Der Beitrag Real-Time EDI Tracking Isn’t Just for IT Anymore erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>And all you can think is: Why didn’t we catch this sooner?
This isn’t just an operations hiccup, it’s a visibility issue. Without proper EDI tracking, you’re not in control. You’re reacting.
In simple terms, EDI tracking means knowing where your messages are at all times. From purchase orders to invoices, it shows whether a message was sent, received or failed. Instead of working in the dark, your teams share the same clear view of what’s happening.
If your system looks quiet, it isn’t necessarily healthy.
In the world of electronic data interchange, silence can be dangerous.
TL;DR summary
- Most businesses have EDI tracking, but only IT can access it
- Limited visibility slows teams down and leads to missed issues
- With ecosio Monitor, everyone can track messages in real time
- EDI insights are also available directly in your ERP system
- Shared visibility helps IT, finance and operations stay ahead
- Better tracking means better decisions, fewer delays and stronger partnerships
- ecosio doesn’t just provide visibility. We fully manage your EDI operations
- From onboarding to optimisation, our team handles the details so you don’t have to
The real problem is that EDI visibility is stuck in silos
Most businesses already have EDI tracking. The issue is that the visibility is often limited to IT. Everyone else, like operations, finance, sales, and procurement is left in the dark. If they want to confirm whether a message was sent, received, or failed, they have to go through someone technical. That adds delays, creates frustration, and increases the risk of missed problems.
When visibility lives with only one team, issues are easy to miss and partners may spot problems before you do.
Here’s what that might look like in practice:
- An order message fails due to a formatting issue
- The supplier assumes the order didn’t come through and holds off shipping
- You only find out three days later when your internal team checks in
- By then, the customer is frustrated and your team is behind
How do you know your EDI is working?
For many teams, the answer is simple. They don’t.
Signs your visibility isn’t what it should be:
- Sales and logistics teams rely on external partners to flag problems
- IT wastes hours tracing errors across disconnected systems
- Operations teams are constantly reacting instead of planning
- Business leaders assume “no news is good news” (until it isn’t)
When you’re depending on silence as a signal of success, you’re not managing your EDI. You’re crossing your fingers.
Why EDI visibility matters more than you think
It’s tempting to see an EDI error as a small IT detail. But one hidden failure can ripple outward, delaying shipments, blocking payments, and frustrating partners. By the time you notice, the damage is already done.
With true visibility, the story is different. Problems surface instantly, fixes are faster, and teams act with confidence instead of guesswork.
That’s why ecosio’s EDI as a Service solution puts visibility at the centre. We fully manage your operations and make every message, every format, every partner, clear and accessible.
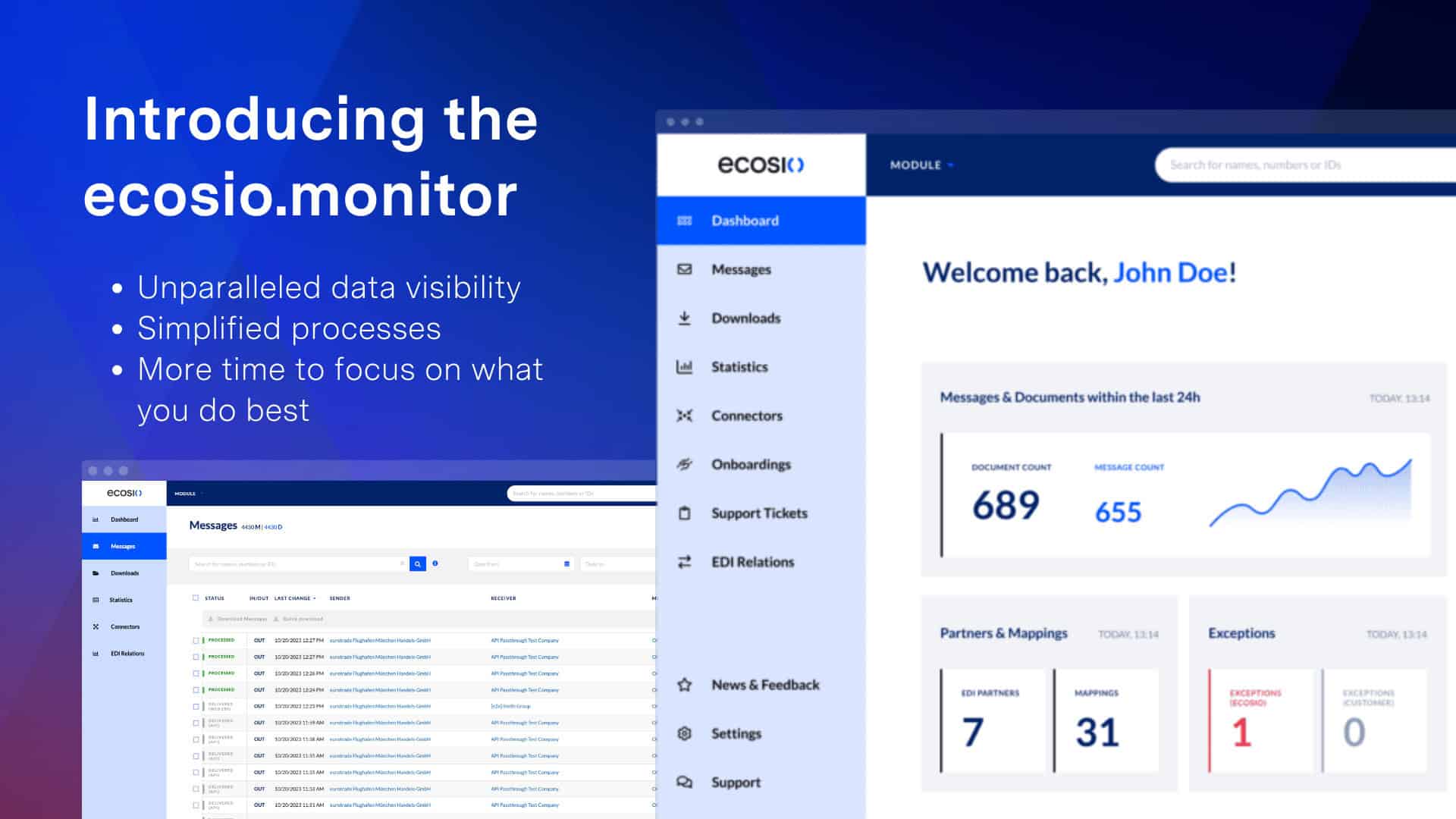
Real-time EDI tracking with Monitor
Visibility is powerful only when it’s practical. With ecosio’s dashboard inside the Monitor, even complex message traffic becomes easy to understand at a glance.
You don’t need to be a developer to use it. You don’t need to dig through logs. You just log in and see everything in one place.
Monitor enables:
- Live EDI tracking across all message types, protocols and partners
- Real-time alerts when disruptions occur
- Detailed error insights to help you resolve issues faster
- Access for any team, not just IT
- Traffic visualisation and filters to spot patterns early
Think of it like your very own EDI cockpit, from which you can not only send messages, but monitor the health of your entire digital supply chain.
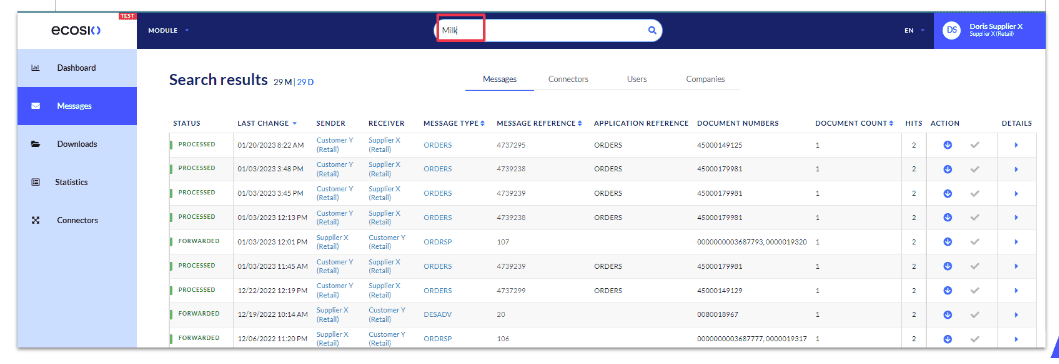
Prefer to stay in your ERP? You can see it all there too!
We get it. Most teams don’t want to switch between tools. They’d rather work where they already are, in the ERP.
That’s why with ecosio, real-time EDI tracking doesn’t just live in Monitor. It’s also available directly inside your ERP interface. You can view message statuses, validation results and delivery updates as part of your regular workflow, with no extra systems to log into.
This means:
- You know instantly when a message is received or fails
- You can troubleshoot without leaving your ERP
- You avoid delays and catch issues early, right from the source of truth
For teams who prefer working in their ERP, this kind of integrated EDI visibility is a game changer. And if you ever need more detail or broader context, you can jump straight from your ERP to the relevant message in Monitor, with no searching and no guesswork.
[Image CTA – Download our report, The Future of B2B Integration: Market Trends]
Why EDI tracking matters to more than just IT
Traditional EDI tools treat visibility as just a technical concern. But EDI impacts everyone, from the warehouse floor to the CFO’s desk.
With ecosio’s real-time EDI tracking, each team benefits
- IT can respond instantly to disruptions
- Operations and logistics know when messages land and when they don’t
- Finance can proactively follow up on missing invoices
- Leadership gets transparency and peace of mind
No more internal bottlenecks. No more “I’ll check with IT and get back to you”. Everyone has the same visibility. Everyone saves time.
Better EDI tracking leads to better decisions
It’s not just about catching issues. It’s about being able to:
- Optimise your partner relationships
- Improve lead times and delivery accuracy
- Minimise disruption and financial penalties
- Provide leadership with accurate operational metrics
When you can see your EDI processes clearly, you can improve them. You can adapt faster, build trust with partners, and free your team from repetitive admin.
A fully managed solution
Visibility is only part of the story. The real strength of ecosio’s EDI as a Service solution is that you’re not managing it alone. We handle your day-to-day operations, providing proactive support, clear processes and a team that knows your setup inside and out.
Here are just a few of the things you get with our fully managed approach:
- Dedicated EDI experts who guide onboarding, support scaling and resolve issues quickly
- Active message monitoring and error resolution, to ensure nothing slips through the cracks
- Automated validation and compliance monitoring, to catch problems before they impact operations
And that’s just the beginning. As your business grows, your EDI setup needs to grow with it. Whether you’re expanding your partner network, entering new markets or migrating to a new ERP system, we keep everything running smoothly while maintaining your valuable real-time visibility. From partner onboarding to long-term optimisation, our team works behind the scenes to ensure you can scale with confidence and focus on what matters most.
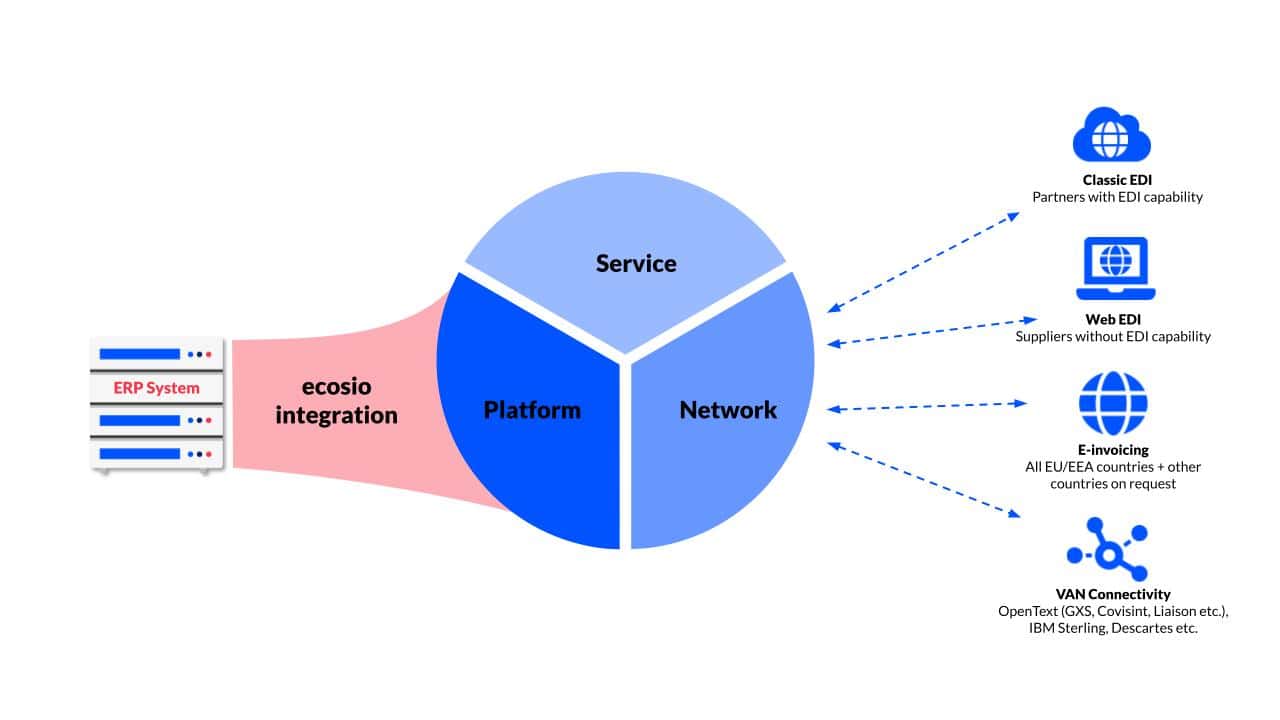
More than just a platform
Unlike providers who offer only tools or infrastructure, ecosio delivers a fully managed service built on three connected pillars: platform, service and network. At the centre of everything is service. This means not just ticket-based support, but a dedicated team that actively manages your integrations, resolves issues before they escalate and works directly with your partners when needed. The platform provides real-time visibility and deep ERP integration, while the network ensures seamless connection with all your trading partners, regardless of format or protocol.
Together, these pillars give you everything you need to scale EDI with confidence and clarity, without adding to your internal workload.
Ready to stop flying blind?
If you’ve ever been caught off guard by a message failure, or if you simply don’t know what happens after “Send,” then it’s time to rethink your EDI tracking.
ecosio’s fully managed solution ensures EDI is no longer a black box. You gain insight, control and the confidence that nothing is slipping through the cracks.
Get in touch with our EDI experts today and see how effortless visibility can be.
Der Beitrag Real-Time EDI Tracking Isn’t Just for IT Anymore erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag AI and EDI: strengths, challenges and what to expect erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- AI can enhance EDI through error detection, data mapping, and predictive analytics, helping teams spot issues earlier and automate manual tasks
- OCR tools powered by AI enable fast document conversion, reducing reliance on manual data entry
- Key challenges include technical inaccuracies, legacy system compatibility, and data privacy concerns, requiring careful implementation
- AI is a valuable complement to EDI, but still needs human oversight to ensure accuracy and business context
AI is everywhere these days. From online shopping to booking a taxi, artificial intelligence is quietly transforming all sorts of everyday processes. But what about in the world of B2B communication – specifically electronic data interchange (EDI)? Can AI and EDI work together to improve your business operations?
In this article, we’ll explore how AI is starting to reshape EDI processes, where it shines, where it struggles, and what you should be aware of if you’re considering making AI part of your EDI strategy.
The rise of AI across business operations
Over the past decade, the adoption of AI across business sectors has skyrocketed. From a distant concept, AI has quickly become mainstream, with a recent Accenture report finding that 84% of executives “believe they won’t achieve their growth objectives unless they scale AI”. Amazingly, the same report also states that 75% of executives “believe they risk going out of business in five years if they don’t scale AI”.
More than many other sectors, supply chain businesses have been profoundly impacted by AI, largely due to their reliance on fast, high-volume data exchange and complex transactional processes. Among other things, these businesses are now leveraging AI to:
- Predict inventory needs
- Automate procurement workflows
- Optimise delivery routes
- Detect anomalies in real-time supply chain data
EDI and AI: potential utilisations
Error detection and correction
Possibly the simplest and most powerful way that AI and EDI can be combined is by using AI to spot errors. Specifically, as AI is extremely good at being able to spot anomalies in data patterns, it can be used to flag possible issues that humans might miss.
In traditional EDI, individuals only notice something is wrong when a shipment is late or an invoice goes missing. With AI, patterns are continuously monitored. If something’s off even a little bit, AI can raise the alarm early.
For example, if you usually receive 500 purchase orders every Wednesday and one week you only get 250, this change itself is not an error. However, such a pattern change can indicate something has gone wrong, and flagging this early enables relevant teams to investigate and rectify any possible issue before it develops.
Data mapping
Traditionally, setting up document mappings requires hours of manual effort and a great deal of technical expertise. Hypothetically AI can help automate parts of this process by “learning” from existing mappings and making appropriate suggestions.
Predictive analytics
AI doesn’t just see what has happened; crucially it can also predict what might happen next. By analysing past EDI data, AI can anticipate supply chain disruptions, helping you to plan ahead and avoid potential issues before they happen.
Document conversion
Imagine feeding a paper invoice into a system and having it instantly converted into an EDI-compliant format. AI-driven OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and data structuring tools are making this a reality, eliminating the need for error-prone manual data entry.
EDI and AI: key challenges
Although the potential of AI to streamline and simplify B2B processes is huge, it’s important to stay grounded. AI isn’t a magic wand… yet. There are still several issues and potential hazards associated with AI usage, including…
Technical inaccuracies
EDI isn’t a “one-size-fits-all” world. There are countless EDI formats (like EDIFACT, ANSI X12, and XML), as well as standards that vary by industry and region. Teaching an AI to handle all these perfectly is tricky and the results typically require significant fine-tuning.
In EDI even the smallest error can have a big impact. Consequently, if you ask an AI tool to convert a document into a certain EDI format, it may do it 99% correctly… but that 1% is a problem.
Diverse protocols of trading partners (when onboarding)
Different partners prefer different EDI protocols (AS2, OFTP2, SFTP, and so on). AI can help recommend configurations, but ensuring protocol compatibility still needs human oversight to ensure success.
Legacy systems compatibility
Many companies still rely on legacy ERP systems that weren’t built with AI in mind. Integrating modern AI solutions with these older environments can feel like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole.
Data privacy
Handling sensitive business data demands strict privacy controls. Using AI can introduce compliance risks if not managed carefully, particularly where cloud solutions are involved. It’s important to ensure that any AI system you use adheres to GDPR and other relevant standards.
Lack of context
AI can be impressive, but it doesn’t “understand” your business context the way a human does. It might suggest a mapping that looks technically correct but doesn’t make sense operationally. Without context, errors can easily slip through the cracks.
Conclusion
AI and EDI are a powerful combination, offering real potential to streamline processes, reduce manual work, and spot issues before they become problems. However, like any new tool, AI needs to be applied carefully, with an understanding of both its strengths and its current limitations.
See how ecosio can help you streamline your EDI processes
At ecosio, we’re passionate about making B2B integration effortless and that includes harnessing the best of AI where it genuinely adds value. If you’d like to learn more about how we can help you future-proof your B2B integration processes, get in touch today!
Der Beitrag AI and EDI: strengths, challenges and what to expect erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Why EDI Transformation is Critical to the Success of Your Organisation erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- An EDI transformation project typically includes analysis of the current infrastructure, target definition, modernisation of existing EDI architecture, and implementation of new components
- Benefits include increased efficiency, improved data quality, more time for value-adding tasks, greater flexibility, easier partner integration, and future-proof systems
- Challenges include high investments, technical complexity, and resistance to change
- Tips for success are don’t underestimate internal effort, take future requirements into account, and don’t put the project off
Nowadays it’s no longer enough just to optimise processes – companies need to fundamentally rethink their approach to data communication in order to maintain their position in the market. To secure fast, automated and error-free communication with business partners, many businesses today are embarking on ambitious EDI transformation projects. But what exactly does an EDI transformation project involve, and how exactly can a successful project benefit your company?
What does an EDI transformation project involve?
An EDI transformation project typically consists of the following key steps:
- Analysis of the current infrastructure: evaluation of existing systems to identify weaknesses and opportunities for optimisation
- Target definition: Definition of requirements and targets, e.g. higher data quality or cost reductions
- System migration: Conversion to a more modern, often cloud-based, EDI solution
- Integration: Connection of new EDI solution to existing ERP system to ensure seamless communication
- Change management: Comprehensive training and clear process communication to make the transition easier for employees
Why is EDI transformation crucial for companies?
Companies that neglect to modernise their EDI systems run the risk of being left behind. Outdated systems can slow down data exchange, affect data quality and create security gaps. In order to remain competitive, companies must integrate modern technology in the form of cloud solutions, APIs and automated processes.
For those companies that do this successfully, the advantages are numerous, including…
- Increased efficiency: the automation and optimisation of processes reduces manual intervention and speeds up workflows
- Improved data quality: Modern EDI systems ensure accurate, error-free data transmission
- More time to focus on value-adding tasks: Automated processes ensure employees have more time for strategic activities
- Increased flexibility and scalability: With more streamlined EDI processes and better data visibility, companies can react quickly to market changes and adapt their processes accordingly
- Easier integration of new partners: A modern EDI infrastructure simplifies the integration of business partners and increases collaboration
- Future-proof systems and processes: With a continuously customisable EDI solution, companies remain competitive in the long term
What challenges do EDI transformation projects pose?
As with all large IT projects, success isn’t guaranteed, and there are generally hurdles along the way. When it comes to EDI transformation projects, the most common issues companies experience include…
High investments
Although not always the case, EDI transformation projects often require significant upfront investment. The costs can include new software and infrastructure, integration work, consultancy fees, and the time and personnel needed to manage change across systems and processes. For many organisations, this initial outlay can seem daunting, especially when existing systems are still operational, albeit inefficient. However, while the short-term costs are substantial, these investments are typically offset over time through improved operational efficiency, automation of manual tasks, fewer errors, and reduced long-term operating expenses. In this way, a well-executed EDI transformation not only pays for itself but also creates measurable value for the business.
Technical complexity
Integrating modern systems into existing IT infrastructures can be a challenge, especially if the old software has been heavily customised. This often requires complex customisations to make new technologies compatible with the old systems. These customisations require in-depth technical knowledge and careful planning to ensure a smooth integration. It’s important that the new systems work efficiently with the existing infrastructure without interrupting business processes. A strategic approach is therefore crucial for the long-term success of the integration.
Resistance to change
Employees who are used to old ways of working may resist the new technologies. However, thorough training and clear communication will help overcome this resistance.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning and expert support.
Three important tips for a successful EDI transformation project
- Don’t underestimate the internal effort: a successful transformation requires co-operation and the right resources in the team. Ensure that everyone involved is adequately trained and supported.
- Take future requirements into account: Choose an EDI solution that will grow with your business and can adapt when your needs change.
- Don’t put the project off: Start your EDI transformation as early as possible to avoid missing an opportunity to increase efficiency and gain a competitive advantage. By delaying, your existing solution will only become even more
Let us help you achieve EDI transformation success!
EDI transformation is not only a technical necessity, but also a strategic step to secure your long-term competitiveness. With ecosio, you can modernise your EDI processes and successfully meet the challenges of the digital future. Are you ready to take your EDI systems to the next level? Contact us to find out how you can become more efficient, flexible and future-proof with ecosio’s unique ED-as a Service approach.
We’re always happy to help!
Der Beitrag Why EDI Transformation is Critical to the Success of Your Organisation erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag ecosio Insights: The Future of the Supply Chain: EDI, RFID, and Digital Transformation erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>We sat down with Marcel Ducceschi, EDI Strategist at ecosio and an expert in the field of digital supply chains, to explore the key measures and challenges associated with digital transformation.
To what extent do you see EDI as an essential component of end-to-end responsibility in the supply chain?
EDI is a crucial component for automated, seamless, and uninterrupted information exchange among multiple partners along the supply chain. Due to the different IT solutions used by individual partners, the use of uniform, globally accepted standards (formats and protocols) is essential, as it ensures that data can be accurately understood and processed across diverse systems. Service providers like ecosio can provide significant support in converting various standardised formats and protocols.
What significant advantages do you see in the digitalisation of supply chain processes through technologies like EDI and RFID compared to traditional, paper-based methods?
Digitalising supply chain processes with technologies like EDI and RFID has three key benefits over traditional paper methods.
First, it greatly reduces lead times by allowing automatic and instant information sharing, which speeds up the synchronisation of goods and information.
Second, automation enhances process quality by minimising human errors and improving data accuracy, making processes more reliable.
Third, digitalisation lowers costs by reducing the need for manual work and creating more efficient workflows, which helps manage inventory (product stock) and labour costs (employee expenses).
These advantages make digitalisation essential for success in modern supply chains.
How do EDI, RFID, and barcodes work together in the supply chain?
EDI and EPCIS (Electronic Product Code Information Services) are methods for companies to share information. Barcodes and RFID help track products automatically.
It’s important to use these tools with standard numbers like GTINs (Global Trade Item Numbers), so everyone understands them. When companies combine EDI and EPCIS for sharing information with AutoID technologies, it ensures that product information matches what’s in stock. This connection is key for a smooth supply chain and helps automate tasks, making everything faster and more efficient.
How important is the synchronisation of information flows (e.g. through EDI) with physical material flows?
Only through continuous synchronisation between information flows and physical goods flows can the full benefits of the digitalisation of the supply chain be realised. Information, even when exchanged electronically, can lead to errors and additional costs if received too early or too late relative to the goods and recorded without synchronisation with the movement of goods.
What role do RFID and barcodes play in improving synchronisation, and where can we improve further?
AutoID technologies, like barcodes and RFID, are crucial for the automated identification of logistics items and tracking of goods movement. Without these technologies, keeping goods and information synchronised is either impossible or requires a lot of manual effort and time.
There’s significant potential for improvement, especially in automating the way we capture data using AutoID technologies. This includes better positioning of optical data carriers (like barcodes) and using RFID to capture multiple items at once, known as bulk capture. Modern 2D codes combined with advanced cameras or scanners represent an exciting advancement in this area.
Additionally, using new capture devices that leverage augmented reality (AR) technology, such as Microsoft HoloLens, can greatly enhance manual processes like picking by integrating AutoID technology with digital information.
How are new technologies like IoT, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain changing the digital supply chain in retail? Do you think there will be a shift away from EDI?
After 30 years of working with EDI, I believe there are valuable additions, like EPCIS, but I don’t see any real alternatives to EDI for exchanging information in the supply chain. While API (Application Programming Interface) solutions can complement EDI, they aren’t yet reliable or easy enough to replace it.
I think both IoT (Internet of Things) and artificial intelligence can greatly help with the digitalisation of the supply chain. However, I don’t see blockchain technology adding real value for sharing logistical information in the supply chain, especially compared to established technologies. In many cases, I feel like we have a blockchain solution, but we’re still trying to find a problem for it to solve.
How can an end-to-end EDI system tackle future challenges in the supply chain?
I believe that end-to-end information flows using EDI and EPCIS, which must align with physical goods movements, will be key to making supply chain processes faster, safer, more cost-effective, and more resilient. Emerging technologies like IoT and AI, along with established technologies such as RFID and 2D codes, will play an important role. The effectiveness of these technologies relies on their integration with modern software tools (like ERP and WMS systems) and the automation of distribution centres. For instance, a fully automated distribution centre, such as one based on SAP EWM (a SAP software solution for optimising warehouse management), cannot deliver real value without accurate data and proper identification of the items being processed.
Which trends or technologies do you think will most influence the development of EDI in retail?
Technologies like EDI, RFID, and AutoID are crucial for information exchange and synchronising flows. While EDI remains central, complementary technologies such as APIs and blockchain will enhance its capabilities. Their integration is essential for developing a more agile and resilient logistics system.
Want more advice on how to optimise your supply chain?
At ecosio are experts when it comes to improving your processes and reducing costs. Make an appointment with us today to discover customised solutions for your company!
Technical terms used in this interview
Here is an overview of the technical terms used in the interview. You can find many more in our EDI glossary.
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange):
A standardized system for electronically exchanging business documents, such as purchase orders and invoices, between organizations. EDI eliminates the need for manual data entry, which reduces errors and speeds up document processing, ensuring smoother and faster transactions between supply chain partners.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification):
A technology that uses radio waves to automatically identify and track tags attached to goods, enabling real-time visibility of inventory. RFID helps improve inventory management by making it possible to locate, monitor, and update stock levels quickly and accurately, which enhances transparency and efficiency throughout the supply chain.
AutoID (Automatic Identification):
A broad category of technologies, including RFID and barcodes, that enable the automatic identification and data capture of items. AutoID provides fast and reliable product identification, ensuring the continuous flow of synchronized goods and information, which supports seamless inventory management and logistics processes.
GTIN (Global Trade Item Number):
The GTIN is a globally unique product number that identifies each product and facilitates international trade. GTINs are typically displayed as barcodes on packaging and enable the automatic identification and management of items across the supply chain, ensuring error-free and efficient product tracking and traceability.
EPCIS (Electronic Product Code Information Services):
EPCIS is a standard that allows for the sharing of data about the movement and status of products in the supply chain. It provides a framework for capturing and sharing information regarding the physical movement of goods, enabling better visibility and traceability of products. EPCIS helps organizations leverage data from RFID and other identification technologies to improve operations and enhance supply chain management.
SAP EWM (Extended Warehouse Management)
SAP EWM is a software solution that optimizes warehouse operations by providing tools for efficient inventory management, tracking of goods movements, and integration with supply chain processes, leading to improved efficiency and visibility within logistics operations.
Der Beitrag ecosio Insights: The Future of the Supply Chain: EDI, RFID, and Digital Transformation erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Can Increased Automation Build Supply Chain Resilience? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- The last five years has seen a surge in recognition by businesses of the importance of building supply chain resilience
- Automating key B2B processes minimises the potential for human error, improves speed, and frees up staff to focus on more valuable tasks
- In a survey of supply chain executives, 88% believe that optimising automated B2B processes can improve supply chain resilience, and over half predicted that efficient automation would improve it “substantially
- 62% of respondents saw automated B2B communication as “very important” to the success of their business moving forward, with none seeing it as unimportant or irrelevant
The last five years has seen a surge in recognition by businesses of the importance of building supply chain resilience. Global events have highlighted the dangers of being unable to react to disruptions, and organisations are increasingly aware of the value of flexibility and adaptability, particularly when it comes to critical B2B processes. Yet despite this, according to a recent KPMG survey, 47% of supply chain executives believe they are still “vulnerable to disruption”.
While there is obviously no way to predict the future, there are pragmatic steps that businesses can take to boost supply chain resilience. Perhaps the simplest and fastest of these to achieve is improving B2B automation. Not only does automating key processes minimise the potential for human error, it can also improve speed and free up staff members to focus on more valuable tasks. In the event of unforeseen circumstances, businesses thus benefit from increased flexibility, as the majority of business-critical tasks aren’t dependent on human intervention.
What our research shows
As part of a wider research project concerning B2B integration trends, we recently conducted our own cross-industry survey in which we asked people their views on the importance of B2B automation.
Of the over 100 supply chain executives we surveyed, 88% believe that optimising automated B2B processes can improve supply chain resilience. Further, over half of those surveyed predicted that efficient automation would improve supply chain resilience “substantially”.
Similarly, 62% of respondents saw automated B2B communication as “very important” to the success of their business moving forward, with none seeing it as unimportant or irrelevant.
What can you do?
Improve and expand automation of business-critical processes! Not only will expanding and optimising automated processes streamline processes and minimise the possibility of human errors, it will also free up internal teams to be able to focus on more value-adding activities.
In particular, introducing electronic data interchange (EDI) and e-invoicing can make a huge difference to the efficiency of day-to-day messaging and drastically improve supply chain resilience.
“As more of the supply chain becomes automated, roles can be redefined to focus on higher-value customer services, and new roles will emerge for humans that drive strategy and innovation.”
Questions to ask yourself
- Are existing B2B integration processes inhibiting your company’s ability to react quickly to market changes?
- Do you currently have business-critical processes that could be automated?
- Are any key supply chain operations reliant on one or two individuals?
- Have you considered investing in a Web EDI solution to extend automation across your entire partner landscape?
- Would internal team members be able to add more value elsewhere if EDI tasks were outsourced?
Want more information on EDI trends?
This article is based on a chapter from our white paper “The Future of B2B Integration – Market Trends Report”, in which we share survey results as well as predictions concerning the evolution of B2B integration. To download your free copy now, simply visit the white paper page and enter your details!
Discover more about our updated product, ecosio.flow.
Der Beitrag Can Increased Automation Build Supply Chain Resilience? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag The AS2 EDI Protocol Explained erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) is a protocol used to exchange business data safely and securely via HTTP, making it one of the most popular methods for EDI message exchange with partners
- Today the AS2 EDI protocol is increasingly recognised as the most reliable and attractive way for businesses across industries to exchange EDI messages
- AS2 operates over HTTP and is optimised for secure EDI transmission, providing a standardised method for structured data exchange
- AS2 ensures data integrity and confidentiality through encryption, digital signatures, and message disposition notifications (MDNs)
Applicability statement 2 – more commonly referred to as AS2 – is a protocol which is used to exchange business data in a safe and secure way via HTTP. Today the AS2 EDI protocol is one of the most popular ways that businesses exchange EDI messages with their partners.
In this article we’ll explore how the AS2 protocol works and why it is so popular in the EDI sphere.
AS2’s growing usage
On the face of it, AS2 is simply one of a number of different protocols that are available to businesses when it comes to exchanging EDI data with one another. However, AS2 is increasingly being recognised as the most reliable and attractive EDI protocol for businesses across all industries.
The reason for AS2’s impressive reputation can be boiled down to three key benefits that it offers users:
- Security
When messages are sent via AS2 they are encrypted by the sender and have to be decrypted by the receiver. This provides a layer of security that is crucial given the business-critical nature of the information being exchanged.
- Transparency
When using AS2, the sender will always get an acknowledgement notifying them if their partner has successfully received the message or not. Plus every message has a unique identifier, which makes tracing very easy.
- Convenience
AS2 is extremely popular with large supply chain organisations. In the retail sphere, for example, Walmart, Amazon and Migros all require suppliers to use AS2 – with Walmart having done so since 2002. This has had a knock-on effect on supply chains across the world, meaning AS2 is now the logical choice for customers and suppliers alike. Moreover, the fact that AS2 uses HTTP to exchange messages is also beneficial, as HTTP’s own popularity and high level of standardisation makes debugging simple.
What are the key attributes of the AS2 protocol?
Keys and certificates
One central feature of the AS2 protocol is the use of keys. In AS2 exchanges, sender and receiver have both a public and private key. These public and private keys are mathematically related, with the public key being calculated using the private key.
Public keys are meant to be shared with partners, and allow recipients to verify message authenticity without requiring the sender’s private key. If the system just required each party to have a public key, there would be no way to verify that a message wasn’t sent by a fraudulent party.
In AS2 exchanges, a certificate contains the public key of a party, together with a signature, which can be made using the private key of a trusted certificate authority (CA).
Key stores
Key stores are containers that hold several private keys and certificates. Two common use cases of containers are identity stores and trust stores. The first holds a private key with the corresponding public certificate. The latter holds a set of certificates, e.g. from CAs.
Key stores are usually single files with different extensions. Common extensions are .jks (Java Key Store) and .p12 (present industry standard).
Encryption
Data encryption is a key aspect of the AS2 protocol as it ensures the security of the data being transmitted. In exchanges sent via AS2 the sender encrypts the payload with the public key of the receiver. This ensures that only the receiver (who has the relevant private key) can decrypt the message.
Most commonly used AS2 encryption algorithms = Triple DES (3DES) and AES-256 (both state-of-the art encryption algorithms)
Digital Signatures
In addition to encryption, AS2 also uses digital signatures, which allow the user to guarantee the authenticity of the sender/receiver. First, the sender signs the payload with a private key. The receiver then verifies the origin and authenticity of the message using the sender’s public key.
Most commonly used AS2 signature algorithms = SHA1, SHA256 and SHA512
Acknowledgements
In AS2 EDI exchanges, a Message Disposition Notification (MDN) serves as an acknowledgement of the message transfer to ensure non-repudiation. It is a digitally signed receipt of a file which is received by the recipient and sent back to the message sender.
Hash Function / MIC
The message integrity check (MIC) is connected to the MDN, and ensures the integrity of the message content. It is calculated with a secure hash function over the payload. The receiver calculates the MIC over the received payload and sends the MDN, including the MIC value, back to the sender. If the returned MIC value equals the original calculated MIC value, the payload is an integer.
How AS2’s secure transmission loop works
The diagram below shows how a message is transmitted from sender to receiver, and how the receipt of the message is communicated back to the sender.
[click to enlarge]
On the sender’s side…
1) The message integrity check (MIC) is completed using a secure hash function.
2) The sender then digitally signs the message content with their private key and the file content (including the signature) is placed in a MIME message.
3) The MIME message, which includes the file content and the digital signature, is encrypted using the receiver’s public key (certificate).
4) Before the data is transmitted via HTTP, specific AS2 EDI headers are added, e.g. AS2-FROM and AS2-TO. Additionally, a request for the return of a signed receipt is requested.
On the receiver’s side…
5) The message AS2 headers are checked to verify if sender and receiver are correct.
6) The receiver then decrypts the message with their private key.
7) To verify the sending partner (and that the payload wasn’t changed), the signature is verified with the sender’s public key (certificate). If both steps are successful, the integrity of the data and authenticity of the sender can be guaranteed.
8) The receiver returns the signed receipt as confirmation (MDN). This receipt contains the hash value of the message (MIC). Therefore, the sender has confirmation of the proper authentication and decryption of the receiver. The MDN is also transmitted via HTTP, either synchronously during the same session or asynchronously within a different session than the sender’s original session.
Back on the sender’s side…
9) The signature of the MDN is verified with the receiving partners certificate, confirming that the MDN was digitally signed.
10) The MDN is stored for non-repudiation or troubleshooting purposes.
Setting up an AS2 EDI connection
Before you can start exchanging messages via AS2 with partners, it is necessary to complete several steps. The first and most important of these is setting up the relevant AS2 software.
Software setup
For businesses in this position there are three distinct approaches to choose between: installing the software on-premise, installing via the cloud, or opting for a Software as a Service (SaaS) solution.
1) Installing on-premise
Traditionally, on-premise installation has been the most popular approach for achieving AS2 compatibility (be it on company servers or virtual machines).
Pros
- Simple to meet data localisation requirements
- Tight integration with internal systems possible
Cons
- Expensive, especially when operational and maintenance costs are accounted for
- Integration with cloud-based systems (e.g. Google storage) can be difficult
2) Installing via the cloud
A cloud-based approach offers a simple way to satisfy regulatory requirements while leveraging the flexibility and availability of the cloud.
Pros
- Excellent scalability and availability
- Greater capacity for integration with cloud services
- Lower cost than in-house installation thanks to much simpler operation and maintenance
Cons
- Integrating with legacy in-house technology can be difficult
3) Utilising an SaaS provider
Using a SaaS provider offers a quick way to achieve AS2 EDI connectivity, with users able to sign up and configure AS2 settings themselves via a web interface.
Pros
- High potential for cost savings, particularly for businesses sending a low volume of messages via AS2, as payment is typically managed on a per use basis
- AS2 connectivity can be achieved extremely fast
- No maintenance or operational costs
Cons
- Can be difficult to meet specific data localisation or network requirements.
- As with cloud-based installations, integration with in-house legacy technology may be tricky
Creating a partner profile
Once access to AS2 EDI software has been achieved (either via on-premise installation, the cloud or an SaaS solution) both you and your partner must provide the other with your AS2 identifier, URL and certificate.
Both parties must then create a ‘Partner’ entity within the AS2 software using this information.
Testing
After partner profiles have been created, the next step is to test connectivity. This is done by exchanging basic text files, which can then be verified for integrity by the receiver. During this stage it is also advisable to test the sending and receiving of MDNs.
The AS2 connection is deemed complete and validated only when both partners can exchange files successfully.
Final setup and go-live
Once testing has been successfully completed, the AS2 connection can be made live.
Looking to experience the benefits of EDI with minimal internal effort?
Whether it’s setting up an AS2 EDI connection, handling complicated EDI mappings, or simply liaising with partners during onboardings, EDI processes can be technical and time consuming.
Thankfully, however, effective EDI doesn’t have to be difficult!
At ecosio we understand the importance of successful, reliable EDI connections, and are passionate about helping our clients to experience EDI’s full potential. As we know that supply chain organisations don’t always have the time or expertise to integrate, run and maintain an EDI solution, we offer a fully managed service, allowing businesses to experience all the benefits of efficient EDI with none of the hassle.
With a single connection to ecosio’s cloud-based EDI solution (our Integration Hub), you can achieve hassle-free connections to all your partners, no matter how complicated your routing or mapping requirements.
In short, we take care of all your EDI needs, from liaising with partners and setting up connections to message monitoring and error resolution, leaving you to concentrate on what you do best.
For more information, contact us today!
Der Beitrag The AS2 EDI Protocol Explained erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag EDI vs API: A Battle of Brothers erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Before we answer these questions, let’s first explore how EDI and APIs work and the pros and cons of each.
How EDI works
EDI itself isn’t really a technology; it’s more like a method of B2B communication. In a nutshell, EDI is the means by which business partners exchange structured information such as orders, invoices and delivery notes with one another.
Sending an EDI message involves condensing the relevant data that one wishes to send into a specific computer-readable file format. This simple file is then transmitted to the recipient via an agreed transfer protocol, after which the recipient’s system then automatically reads, extracts and stores the data.
For a more detailed breakdown of how EDI works, please see our “What is EDI?” article.
The benefits of EDI
- Security. EDI is conduced using closed networks such as X.400 or VANs or by using dedicated point to point connections – e.g. based on AS2, SFTP or OFTP2. The security credential exchange with the business partner is usually done via a secure channel – e.g. in case of ecosio using the ecosio.monitor. Plain APIs are often secured with HTTP Basic Authentication or Bearer Tokens, whereby the exchange of the security credentials is not clearly defined. More modern approaches such as OAuth2, however, are successfully trying to overcome this limitation, by introducing a central identity provider.
- Popularity. As it has been around for decades, EDI is used by businesses worldwide and across all industries. Today it is by far the most popular method of exchanging business-critical information with partners and is thus the logical choice for those debating EDI vs API.
- Time-saving. By vastly reducing the number of manual tasks involved in sending/receiving B2B documentation, EDI allows internal teams to focus on more value-adding tasks while simultaneously reducing the potential for human errors.
- Low message size. Compared to other methods of exchanging data, such as via email or JSON, sending messages via EDI standards (with the exception of XML) requires much less bandwidth..
The limitations of EDI
- Batch processing. In most EDI scenarios messages are sent and received in batches (e.g. once a day) rather than one at a time. While this may not be a big issue for some, it does prevent real-time data visibility. This in turn impacts the ability of businesses to respond quickly to new information – e.g. by updating inventory levels.
- Partner-specific communication channels. Though EDI can be used by companies to connect them with thousands of partners, each partner connection must be set up individually. For customers, this typically involves providing suppliers with a message implementation guide (MIG) which specifies the desired file format and transfer protocol. The supplier then needs to conduct technical mapping to ensure information can be correctly converted from their inhouse format to the required EDI format. Once this is done, they must then send test messages via the agreed protocol before the connection is made live.
- Limited traceability. In traditional EDI exchanges, it generally isn’t possible to see whether or not a message has been received by the final recipient. Even when modern protocols such as AS4 are used, the sender can typically only see when a message reaches the EDI service provider (a bit like seeing just one grey tick on WhatsApp and not two blue ticks).
What is REST API?
REST stands for Representational State Transfer. REST itself isn’t a protocol. It’s a widely employed method of writing APIs. APIs inherently lack a standardised composition. Instead, their structure is dependent on messaging formats such as JSON, with REST relying on HTTP(S).
The benefits of APIs
- Speed. With APIs there’s no need to wait for the other side to send information; instead relevant data can be pulled automatically as soon as it becomes available. In fast moving supply chains this can be extremely useful.
- Flexibility. APIs are by their nature flexible, as there are few rules and standards concerning how data must be used. This makes APIs a fantastic tool for software developers as they can be integrated into existing and emerging solutions to boost performance, whether this involves pulling relevant data periodically or receiving data instantly via POST.
- Simplicity. Unlike with EDI, with APIs there’s no need for data to be transformed to and from different encrypted formats. Instead, the API connects systems (e.g. ERP systems) directly, meaning data is automatically updated in the relevant place.
- Less specialised. As APIs are used in a myriad of different scenarios, knowledge of how to use APIs is not limited to individuals with experience in certain industries – something that cannot be said for EDI expertise. All web developers should have at least a basic understanding of how to use APIs.
The limitations of APIs
- Scalability. As every business’s data is structured and stored differently, no two APIs are the same. As a result, unlike with EDI, where mappings between common EDI file formats and your inhouse format can be reused as the semantics of the data being exchanged is standardised, every API-based connection requires a bespoke technical setup. Similarly, there is also no standardised way of designing APIs, meaning there is no agreed process choreography. For example, whereas one partner might request a purchase order response, another may simply take a successful order placement as confirmation – a situation that can easily lead to issues.
- Popularity. When it comes to the EDI vs API debate concerning B2B interactions, this is a key issue. Thanks largely to the lack of scalability offered by APIs, the vast majority of supply chain organisations prefer to exchange information via EDI, with many larger customers simply refusing to work with suppliers who cannot conduct EDI.
- Security. While an API may be extremely useful in some cases – e.g. allowing all potential partners to see your full product catalogue master data – it isn’t suitable for exchanging sensitive information.
- Missing information. APIs typically don’t include information such as logical sender address, receiver address or document type definitions. Although these aren’t required in point-to-point scenarios, they are extremely important when communicating with the third-party-networks used by large businesses.
- Internet-dependent. As APIs depend on a stable internet connection, if and when you experience internet connectivity issues, it will not be possible to retrieve information via API.
Why APIs won’t replace EDI
Having examined the benefits of APIs, one could be forgiven for concluding that APIs will replace EDI as the main method by which B2B partners exchange information. Undoubtedly, APIs do offer considerable advantages when it comes to streamlining B2B interactions. In particular, EDI cannot compete with the speed with which APIs allow information to be fetched, the depth of integration API’s offer into existing systems, or the data visibility APIs provide.
However, there is one key reason why APIs will never ultimately win the EDI vs API battle… the need for bespoke processes.
Until such a time as universally acknowledged rules are created for APIs and their usage in supply chains, all API integrations will involve unique technical requirements and must therefore be handled individually. Although APIs may be great for a single point-to-point connection between two partners, it is simply not possible to use the same approach for a wide partner landscape. Imagine a supplier with hundreds of customers, for example. If APIs were used for each connection, potentially every customer could demand that the supplier follows a different process. This would involve a huge amount of time and effort.
By contrast, EDI usage has continued to grow over the decades as its insistence on the use of accepted file formats and standardised processes enables connections to be established much faster and for previous mapping work to be reused. Similarly, EDI’s methodology and focus on standardisation also ensures the right data is exchanged and makes it easy to test multiple different business scenarios, in turn helping to avoid issues further down the line.
Why the future is EDI + API, not EDI vs API
While APIs will never replace EDI for the reasons explained above, this doesn’t mean that APIs can’t help to boost the efficiency of B2B communication. In fact, used properly, APIs can transform EDI solutions by providing functionalities previously out of reach to EDI users.
For example, two of EDIs major limitations – namely its limited data visibility and reliance on batch processing – can be essentially eliminated by incorporating APIs. While converting internal data into agreed formats and transmitting this data to partners via secure protocols still offers the most efficient solution for exchanging critical B2B information, APIs can streamline the process at either end by allowing relevant systems to talk to one another. By incorporating APIs into EDI processes, users can experience end-to-end message visibility, allowing them to see whether or not partners have received or acknowledged a message in real time. Meanwhile, by integrating an EDI solution into your ERP system via API, EDI data can be made accessible to any and all relevant individuals within your existing user interface, ensuring that EDI doesn’t become a black box.
Similarly, the rapid rise of country-specific e-invoicing requirements presents another arena where APIs can improve the efficiency of EDI solutions, with API usage even mandated by public administrations in some countries.
In conclusion, although there is certainly some overlap in what API and EDI do, they each have their own separate domains. It’s therefore pointless to picture the situation as EDI vs API. They aren’t enemies, but rather tools that can be combined intelligently to create flexible yet secure B2B integration solutions.
How ecosio EDI solution works
At ecosio we’re acutely aware of the benefits of combining EDI expertise with a powerful API and have developed a unique solution incorporating API to help our clients achieve maximum automation with minimum effort.
As illustrated below, the technical hub of ecosio EDI solution is called the Integration Hub. This is located in the cloud, and is where all the technical mapping and routing work is done by ecosio’s EDI experts to connect you to your partners. Crucially, rather than requiring clients to send data to the Integration Hub manually, ecosio EDI solution is integrated directly into clients’ ERP systems.
This deep integration enables you to benefit from unmatched data visibility and real-time monitoring within your existing user interface. The result? No need for additional systems, no more frustrating bottlenecks, and no more silent message failures.
What’s more, thanks to ecosio’s ongoing message monitoring, when errors do occur, they are identified and resolved proactively by our EDI experts, leaving your team free to focus on more value-adding activities.
Discover more about our updated product, ecosio.flow.
Der Beitrag EDI vs API: A Battle of Brothers erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag EDI Interfaces Explained erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- EDI interfaces enable automated exchange of structured business data, converting internal formats into standardised ones like EDIFACT or XML to reduce manual input and errors
- The process relies on connectivity, conversion and communication, involving agreed formats, mapping to EDI standards, and secure protocols such as AS2, OFTP2 or REST API
- Common problems include lack of user-friendliness, limited flexibility, dependence on in-house expertise, and rushed implementation
- A good interface offers seamless integration, flexibility, security, scalability, monitoring, and especially data visibility, which is enhanced through API connections enabling real-time status tracking and error resolution
As the old saying goes, time is money; and nowhere is this more relevant than in the world of B2B transactions. From data entry errors to message failures and delays, inefficient B2B processes can cost businesses dearly. By offering a means to automate B2B communication, electronic data interchange (EDI) and EDI interfaces enable businesses to both save time and improve efficiency – in turn resulting in significant cost savings!
Contrary to what many think, setting up a successful EDI interface isn’t rocket science. In fact, with the support of the right EDI provider, you can start reaping the benefits of a good EDI interface in no time. But what exactly makes a good EDI interface? How does an EDI interface work, and what benefits can a good interface offer? In this article we’ll answer all of these questions and more.
What is an EDI interface?
An EDI interface is a technical platform that enables the electronic exchange of structured business data between different systems. EDI interfaces are crucial in business communication, where they automate the manual exchange of documents (such as purchase orders, invoices and shipping notifications).
Simply put, an EDI interface converts data from internal systems (e.g. accounting software) into a standardised format – and vice versa. Once in standardised format, the data is automatically sent to the relevant external party (e.g. a customer or supplier). Not only does this automated process save time, it also greatly reduces the potential for errors, as the need for manual data input is removed on both the sender and receiver’s sides.
How does an EDI interface work?
An EDI interface can be set up via different communication channels: via the internet, via direct connections between systems or via special EDI networks.
The data transfer between sender and receiver is based on the three “C”s: connectivity, conversion and communication.
- Connectivity. Before anything else, the sender and receiver must define a common, structured data format, e.g. EDIFACT or XML, which is then used for all exchanges via the EDI interface. In most cases the format to be used is dictated by the customer via a message implementation guideline (MIG).
- Conversion. Once this format has been chosen, mapping must be done to ensure that data is correctly converted from whatever inhouse format is being used (e.g. IDocs in SAP systems) to the agreed EDI format. This step involves a lot of technical expertise and testing.
- Communication. Once mapping has been set up, the next step is handling how the data is transferred – i.e. what transfer protocol should be used. Protocols are the means by which data is securely transferred to the recipient, with popular protocols including AS2, HTTP, OFTP2, REST API and web services.
On the recipient’s side, the process then takes place backwards: they receive the data via their EDI interface and convert it into its internal format before validating and processing it. After processing, the receiver sends a response to the sender to confirm the successful receipt of the data as well as its processing. In the event that processing problems occur, the response may also include error messages.
The four most common problems with EDI interfaces
As we’ve mentioned already, when implemented well, an EDI interface can provide many benefits, from helping businesses save time and money, to reducing risk and boosting attractiveness to partners. However, there are many things that can prevent an interface from delivering maximum value. These include…
- Not being user-friendly. Given the extent of the technical work required to send and receive EDI messages, EDI interfaces are often complicated to use, with data accessible only to IT personnel. In such situations, IT can easily become a bottleneck, and the potential value that EDI can offer is limited.
- Lack of flexibility. Whether due to internal or external factors, EDI requirements inevitably change over time. Unfortunately, not all EDI interfaces lend themselves to quick adjustments, however. For example, if an EDI interface is maintained by in-house staff members who have other responsibilities – as opposed to external experts – tasks such as onboarding new partners or changing complicated mappings may take a long time to complete.
- Dependence on in-house technical expertise. The implementation of a good EDI interface requires a lot of technical expertise, both during setup and ongoing operation. If EDI tasks are to be handled internally and inhouse resources are lacking, this can be a real issue.
- Rushed implementation. Despite the fact that EDI is essential in modern B2B relationships, it’s rarely given sufficient consideration in ERP migration projects. As a result, EDI interfaces are often implemented at the end of migration projects, with ERP customisers rushing to find something that can do the job rather than taking the time to select a well-suited, futureproof solution.
What makes a good EDI interface?
A good EDI interface is characterised by several features.
- It should allow seamless integration to ensure smooth data exchange between different systems.
- It should be flexible and support diverse data formats to meet the requirements of different business partners.
- It should be secure and provide mechanisms for data encryption and authentication in order to guarantee the confidentiality and integrity of the transmitted data.
- It should be scalable and able to adapt as your EDI needs evolve over time.
- It should have extensive message monitoring and error handling functions to allow for errors to be spotted and resolved quickly.
Perhaps the most important feature of a successful EDI interface, however, is data visibility.
Given the significance of the data being exchanged via EDI, relevant departments having real-time visibility of key information – such as whether or not a partner has received or opened an invoice – is extremely important. Similarly, having access to an EDI dashboard which offers a helpful overview of EDI message flow can make message monitoring much easier.
Despite this, such functionality is only offered by a minority of EDI interfaces – namely those which utilise an API connection…
How an API connection can boost efficiency
As a collection of rules and protocols, an API connection defines how the various exchange formats, exchange protocols and security requirements of an EDI interface should interact. The main advantage of EDI interfaces based on API connections is that the data is accessed directly. This means that no metadata is lost and important information such as whether an invoice has been received by the EDI service provider or by the final message recipient can be displayed in real time in the existing user interface of the user’s ERP system. This improves supply chain efficiency and minimises the occurrence of errors.
When errors do occur, the data transparency offered by API connections is also extremely helpful, as the user can easily determine where the problem lies and what needs to be done to resolve it. EDI interfaces which utilise API connections may also offer added benefits such as full-text search functionality, which allows EDI messages to be found quickly by searching for any known identifier, such as article number or transmission ID.
Another key benefit of connecting an EDI interface via API is that specialist teams such as sales or purchasing don’t need to go through IT to get key information. By improving data visibility and accessibility and allowing relevant employees to access data directly in their ERP system, using an API connection eliminates internal bottlenecks.
In short, EDI interfaces that utilise an API connection help businesses to streamline B2B processes by ensuring that all relevant parties have real-time visibility of important information, that information can be located easily, and that errors can be resolved quickly.
Want to know more?
Want to know more about EDI and how ecosio’s unique EDI as a Service solution could help you? Then contact us today! Our EDI experts will be more than happy to show you how you could leverage efficient EDI to save time, save money, reduce risk and boost your competitive advantage.
Discover more about our updated product, ecosio.flow.
Der Beitrag EDI Interfaces Explained erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag How EDI Can Reduce Your Carbon Footprint erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Although wanting to make a difference is certainly a large driver for many businesses, implementing positive changes often makes just as much sense from a financial standpoint. More and more customers are looking at businesses’ environmental credentials when making decisions. Plus, often the same actions that reduce a business’s carbon footprint will deliver real cost savings too.
Implementing or upgrading an electronic data interchange (EDI) solution is a perfect example of just such an action.
But let’s first take a step back to explain what electronic data interchange actually is.
What is EDI?
EDI refers to the method via which businesses exchange documents with one another automatically. The messages themselves are typically not readable by humans. Instead they are formatted according to specific computer-readable standards. For this reason, a typical EDI invoice looks very different to a PDF invoice that you might receive via email.
EDI standards were developed so that businesses could interchange documents efficiently between each other without human intervention and without errors, as the standards dictate exactly where each piece of data must go in the document. This in turn allows the recipient’s machine to extract the data automatically.
Importantly, EDI standards and the message protocols used to transmit them also mean that sending and receiving EDI messages requires less energy than via email… but we’ll come to that later…
For a more detailed overview of what EDI is, you may want to check out our video on this subject here.
How popular is EDI?
One estimate puts EDI usage in the supply chain sector somewhere between 59% and 85%. For example, nearly 70% of all sales in the manufacturing industry in the USA in 2021, for example, were carried out through EDI systems.
For more interesting EDI stats, why not check out our infographic on the business benefits of EDI?
How EDI directly reduces your carbon footprint
The most obvious direct effect of EDI is in paper consumption. Using EDI virtually obliterates paper consumption relating to common B2B messages such as orders, invoices, delivery notes, and so on.
If we just look at invoices, for example, a typical mid-sized business produces 18,000 invoices in a year. That equals two tonnes of paper!
But invoices are barely a drop in the ocean. Considering that the average UK employee prints 8,000 A4 pieces of paper a year, we’re looking at 80,000 pieces of paper for a company of 10 people. If one tree can produce 10,000 sheets of paper, we’re looking at eight trees lost in a year for all that paperwork.
Multiply that by all the companies in the UK, and their size, and we’re looking at a truly mind-blowing number.
The loss of trees not only means that less CO2 gets removed from the environment. Cutting trees and turning them into paper also adds CO2 due to the high carbon footprint of the papermaking process from beginning to end.
One kilo of paper produces about a kilo of CO2 during its production lifecycle.
How EDI indirectly impacts your carbon footprint
In addition to the direct impact that EDI has on paper consumption, there are significant indirect effects of using EDI as well…
Fewer emails = a smaller carbon footprint
Though it is often overlooked, emails do have a carbon footprint. The size of this footprint depends on several factors:
- How long the email is stored for. Emails stored for longer require more space on a hard drive somewhere, even if that hard drive is on the cloud. The more space is required, the more energy is needed.
- How large the email is. The larger the email, the more energy is used to send it.
- How many people are cc’ed in the email. Sending an email has a carbon footprint and so multiplying the number of people it is sent to multiplies the carbon footprint.
- If the email has attachments, and how many. Email attachments add to the email’s size. Generating the attachment also takes up energy depending on the software used.
This is nothing nebulous. It’s a matter of hard fact. A study conducted in 2019 discovered that Brits send 64 million unnecessary emails a day and that sending one less “Thank you” email a day would save 16,433 tonnes of carbon a year, or as much carbon as is produced by 81,152 flights to Madrid from the UK!
As Mike Berners-Lee, professor at the environment centre in Lancaster University, and brother of the man who invented the internet, said: “Whilst the carbon footprint of an email isn’t huge, it’s a great illustration of the broader principle that cutting the waste out of our lives is good for our wellbeing and good for the environment.“
EDI improves efficiency and reduces errors
Implementing EDI means companies need to send thousands of emails less, which greatly reduces energy use. Instead of email, EDI takes care of most of the communication between business partners.
In addition, EDI also improves efficiency and reduces errors – such as those resulting from manual data entry. Typically such errors result in a lot of runarounds, lost time, additional emails, and unnecessary use of machinery, which in turn increases a company’s carbon footprint.
How to get started with EDI
Want to start experiencing the benefits of EDI or keen to upgrade to a more efficient solution? At ecosio we’re experts when it comes to B2B integration. With our help you’ll not only be able to improve your carbon footprint and boost the sustainability of your business; you’ll also save time, save money and reduce risk.
Find out more about our unique EDI as a Service solution, or get in touch. We are always happy to help!
Der Beitrag How EDI Can Reduce Your Carbon Footprint erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag A Guide to Efficient EDI Systems erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>What is an EDI system?
An EDI system is the means by which a business exchanges electronic documents (such as orders, invoices and delivery notes) with its customers and suppliers automatically. While EDI systems can take several different forms, they can be broadly grouped into three main categories:
- On-premise (AKA local EDI converter) systems
- Platform as a service (AKA “managed”) systems
- EDI as a Service (AKA “fully managed”) solutions
As we break down in our infographic comparing these solutions, they differ significantly in terms of how much internal work is required to operate them. However, regardless of who does the work, all do largely the same job – allowing you to trade key documents with business partners quickly, easily and accurately (as minimal human intervention is required).
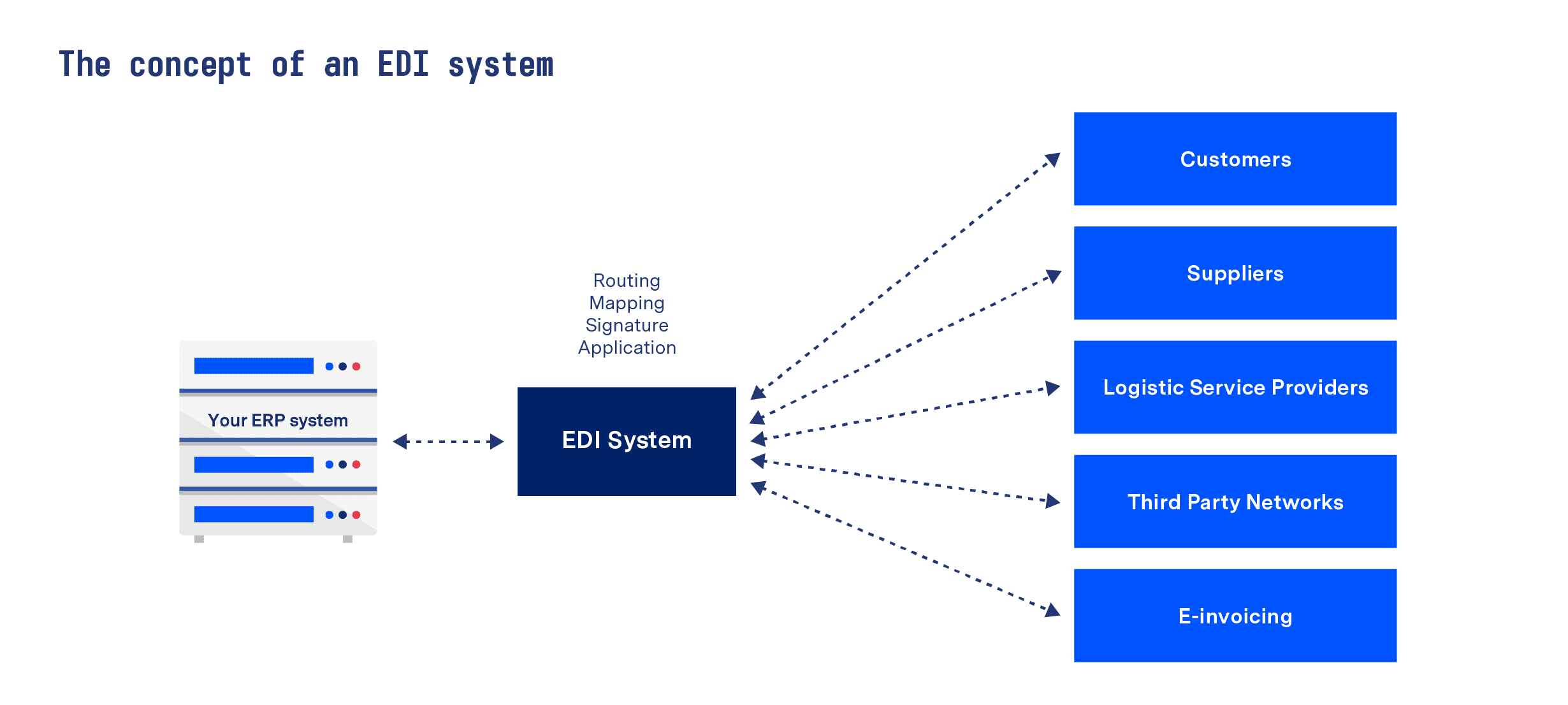
Why EDI systems are increasingly central to business operations
Businesses have never been so dependent on one another as they are today. Because of this, as recent supply chain issues have shown, things can easily snowball when problems arise. As a result, it’s no surprise that more and more companies are taking steps to safeguard the sustainability of their supply chains by optimising automated B2B communication processes.
While EDI has long been essential for retail and automotive supply chains, going without EDI is simply not an option for any industry today. One reason for this is the benefits automated data exchange can offer – allowing businesses to react quickly (usually in real time) and ensure message exchange remains error-free. Another key reason is the fact that it is now demanded by an ever-growing number of businesses, with large businesses in particular keen to eliminate manual processes in exchanges with smaller suppliers in order to enjoy automated connections to all partners. Likewise, governments across the world are introducing mandatory e-invoicing for both B2G and B2B exchanges – meaning businesses have no choice but to implement a solution.
What makes an efficient EDI system?
To be successful, an EDI system must…
- …Be able to cover all of your needs. Which formats do you need to be able to map to? Is onboarding partners fast a priority? Is it important that your EDI data is protected in the event of system failure? While questions like these may seem obvious, many businesses fail to conduct an appropriate assessment of what their existing EDI needs are, which often results in a sub-optimal solution.
- …Fit your internal resources/expertise. There is no such thing as a one-size-fits-all EDI solution, so it’s important to select one that aligns with your internal capabilities and resources. For example, if you have substantial EDI expertise and personnel in-house, local EDI converter software may be an option for mapping setup, while message transmission may be outsourced to an expert provider. Alternatively, if you don’t have internal EDI expertise and want other departments to have the ability to access EDI data, an EDI as a Service solution makes more sense.
- …Streamline crucial processes. Obviously all EDI streamlines message exchange to some extent, but some EDI systems go further than others. For example, with an EDI as a Service solution all partner onboarding (from first contact right through to go-live) is handled by external EDI experts – reducing internal effort to next to nothing. Plus such solutions also help to optimise internal processes, as specialist departments are able to search for and access EDI data directly.
- …Be flexible. EDI requirements change over time, and it’s important that your EDI system is able to adapt if it is to continue to offer maximum value. With this in mind it’s best to steer clear of any EDI contracts that include steep “price cliffs” for changes in message volume or additional capabilities.
- …Work for you! Running an EDI system shouldn’t feel like a headache. A good EDI system should be something that works for you in the background, helping you to reduce risk, lower costs, save time and generally streamline connections in a futureproof way.
How difficult is migrating to a new EDI system?
Not difficult at all… if you pick a system that meets your needs and resources that is.
Unfortunately, fear of changing a running system is one of the main reasons that businesses persist with outdated and inefficient EDI systems. However, ignoring a problem will never make it go away, and putting off a necessary migration project will only further damage your chances to gain a competitive advantage over others in your industry and delay your ability to enjoy the benefits good EDI can deliver.
While some businesses do make expensive mistakes when it comes to EDI, for those who plan their migration project properly and select the right EDI solution, migration can be a breeze. In particular, if you opt for an EDI as a Service solution (such as that offered by ecosio), everything from initial technical setup to ongoing operation is handled by your EDI provider – including partner onboardings, message monitoring and proactive error resolution. When switching to such an EDI system there is no need to worry about the migration disrupting ongoing operations, as all connections undergo rigorous testing and parallel operation before being put live.
Things to remember when selecting an EDI system
1) Preparation is key
As with any major project, planning = success. The more thorough you are when assessing your current capacity and requirements, the better placed you will be to select the right solution.
For more advice on planning your EDI project, see our dedicated blog article here.
2) Assess your internal resources
Although one of the main benefits of EDI is the fact that it streamlines previously time-consuming manual tasks, implementing and maintaining an EDI solution still requires effort. With this in mind it is important to consider both what your internal team can realistically handle and whether or not certain tasks would be better left to your provider.
Unfortunately many businesses overestimate internal capability and end up struggling to operate the solution or having to invest in additional personnel.
3) Think ahead
As we mentioned earlier, requirements can change quickly in EDI. Significantly, too, with governments across the world introducing e-invoicing regulations, and businesses demanding more and more data from their partners, changes may be outside your control.
By factoring in potential future needs (such as a Web EDI portal or routing via new protocols/VANs) when selecting an EDI system, you will avoid the possibility of being stuck with an ill-fitting, inflexible solution a few years down the line.
Could an EDI as a Service solution benefit your business?
At ecosio we have helped hundreds of businesses to revolutionise their B2B integration processes and experience the true potential of efficient EDI.
Our EDI as a Service solution takes all the hassle out of EDI, leaving you free to concentrate on what your business does best. From initial technical setup, partner onboarding, testing and go-live, to ongoing message monitoring and error handling, we manage everything so you don’t have to.
To find out more about our unique solution, click here. Alternatively, feel free to get in touch – we are always happy to help!
Der Beitrag A Guide to Efficient EDI Systems erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>