide.
What are the biggest challenges businesses face when integrating and upgrading e-invoicing systems?
One of the primary challenges is being able to extract the required information from multiple systems. Many multinational organisations utilise a variety of ERP systems, which makes data identification and retrieval extremely difficult. Once the data is located, businesses must generate compliant invoices and establish connections with solution providers capable of handling requirements and meeting e-invoicing mandates across multiple markets.
Another major challenge is ensuring the data meets the necessary quality standards for these systems to function effectively. While solution providers can help to some extent here, issues concerning data quality will require significant internal commitment to resolve.
What lessons can businesses learn from early adopters of e-invoicing systems?
From what I have seen, one of the most crucial mistakes businesses make when implementing an e-invoicing solution is failing to assemble a cross-functional team with expertise in IT, finance, and tax. Without the input of experts in each of these areas, projects are much more likely to encounter challenges down the line.
Many early adopters – particularly those operating cross-border – also underestimated just how complicated managing e-invoicing internally would become, as e-invoicing mandates grew steadily more numerous and complex. Thankfully, partnering with a specialised solution provider can alleviate much of the burden, from handling country-specific connectivity requirements to ensuring compliance with technical specifications.
How important is employee training in the successful implementation of e-invoicing?
It’s crucial! While solution providers like ecosio manage most e-invoicing processes, businesses must ensure their internal teams have the expertise to manage responsibilities within their ERP systems. This includes understanding required data fields, output formats and transmission protocols like APIs or AS4.
Trained employees are also essential for managing e-invoicing workflows and addressing unique use cases. Without this internal knowledge, businesses may face significant challenges during implementation and will find it much harder to achieve long term success.
Do you have any advice for managing the increasing complexity of e-invoicing mandates?
My first recommendation would be to prepare for upcoming e-invoicing mandates and requirements as soon as new regulations are announced… if not before! Implementation of a new solution can be a lengthy process, particularly for larger companies with multiple ERP systems. Plus companies also need to understand technical compliance demands and build a capable project team. Proactively adapting systems in advance of upcoming mandates not only eliminates the danger of non-compliance penalties, which can be very severe in some jurisdictions (such as jail time for CEOs in Malaysia), but also provides a competitive advantage.
My second recommendation would be to invest in external e-invoicing expertise. As more and more countries introduce e-invoicing mandates, it is becoming increasingly unrealistic for internal teams at multinational companies to stay on top of constantly changing requirements. External providers can prove invaluable in helping to minimise risk and futureproof e-invoicing processes.
Der Beitrag ecosio Insights: E-invoicing Mandates and the Growth of B2B Process Automation erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag ecosio Insights: VAT Compliance erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>To provide insights into how organisations can prepare for these changes and remain compliant, we spoke with Gunjan Tripathi, EMEA Director, Solutions Marketing at Vertex Inc. In the following interview, Gunjan shares her expert perspective on the impact of digitalisation on VAT compliance, the challenges posed by real-time reporting requirements, and what businesses must prioritise to stay ahead of regulatory developments.
————————————————————————
How has the global movement towards digitalisation impacted businesses’ VAT compliance and reporting requirements?
In recent years, governments have made a conscious effort to upgrade their technological capabilities in order to collect, analyse, and compare taxpayer data more efficiently and accurately. In the European Union, Member States now consolidate and analyse tax data, meaning businesses are required to provide more detailed information more frequently. The shift from paper-based VAT returns to online submissions and API-driven processes reflects this evolution, with a growing emphasis on improving data quality, transparency and security.
Processes that previously allowed for extended preparation times now demand near real-time data reporting with upfront accuracy and granular transactional information. This has compressed compliance & reporting timelines, increased complexity, and necessitated updates to current systems and workflows to ensure data is clean, accurate, and compliant from the outset.
How do you see VAT regulations evolving over the next few years?
Over the coming years we’re likely to see a continuation of the current trend towards digitalisation and transparency. We’re also already seeing a greater focus on cross-border regulations as governments seek to eliminate opportunities for Missing Trader Intra-Community (MTIC) fraud, with initiatives like VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) bringing more cross-border transactions under scope of local VAT reporting. Enabled by technology, tax authorities will soon be capable of collecting, sharing, and analysing data across jurisdictions, providing greater visibility into business operations and allowing for benchmarking against industry standards.
While tax authorities have historically been focussed solely on theoretical and legal frameworks, modern legislation now also mandates specific IT processes for data reporting and compliance. This trend towards a more detailed “show your working” approach reflects tax authorities’ growing appetite for visibility of how businesses derive and report their VAT calculations.
As supply chains become more complex and commerce accelerates, technology is transforming compliance from a reactive process into a real-time – sometimes even predictive – activity, allowing businesses and tax authorities to track and allocate tax obligations seamlessly.
How do you see VAT regulations influencing business decisions?
As VAT is inextricably tied to a business’s bottom line, having a proper understanding of VAT requirements is essential for developing pricing strategies and fostering smoother interactions with customers and partners. Proactively addressing VAT considerations with business partners can also reduce friction, improve cash flow, and minimise delays in payments, ensuring that tax compliance doesn’t become a barrier to successful commercial transactions or international expansion.
What should companies prioritise in their VAT compliance strategy to stay ahead of potential regulatory changes?
For me, the key priority should be data integrity. Ensuring clean, traceable data that originates from a single source of truth is critical for accurate and efficient reporting. Good data integrity enables businesses to adapt data for varying requirements across tax authorities while maintaining a consolidated and centralised view of operations.
Tax should also never be treated as an afterthought. It needs to be a central component during planning. By integrating tax compliance into operational and technological frameworks from the outset, businesses enable direct, real-time access to accurate data, reducing the need for retrospective corrections and building resilience against future regulatory changes.
What are the primary ways businesses can optimise their VAT processes to remain competitive?
I would recommend that businesses focus on standardising their processes across jurisdictions wherever possible. A unified approach to VAT reporting, with minimal reliance on country-specific solutions, allows for better oversight, reduced resource dependency, and improved efficiency. Investing in holistic systems or partners that cater to multiple requirements will streamline operations and maximise the return on technology and personnel investments. While some edge cases may require tailored solutions, maintaining a centralised, flexible framework is key to sustainable and continuous VAT compliance, while staying competitive for business operations.
As tax authorities adopt new digital reporting tools, what compliance issues should companies anticipate?
Tax audits today are not simply concerned with whether or not you have interpreted the law correctly. Increasingly, auditors are analysing data trails and identifying anomalies through statistical testing and regressions. In order to withstand this increased technical scrutiny, businesses should ensure data is as clean and consistent as possible.
How do you anticipate the EU’s VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) initiative will impact VAT compliance and reporting for businesses?
In a nutshell, ViDA’s goal is to streamline cross-border transactions and enhance transparency by introducing uniform e-invoicing standards for even domestic transactions across Member States. This harmonisation will require businesses to adopt invoicing systems that comply with the new EU-wide standards, moving away from disparate national regulations. Consequently, companies must invest in technology and training to ensure their invoicing processes align with these forthcoming requirements.
Additionally, ViDA’s emphasis on real-time or near real-time reporting will mean that businesses will have to maintain up-to-date and accurate transaction records. This shift is designed to improve VAT collection efficiency and reduce fraud. However, it also means that companies will need to enhance their data management practices and ensure seamless integration between their accounting systems and tax authorities’ platforms. While these changes may present initial challenges, they should ultimately lead to a more efficient and transparent VAT system across the EU.
What steps should companies start taking now to prepare for the upcoming changes associated with the ViDA initiative?
There are two clear things that companies should be doing to prepare for ViDA. First, as we’ve already mentioned, companies must prioritise data quality and consistency, as without good data all optimisation initiatives are doomed to fail. Secondly, businesses should consider transitioning from a point solution approach to a centralised process and technology solution. Given the complexity of new reporting regulations and the speed at which country-specific legislation is being introduced, attempting to handle changes manually would be unfeasible. By contrast, enlisting the help of a dedicated solution provider offers an efficient and cost-effective way to ensure compliance and audit-readiness moving forward.
What are the top three pieces of advice you would give businesses to prepare for future VAT and tax policy shifts?
Firstly, it would be advisable to establish a centralised tax policy and operational methodology to maintain consistency across jurisdictions. Secondly, businesses should conduct a thorough supply chain analysis to understand and manage tax exposures effectively. And last, but not least, businesses should get IT and finance teams to implement standardised and compliant processes, as standardisation is a prerequisite for optimisation.
But these steps take time, so it’s important not to put them off!
Der Beitrag ecosio Insights: VAT Compliance erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag How to Manage the Growing Challenges of Tax Reporting, B2B integration and E-invoicing erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- Tax reporting is becoming more complex due to diverse national regulations and frequent legislative changes, requiring adaptable solutions
- B2B integration demands the ability to connect with multiple systems, formats, and protocols while maintaining data accuracy and process efficiency
- E-invoicing compliance involves meeting varying legal requirements, integrating with ERP systems, and handling real-time reporting obligations
- ecosio enables seamless data exchange, ensures compliance with country-specific regulations, and reduces the internal effort needed for integration and reporting
To the objective observer, modern B2B transactions are faster, more secure and more detailed than ever. Yet this constant drive towards efficiency is only partly due to organic process improvement within these organisations. Another key piece of the puzzle is the growing maze of mandates covering everything from tax reporting to logistics documents such as waybills and e-invoices.
Despite being largely responsible for the speed of improvement of B2B payment processes worldwide, increasingly complex requirements are becoming an issue for many businesses.
With governments around the world tightening regulations and increasing their focus on transparency, companies today are under growing pressure to meet stringent requirements that often seem to pull them in conflicting directions. At the same time as being required to prioritise accuracy and data visibility to comply with new tax responsibilities, businesses are also required to adapt their systems to accommodate new electronic invoicing regulations. Meanwhile, there’s also a constant internal push to expand automation in order to improve efficiency.
As a result, many organisations find themselves struggling to keep up, unsure of how to manage the intersection of these key areas.
In this article, we’ll explore the implications of this situation and discuss strategies for effectively balancing compliance and automation moving forward.
Before we discuss the relationship between compliance and automation, however, let’s first look in a bit more detail at the recent explosion of mandates across these areas…
The growing governmental appetite for data
In recent years we’ve seen a significant shift in how governments worldwide approach tax collection. CTC mandates are popping up at a rapid pace, driven by a hunger for real-time data. No longer are governments content with just the basic information; they want to know every detail about every transaction.
By far the clearest evidence of the growing appetite for data over the past decade is the pace at which countries across Europe and beyond have introduced e-invoicing requirements for various types of transaction. The start of this wave can be traced back to the passing of the EU Directive 2014/55/EU on 16 April 2014, which set deadlines for invoice recipients in public tenders to be able to accept e-invoices. Since then, many countries have gone much further – extending e-invoicing requirements beyond B2G connections to many (and sometimes all) B2B transactions.
But the hunger for data doesn’t stop at invoicing. We’re already seeing signs that the same will happen for logistics processes, with Romania, India, and Turkey having recently introduced waybill systems. When looking at B2G processes, we also see a trend towards electronic purchase orders, particularly in the Scandinavian countries. Since B2G often paves the way for B2B mandates afterwards, we are quite likely to see electronic purchase orders becoming part of future mandates.
Realistically, it’s only a matter of time before the need for detailed, real-time data becomes the norm across all aspects of business transactions.
Why is the demand for data growing?
To understand why there’s such a growing demand for data, we need to take a step back and look at the bigger picture. Taxation, at its core, is a means for governments to collect revenue for public services. But to ensure that taxes are being accurately assessed and collected, there needs to be a robust system in place for verifying the legitimacy of the transactions on which these taxes are based.
This is where data comes into play. To determine if the tax associated with a delivery of goods or services is legitimate, one needs to follow the audit trail of that transaction. This means not only looking at the invoice but also cross-checking it against the associated delivery and order documents.
For example, if a company reports an invoice for a delivery of goods, rather than taking the invoice at face value, the tax authority often verifies that the goods were actually delivered and that the terms of the invoice match the original purchase order. Such validations usually happen on a random sample basis post audit.
In order to allow for a real time verification and accurate cross-referencing of invoice documents against the underlying purchase order and delivery documents, authorities will need to have relevant information available in real time on their side. The following figure shows the concept of data reconciliation between an invoice document and an underlying purchase order and despatch advice document.
Consequently further mandates requiring delivery and purchase order information to be made available to the authorities (such as the recent waybill mandates in Turkey) are likely to be implemented more widely. Similarly, China also offers a useful window into what the future may hold here. Instead of managing tax collection through an invoice document, China wants to manage tax through big data. While data protection and legal regulations might prevent such an extensive approach in most countries, the direction in which tax collection is heading is clear.
But the push for greater data transparency is about more than just ensuring accurate tax collection. The recent tidal wave of e-invoicing mandates was principally inspired by a desire to combat fraud and reduce the shadow economy (as evidenced by the rigour with which the EU is tracking the reduction of the VAT gap). By requiring businesses to submit detailed, real-time data, governments can more easily detect suspicious activity, such as underreporting of sales or over-inflating expenses. In this way, the growing demand for data serves as both a revenue assurance measure and a tool for maintaining the integrity of the tax system.
The graph below shows the difference between the VAT gap in EU countries between 2020 and 2021:
Source: https://taxation-customs.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2023-10/VAT%20Gap%20Report%202023_0.pdf
What does the future hold?
As we’ve already touched on, the future of tax reporting and data collection is likely to see an even greater emphasis on detailed, real-time data. When we examine the current trends in international mandates, it’s clear that governments aren’t just content with capturing invoice data. They’re also increasingly interested in data relating to logistics and ordering.
“Peppol was not built as simply a tool to streamline e-invoicing, but rather as a comprehensive network infrastructure. All the technologies necessary to fulfill further mandate requirements covering purchase orders and dispatch advice messages are already there ready to be used.”
Philip Helger
Over the coming years it’s very likely that we’ll start to see mandates covering a wider spectrum of B2B communications. In particular, it seems logical that submitting purchase orders and logistics documents in real-time will become a requirement in many countries, as this would allow tax authorities to have a complete picture of a transaction, from the initial order right through to the final delivery.
What does this mean for businesses?
If current trends continue as expected, not only will businesses need to be prepared to handle a growing volume of data, they’ll have to ensure this data is accurate, easily accessible and archived appropriately.
Specifically, businesses need to get the following three things right:
- VAT – This is particularly important for cross-border and triangular transactions
- VAT reporting – This is complicated by the fact that every country’s rules are different
- E-invoicing – This involves both technical and functional challenges, including collecting data points properly in the ERP system, realising the transmission to the authorities, and getting government issued IDs back
Further, businesses will also need to invest in robust digital infrastructure that can support real-time data exchange and integrating systems across the supply chain.
Understandably, all this work can seem like a big headache – particularly when tight deadlines are involved. However, new data regulations also bring opportunity for businesses. Approached correctly, tax and e-invoicing mandates can act as a catalyst for positive change and an opportunity to align tax reporting with broader automation efforts.
“Rather than seeing upcoming regulations as a headache, businesses would do better to approach them as an opportunity to enhance system efficiency and data accuracy in the long term.”
Philipp Liegl
Why are so many businesses struggling?
One of the core reasons that many modern businesses are struggling to juggle compliance and automation requirements is that, historically, tax and EDI/e-invoicing have been viewed as entirely separate domains, each with its own set of objectives and mindsets. This siloed approach has led to inefficiencies and confusion as businesses attempt to integrate these areas to meet modern regulatory standards.
Furthermore, many companies still have limited experience when it comes to e-invoicing. In Germany, for example, companies which only do business with German suppliers and customers have not yet been subject to any e-invoicing regulations. Even with large multinationals trading in various different jurisdictions, the ownership of the e-invoicing process has so far been left to the local entities – e.g. Italy and Spain – without any central governance or ownership.
The traditional tax mindset
In the tax world, as a speaker at a recent tax conference put it, “the key goal is to stay out of prison!”. While all good tax compliance service providers naturally seek to improve process efficiency, innovation and development in this direction is driven by two key factors: the need to meet changing compliance requirements, and the desire to perfect tax process accuracy. Although tax engines and tax determination add-ons for ERP systems have greatly improved this process over recent decades, tax has largely remained a company-internal function. With the advent of e-invoicing this has changed, as many different technical requirements (e.g. exchange formats and exchange protocols) need to be taken into account. This typically falls outside the area of expertise of internal tax personnel.
The traditional EDI mindset
By contrast, for professionals working with Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and e-invoicing, automation and data exchange with external parties has long been a central focus. Document standards like EDIFACT or ANSI ASC X12 and exchange protocols like AS2, OFTP2 or X.400 have had a significant impact in improving automated communication between different business partners along the supply chain. These technologies were developed to reduce manual intervention, improve speed, and minimise errors in data exchange, leading to more efficient business processes. Although accuracy is obviously still crucial in EDI/e-invoicing, the principal goal of these areas has historically been to improve efficiency and reduce operational costs of supply chain processes through automation. While the invoice is certainly a part of supply chain processes, it is only one document. The majority of exchanged documents in supply chain processes are logistics documents, such as purchase orders, purchase order responses and despatch advice messages.
Are B2B integration, e-invoicing and tax reporting really that different?
At first glance, B2B integration, e-invoicing and tax reporting might seem like three totally distinct areas, each with its own processes and requirements. However, when you look a little closer, they’re very closely related indeed.
In a nutshell, EDI (the core of modern B2B integration) is a methodology utilised by organisations to exchange business documents such as purchase orders, shipping notices and electronic invoices (among others) with one another in a standardised electronic format. E-invoicing, meanwhile, effectively refers to the exact same process, just relating solely to one type of document, the key difference being that the required data points and standards for e-invoices are typically dictated by the government. In addition, in many jurisdictions the invoice documents are not exchanged between the business partners directly, but via a central service provided by the government.
Similarly, there is a huge overlap between tax reporting and e-invoicing. An invoice, after all, is a record of a transaction, and that transaction is directly tied to the taxes that should be collected.
Ultimately, while there are still differences between these areas, the overall trend is clear: B2B integration, e-invoicing, and tax reporting are becoming more intertwined, and thinking of these areas as islands is no longer helpful.
Governments are increasingly demanding not just invoices but also logistics documents and other transaction-related data. Further, in several jurisdictions official government-issued information must now be brought back to the ERP – usually via dedicated APIs. For example, in some countries with CTC mandates, businesses must submit invoices in a specific XML format through a Web Service, with the state in turn providing an official invoice approval number to confirm the legitimacy of the transaction. That official approval number must be stored in the ERP system in order to be available in case a credit note is issued for the invoice (e.g. in case the invoice is being cancelled). In such cases the official approval number of the state must be part of the credit note.
As processes such as this become more commonplace, businesses will need to adapt to a landscape where EDI, e-invoicing and tax reporting are no longer distinct processes, but part of a unified approach to managing business communications and compliance. This will require a shift in how companies approach their digital infrastructure, with a focus on integrating these processes to ensure seamless data exchange and compliance.
The benefits of a unified solution
Given the growing demand for data and the increasingly blurred lines between B2B integration, e-invoicing and tax reporting, having a single provider who can handle all these related issues offers several significant advantages, including…
- Stress-free compliance. As tax, B2B integration and e-invoicing regulations continue to accelerate and overlap, having a provider that stays on top of country-specific requirements and proactively implements the necessary updates will become increasingly valuable.
- More time for internal teams. Handing key B2B integration, e-invoicing and tax reporting tasks to an external solution provider greatly reduces the strain on internal teams. With more time, individuals can then focus on more value-adding activities and initiatives.
- Reduced vendor complexity. With a single provider managing your B2B integration, e-invoicing and tax reporting, the administrative burden of juggling multiple platforms and processes is lightened. This saves time, reduces the risk of errors, improves data visibility, and makes system integration much simpler. What’s more, when issues do arise, there’s no need to jump between different support portals.
- Cross-functional expertise. With a unified B2B integration, e-invoicing and tax reporting solution you get a partner that understands the complex overlaps between these areas and can offer guidance on how to navigate them effectively.
- Increased flexibility. As the demand for data continues to grow, it’s important that your business is ready to adapt to new regulations and requirements. By selecting a provider that is experienced in B2B integration, e-invoicing and tax reporting, you can overcome new hurdles without the need for a major system overhaul.
- Reduced risk. By streamlining tax clearance processes and automating e-invoicing workflows, a unified tax reporting and B2B integration solution can accelerate approval processes while greatly reducing the frequency of errors and delays.
- Audit readiness. With a single provider handling your business’s tax reporting and B2B integration processes, accessing accurate, jurisdiction-specific tax reporting and e-invoicing data is easy.
How ecosio and Vertex’s collaboration is changing the game
Remarkably, despite the numerous benefits that a unified B2B integration, e-invoicing and tax reporting solution offers multinational businesses, no such solution existed until August of 2024, when EDI and e-invoicing experts ecosio were officially acquired by tax compliance giants Vertex.
The result of this unique collaboration? An unparalleled global solution for indirect tax reporting, e-invoicing and compliance.
Instead of juggling multiple tools and platforms for tax determination, periodic transaction controls (PTC), continuous transaction controls (CTC) and electronic data interchange (EDI), businesses can now outsource all of these issues to a single provider for the very first time.
Via one connection, businesses benefit from the powerful combination of ecosio’s global network and powerful B2B integration technology and Vertex’s end-to-end Indirect Tax offering.
With a single connection you can now…
- Mitigate the risk of non-compliance
- Meet global CTC and reporting requirements
- Eliminate manual processes
- Accelerate revenue
- Streamline data extraction
- Ensure audit readiness
Want to know more?
For more details on how ecosio and Vertex’s collaborative approach could help you simplify and streamline your existing tax, B2B integration and e-invoicing processes, get in touch today.
Der Beitrag How to Manage the Growing Challenges of Tax Reporting, B2B integration and E-invoicing erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag What is Peppol and how does it work? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- Peppol is a standardised framework for electronic document exchange, used for fast, secure, and compliant B2G and B2B communication
- Its four-corner model enables universal connectivity via a single certified Access Point, eliminating the need for custom EDI links
- Documents follow Peppol BIS standards, reducing mapping effort and ensuring compatibility across partners and countries
- API integration with Access Points like ecosio offers real-time tracking and ERP visibility, streamlining compliance and automation
With more and more governments worldwide mandating the use of e-invoicing for transactions involving public bodies, the use of Peppol is growing rapidly among supply chain businesses. As an ever-growing number of companies become Peppol-enabled, Peppol in turn grows increasingly attractive for those businesses not yet connected.
In this article we’ll answer some of the most commonly asked questions surrounding Peppol, how it works, and how it can benefit you.
Peppol basics
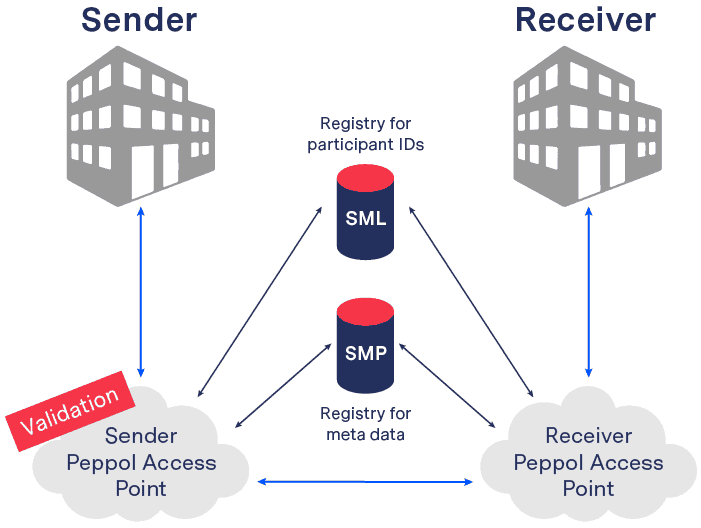
What is Peppol?
Peppol, which stands for Pan-European Public Procurement Online, is not an e-procurement platform. Rather Peppol provides the methodology and technical specifications as well as an agreement framework to send documents between e-procurement partners.
In short, Peppol makes it easier for businesses and public authorities to exchange electronic documents such as invoices and purchase orders in a standardised and secure way. It’s especially helpful for cross-border transactions, as it ensures documents are compliant with local regulations and can be processed quickly.
Why is Peppol popular?
Although theoretically governments could use any common communication protocol, such as SFTP, X.400 or AS2, this would require government bodies to support each one, which would involve significantly more work and increase the likelihood of errors occurring. Peppol solves this problem by offering a single, consistent framework.
Compared to document exchange via traditional EDI channels, Peppol also offers faster connections, reduced partner connection costs, increased message reliability and an all round simpler process for everyone involved.
Given these significant benefits, it’s hardly surprising that Peppol’s usage has grown steadily over the past decade. Today Peppol is not only used across the vast majority of European countries but further afield as well, with countries such as Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Singapore, the USA, Japan among others all now placing their trust in Peppol.
What are the three pillars of Peppol?
Ultimately, what Peppol provides can be boiled down to three factors, which are known as the three pillars of Peppol. These are…
- The Peppol network
- Peppol’s document specifications
- Peppol’s agreement framework
For more information on each of these pillars, please see the following three sections.
What’s required to connect to the Peppol network?
In simple terms, all a business needs to be able to connect to Peppol (in addition to the capability to send and receive automated messages) is a connection to a certified Peppol Access Point, such as ecosio.
Whereas before Peppol, trading with partners may have required connections to several service providers, with Peppol this is not the case. To ensure exchanging key B2B data with partners is as simple and cost-effective as possible, Peppol uses a four corner connection model. Unlike two and three-corner models, this model means that a single connection to a Peppol access point is sufficient to exchange automated documents with any other Peppol-enabled companies.
The two-corner model
Also known as point-to-point transmission, the two corner model requires time-consuming set-up and is usually handled by inhouse IT teams. Due to the high maintenance effort and setup time this model does not scale well. As connections are not reusable for multiple partners, each partner needs a new setup.
The three-corner model
In this model message routing is done via a central hub offered by a service provider. The main downside is lack of flexibility, as both sender and receiver must have the same service provider, meaning it is badly suited to large supply chains such as those for which Peppol was created. In addition there is a ‘lock-in’ effect in regard to the service provider – i.e. one of the parties is usually forced into a contract with the service provider of the buyer or the seller (depending on the market dominance of the party).
The four corner model
This has several advantages over the two corner and the three corner transmission models. Unlike them, the four corner model offers simplicity and flexibility, allowing for quick and cost-effective connections to partners. To exchange information, sender and receiver aren’t required to set up unique point-to-point connections or use the same service provider.
Once a connection to an access point has been established, the Peppol Participant ID is sufficient to send an electronic message to any Peppol partner of choice. Vice versa, after connecting to Peppol a company can be reached by any other Peppol sender.
What are Peppol’s document specifications?
When it comes to the formatting of documents exchanged between Peppol Access Points, all messages must conform to Peppol Business Interoperability Specifications 3.0 (known as Peppol BIS). The Peppol Code list provides standards for >100 message types (most of which are Peppol BIS). Peppol also allows custom document types within a country, if these are officially acknowledged.
This way each access point only needs to be able to process these approved messages. Consequently, systems connected to the Peppol access point only need to convert from the BIS format to the inhouse format and vice versa. Thus, once the mapping is set up, it is valid for all business partners. This is much simpler than building custom mappings for each partner connection.
What are Peppol’s Transport Infrastructure Agreements (TIAs)?
Finally, the existence of Transport Infrastructure Agreements (or TIAs) ensures that all parties conform to the necessary Peppol regulations This protects the reliability of document exchange via Peppol. Peppol Authorities, Peppol Access Point providers and Peppol Service Metadata Publisher providers must all sign these agreements.
Peppol Access Points
What is a Peppol Access Point?
A Peppol Access Point is a software, offered or owned by a company, that can connect others to the Peppol network and exchange documents via the required standards/protocols and in accordance with the necessary regulations.
Why do you need a Peppol Access Point?
Apart from becoming a Peppol Access Point yourself (which involves several complex steps), connecting to a Peppol Access Point provider is the only way to get an officially registered Peppol ID, which all Peppol participants must have in order to experience Peppol’s benefits. Without an Access Point and a Peppol ID, exchanging automated documents with your business partners via Peppol’s international e-invoicing network is impossible.
Isn’t it easier to set up an EDI connection to my partner directly?
In short, no. As we explore in more detail in our introductory video on Peppol, Peppol hugely simplifies automated document exchange for connected companies. Instead of requiring you or your provider to build an EDI (electronic data interchange) connection to your partner from scratch, Peppol utilises a four corner model and enforces the use of specific standards and protocols, meaning there is less work required for each connection. This makes partner onboarding via Peppol faster and more scalable than via classic EDI.
How do I find a Peppol Access Point?
You’ve already found one! At ecosio we are e-invoicing and Peppol experts and can help you get connected to Peppol in no time.
A full list of all certified Peppol Access Points can also be found on the Peppol website.
How do Access Points differ from one another?
Although all Peppol Access Points will enable you to connect to Peppol, not all Access Points offer the same service. For example, the level of help provided by Access Points with regard to setting up new mappings and monitoring messages etc. varies wildly from one provider to the next. Further, some Access Points may be faster than others to adapt when Peppol introduces new technical requirements, such as the recent move from AS2 to AS4.
Different Access Points are also governed by different Peppol Authorities across the globe. While all are able to connect you to Peppol, it makes sense to select an Access Point that operates in the same geographical area to you.
Perhaps most significantly, however, very few Peppol access points provide APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to help their customers achieve the best possible connection to their partners…
What are the benefits of connecting to Peppol via API?
Peppol as a whole has been developed to streamline B2G and eventually also B2B transactions. Conducting Peppol with the help of an API connection simply takes this streamlining to the next level (just as an API connection is able to boost the efficiency of traditional EDI).
An API basically specifies how different applications shall interact with each other, by defining the exchange format, exchange protocol, security requirements, etc. Thereby, APIs can help businesses connect their own internal IT landscape to other third party services. While Peppol perfectly solves the interoperability challenge between heterogeneous B2B networks by introducing a common exchange infrastructure, it does not define the “last mile”. As in telecommunications the last mile refers to the connection piece between the network hub and the end user’s system (e.g. the telephone).
In case of Peppol the network hub is the Peppol access point and the end user’s system is the ERP system of the company. The ERP system is usually the main system, where invoices, orders, despatch advices etc. are being created and consumed. If a Peppol access point provider offers a dedicated API, the ERP system can be seamlessly connected to the access point.
Using such an API for Peppol transactions comes with a number of significant advantages for the customer, including:
End-to-end message monitoring
With an API connection, Peppol can be seamlessly integrated in your ERP system. This enables users to see the delivery status of messages from within their existing user interface, eliminating the need to log into independent external software to check that a partner has acknowledged a message.
Accurate delivery/fetching of messages
Once connected to your Peppol access point via API, requests can be set up at regular intervals to check for new messages. Alternatively, new messages can be transferred proactively from the Peppol access point to the recipient.
Full text search
Thanks to the depth of the integration provided by the API, messages can even be searched directly in the ERP system. For example, users could locate invoice messages by inputting any relevant invoice data such as article number, reference to the underlying despatch advice, etc.
Error handling
Unlike with traditional protocols such as SFTP, where it can be difficult to ascertain where and why sending failed, thanks to the unparallelled data visibility achieved with an API connection, users can immediately see where the issue occurred and what should be done to resolve it.
How long does connecting to Peppol take?
Once you’ve chosen your preferred Access Point (something that should not be rushed), the actual connection process is fast and simple. Your provider will register a unique Peppol ID for you, whereby existing IDs such as VAT-ID or Global Location Numbers can be reused.. After this you will be able to start connecting to other Peppol-enabled partners and exchanging structured invoices etc.
Peppol in SAP systems
Is an SAP Peppol connection easy to achieve?
While achieving an SAP Peppol connection is very possible, its complexity depends on your chosen integration method. The simplest way to achieve an SAP Peppol connection is to opt for a managed service provider that will handle everything from technical setup to message monitoring and error resolution once the connection is live.
How does ecosio achieve SAP Peppol connectivity?
The illustration below shows a connection between an SAP System and Peppol with the help of ecosio. ecosio is a certified Peppol Access Point Provider and can therefore send and receive documents to and from the Peppol network.
The connection between the SAP system and ecosio occurs thanks to the EPO Connector. The EPO Connector is a middleware solution for SAP and entirely programmed in ABAP. The solution is SAP certified for all SAP versions from 4.6 and is thereby also compatible with S/4HANA. IDoc documents can be sent and received through the EPO Connector to the ecosio MessagingHub. For example, one can use INVOIC02 IDocs for e-invoices.
Should an SAP middleware such as SAP PI or SAP PO be the current solution, those components can also be used to connect to the ecosio MessagingHub. Additionally, SFTP solutions can be used for the connection as well. The SFTP server can either be hosted by ecosio or by the company.
After receiving the IDocs, ecosio will determine the sender, receiver and document type, and will convert the message to the correct target format, to finally transmit it to the receiver. If Peppol is in use, the delivery to the receiver’s Peppol Access Point will take place via the PEPPOL network, e.g. to German authorities or a company, which uses Peppol.
This allows for e-invoices to be sent via Peppol straight from SAP and be compliant with the XRechnung standard.
The communication is also possible the other way. For example, purchase orders can also be received over the Peppol network.
Why should you consider ecosio as your Peppol Access Point provider?
ecosio is one of a limited number of certified Peppol Access Point providers that offers Peppol connectivity as part of a comprehensive full service package.
With a single connection to ecosio, your business can trade all relevant e-documents with hundreds of thousands of connected companies and public institutions worldwide. What’s more, as we are able to handle all EDI and e-invoicing tasks for you, from set-up right through to ongoing operation, you don’t need any in-house expertise to benefit from the savings associated with automated B2B document exchange.
To find out more, get in touch today!
Are you aware of our free XML/Peppol document validator?
To help those in need of a simple and easy way to validate formats and file types, from CII (Cross-Industry Invoice) to UBL, we’ve created a free online validator.
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag What is Peppol and how does it work? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag B2B E-invoicing in Germany: An Overview erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Germany’s mandate focuses solely on digitisation, without the requirement for government validation of invoices, although this will need to change to comply with the VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) and digital reporting requirements (DRR) before the European Commission’s deadline of 1 July 2030.
Since our previous article “Germany commits to making B2B e-invoicing mandatory” , The Federal German Ministry of Finance (BMF) published a Draft Letter on 13 June 2024, providing further details on the issuance of invoices according to Section 14 of the German VAT ACT (UStG).
What is covered?
The draft letter expands on The Growth Opportunities Act (Federal Law Gazette | 2024 No.108) and provides guidance on the key topics:
Timelines
- 1 January 2025: All domestic businesses will be required to receive and process electronic invoices
- 1 January 2027: domestic businesses with an annual turnover exceeding €800k must issue invoices electronically
- 1 January 2028: all domestic businesses must issue invoices electronically
Exemptions
- Invoices for total amounts up to €250
- Invoices for services that are tax-free according to Section 4 (numbers 8-29) of the VAT Act
- Travel tickets
Formats
An electronic invoice must conform to the EN 16931-2 (syntax), i.e. Universal Business language (UBL) or UN/CEFACT Cross Industry Invoice (CII) or a format mutually agreed by the invoice issuer and recipient, providing it’s interoperable and complies with the EN 16931-1 (semantic data model).
ZUGFeRD, a PDF/A-3 hybrid with an embedded CII, is also compliant with the EN 16931 from versions 2.0.1 onwards and is already widely used in the German market.
From January 2025, invoices such as paper, PDF and electronic formats which don’t comply with the EN 16931 will be considered as “other invoices”. These will be permissible until the end of the calendar year of 2026 and will be invalid thereafter.
Transmission protocols
Invoice recipients must provide an email account to receive an electronic invoice, although the invoice issuer and recipient can also agree on other electronic transmission protocols i.e. Peppol, AS2, SFTP etc.
Additionally, invoices can be made available to download via a customer portal.
Storage
Invoices must be stored in a manner that ensures authenticity of the origin and the integrity of the content. Plus the legibility of the invoice must also be guaranteed.
How can ecosio help?
Founded in Vienna, ecosio is one of the leading EDI and e-invoicing solution providers in the whole of the DACH region. Germany is at the forefront of our business meaning we are highly experienced and well-positioned to support you and your business comply with the new German regulations.
Our solution
ecosio.invoicing offers a comprehensive global solution for electronic invoice exchange, serving as a single gateway to your customers, e-invoicing networks and tax administrations, and helping to make global compliance hassle-free.
For more information on how ecosio can help, contact edi@ecosio.com.
Der Beitrag B2B E-invoicing in Germany: An Overview erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Germany Commits to Making B2B E-invoicing Mandatory erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>This progressive move toward e-invoicing not only demonstrates Germany’s commitment to leveraging technology for economic rejuvenation, but also positions German businesses at the forefront of digital financial practices.
What does the Growth Opportunities Act aim to achieve?
The act aims to provide tax relief measures to facilitate growth in an economy that has struggled in recent times, with Gross Domestic Product (GDP) having fallen by 0.3% in 2023. In short, by passing this act, the German government hopes to make the country’s economic landscape more efficient, transparent and resilient moving forward.
What changes will the Growth Opportunities Act bring?
A pivotal component of the Growth Opportunities Act is the introduction of a new e-invoicing mandate for domestic business-to-business (B2B) transactions. This development represents a drive to streamline financial operations and reduce the administrative overhead associated with traditional paper invoicing processes. Although debates within the Bundesrat in November 2023 suggested a potential postponement, which would have extended the timeline for adopting electronic invoicing until 2027 for receivers, the initial schedule set forth by the German Ministry of Finance (BMF) will proceed as planned.
What is the timeline?
The timeline for the phased implementation of the e-invoicing mandate is as follows:
- 1 January 2025: All German businesses must be able to receive and process electronic invoices
- 1 January 2027: German businesses with an annual turnover exceeding €800k must issue their invoices electronically for domestic B2B transactions
- 1 January 2028: All German businesses must issue invoices electronically for domestic B2B transactions
What are the technical requirements?
To ensure a seamless transition, electronic invoices must adhere to the EN 16931 standard. However, businesses retain the capacity to negotiate the Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) standards used, provided mutual agreement is reached between invoice issuers and recipients.
Whilst Germany will eventually need to comply with the digital reporting requirement (DRR), as outlined in the European Commission’s VAT in the Digital Age (VIDA) proposal, the mandate is specific to invoice exchange between supplier and buyer and does not include a Continuous Transaction Controls (CTC) / centralised model.
How ecosio can help
For organisations preparing to navigate this change, understanding the specifics of the mandate and beginning the transition early can significantly mitigate the challenges associated with adopting new technological frameworks. Thankfully ecosio’s e-invoicing experts are able to support you as Germany embarks on this journey toward digitalisation.
ecosio.invoicing makes meeting country-specific regulations easy. Our state-of-the-art Integration Hub acts as a single gateway to connect your business to customers, tax administrations and other government platforms all over the world; enhancing automation, driving down costs and helping you to achieve compliance.
Find out more
For more information on ecosio’s unique EDI solution, please contact us at edi@ecosio.com or talk to our Sales team.
Der Beitrag Germany Commits to Making B2B E-invoicing Mandatory erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>