Der Beitrag EDI integration: what is it and how can it help your business? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- EDI integration automates B2B document exchange between ERP systems, eliminating manual input and reducing error
- It can be implemented via local software, cloud platforms, or EDI as a Service, each requiring different levels of internal effort and expertise
- Fully managed EDI solutions save time and cost, offering ERP integration, project management, and proactive support
- Efficient EDI integration improves partner relationships and scalability, while reducing operational risk through automation and monitoring
In modern commerce, messaging automation is becoming increasingly crucial. Not only are order turnaround times shrinking year on year, there is now also a growing expectation that the parties involved in an interaction should have full visibility of the process, from the initial order right through to fulfilment.
As we’ll explore in this article, central to enabling the streamlining of essential business processes is EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) integration – and particularly cloud-based integration, with Gartner recently noting that “there is no business strategy without a cloud strategy”.
But before we look at the different ways integration can be handled, let’s look at what EDI integration is…
What is EDI integration?
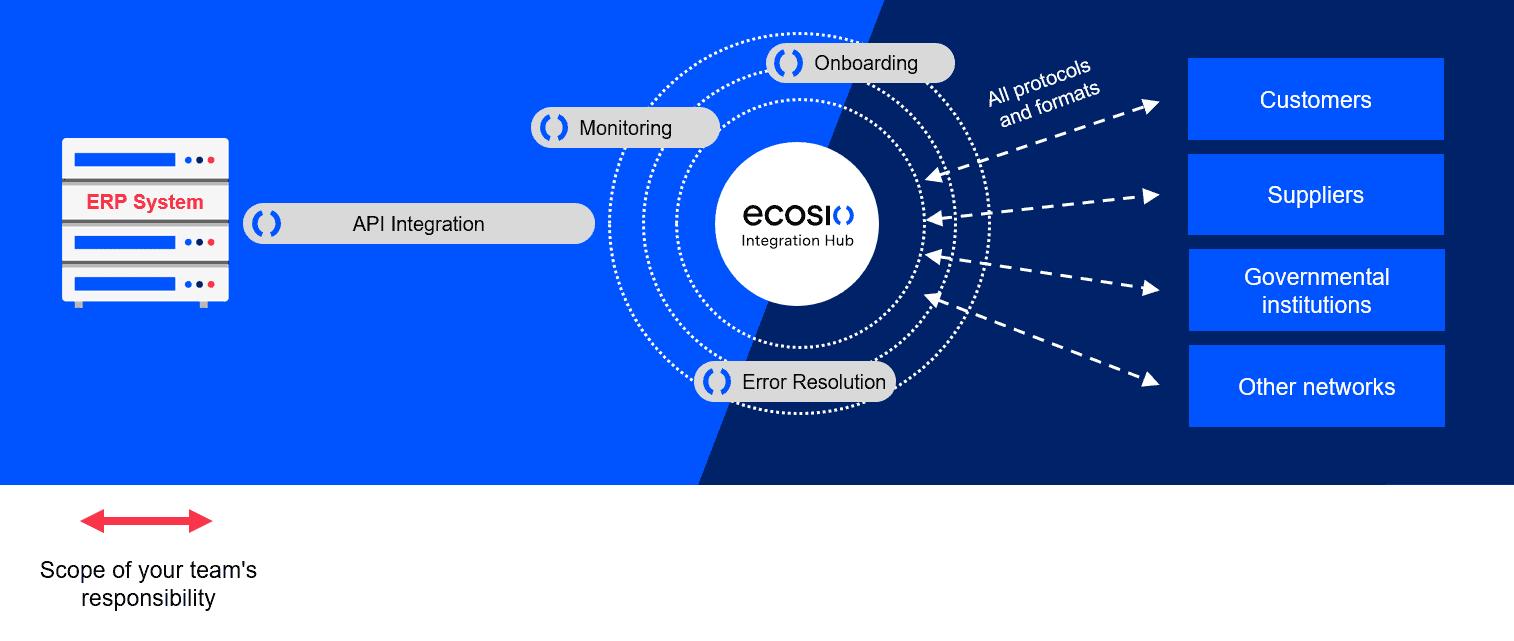
EDI integration is the means by which business partners’ ERP systems are able to exchange business critical messages (e.g. purchase orders or invoices) with one another automatically.
Once EDI integration has been set up, effectively the ERP systems of the companies involved can talk directly to one another via the common EDI language that has been agreed. Unlike sending/receiving an order via email or post, which involves many steps, including waiting for the message to be delivered, opening it, extracting the relevant information and inputting it elsewhere (also referred to as a media break), with EDI integration all this is done instantly and automatically.
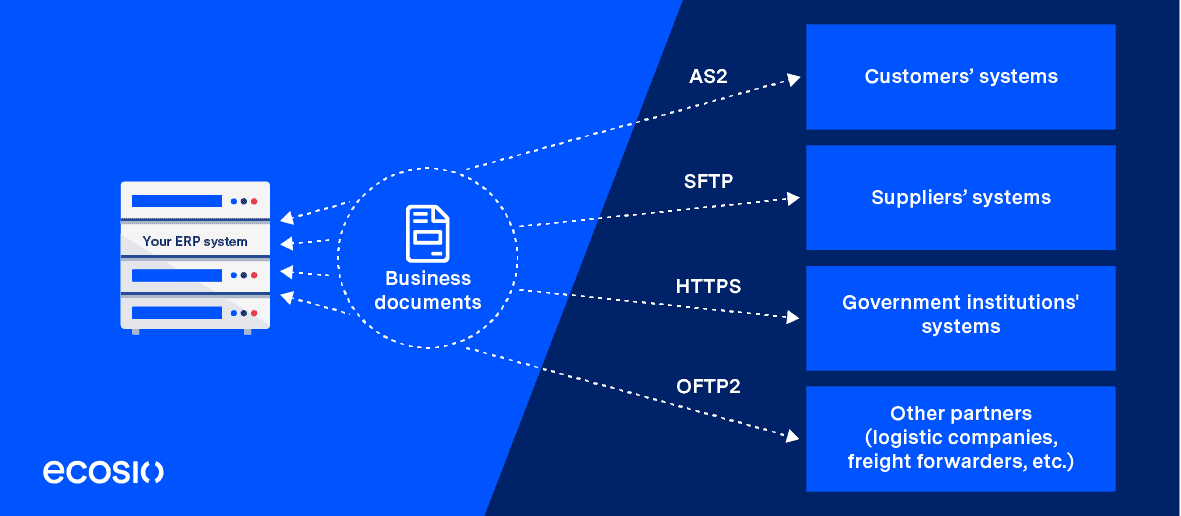
Below is a diagram showing a typical EDI integration landscape. Electronic business documents are exchanged between various business partners using certain electronic protocols. Usually the business partners in an EDI transaction are along the value chain of a company – suppliers on the procurement side and customers on the distribution side. Other partners include logistic service providers, banks, etc. Another growing trend concerns governmental institutions demanding the transmission of electronic invoices via a centralised system – e.g. FatturaPA in Italy or NAV in Hungary.
What’s involved in setting up EDI integration?
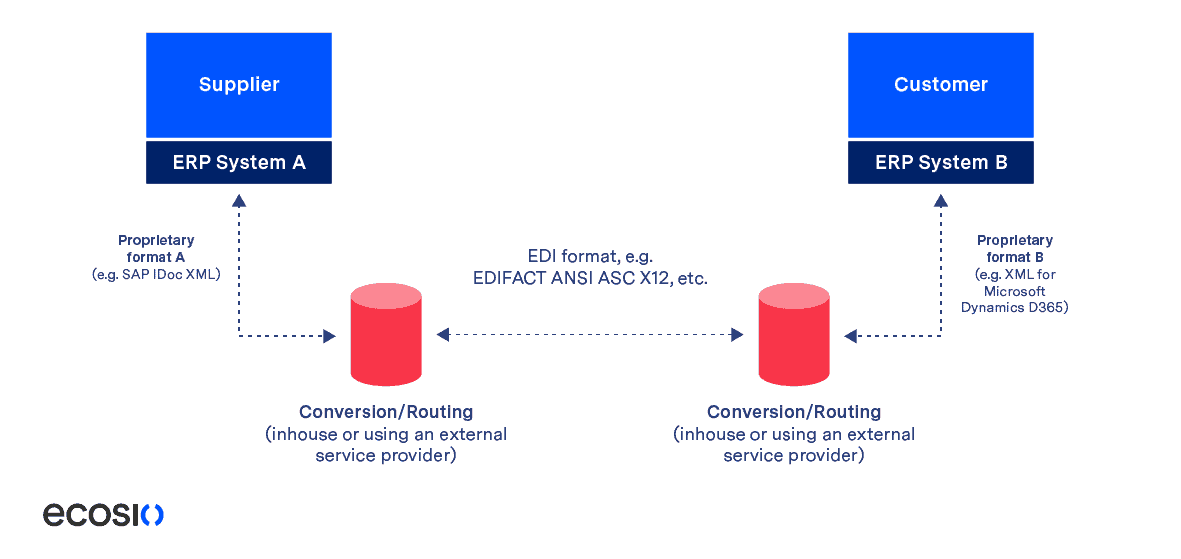
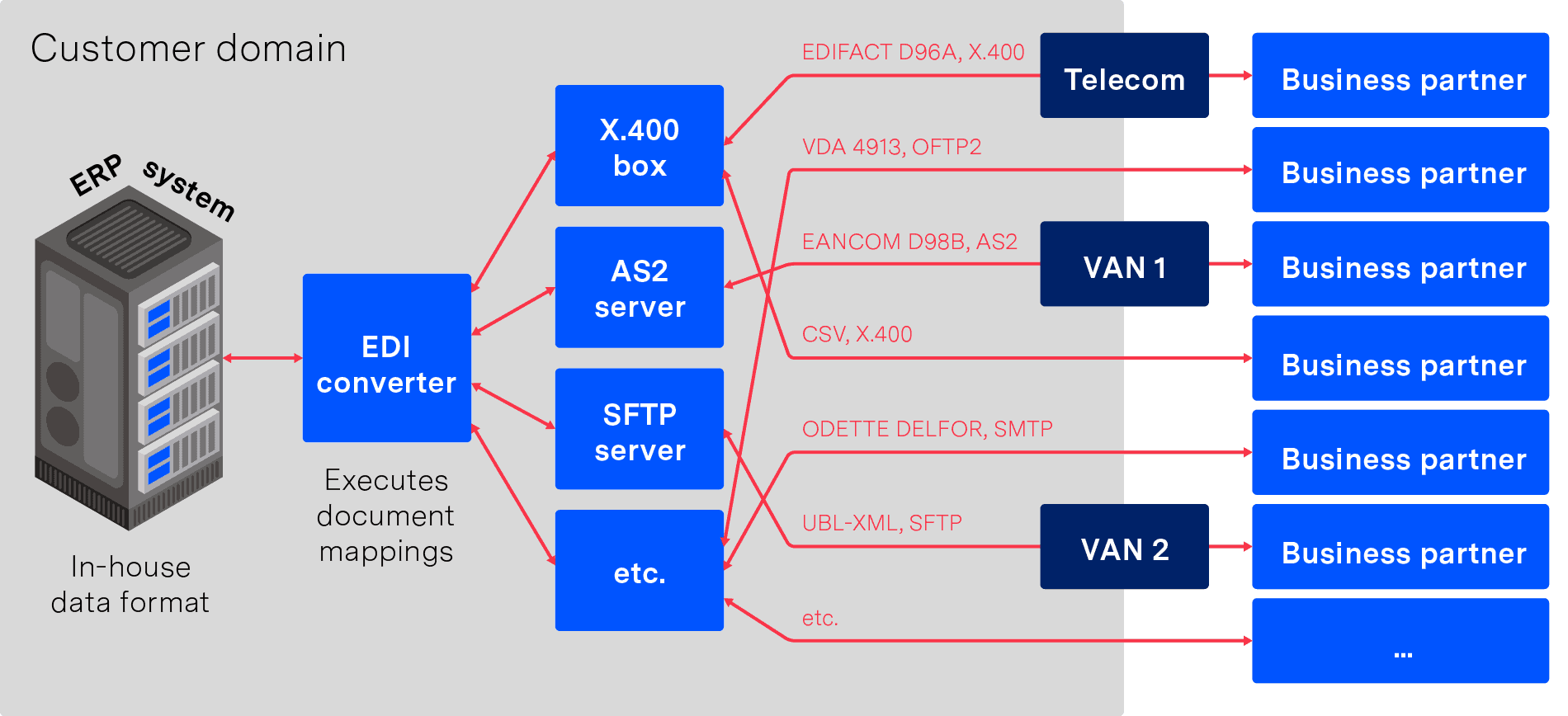
From a technical perspective, for EDI integration to work, both parties must first agree on the transmission protocol to be used and the format of the messages. Both parties must also be able to export messages from their ERP system and convert them to the EDI message format. Vice versa a conversion from the EDI format to the ERP system’s import format and the automated import into the ERP system must also be possible..
The image below shows a technical breakdown of a typical EDI connection between a supplier and customer.
Practically, an EDI integration project involves five stages:
- Assessing your requirements – Before selecting a solution you first need to work out which processes you want to automate, what the technical parameters of your ERP system are, how much internal capacity you have, who your EDI partners are, what document formats might be needed, and what volume of messages you expect to be exchanging.
- Choosing your EDI provider – Armed with the knowledge of your requirements and internal capacity you are in a good position to choose an EDI provider. During this stage it is important to think about future growth and to investigate what providers are really offering – particularly when it comes to support and pricing.
- Planning implementation – This step involves drawing up a project plan with clear priorities and timelines. For example, a key task during this stage is to agree in what order partners should be onboarded.
- The technical implementation – This stage involves agreeing transmission channels, protocols and message formats with partners. It also involves organising and overseeing testing, parallel operation of EDI and existing processes (e.g. based on paper), and then go-live. The extent to which you are responsible for these steps depends on which approach you opt for (as we shall explore in the next section).
- Ongoing operation – Once your system is up and running, it needs to be monitored constantly to make sure any errors that occur aren’t allowed to escalate. Your solution may also need to be updated and adjusted as needs change.
If you would like a more comprehensive breakdown of what the EDI implementation process involves, you can find one here.
How can EDI integration be achieved?
There are three main routes businesses can take when it comes to achieving EDI integration. These are…
1) Use a local EDI software (aka EDI converter)
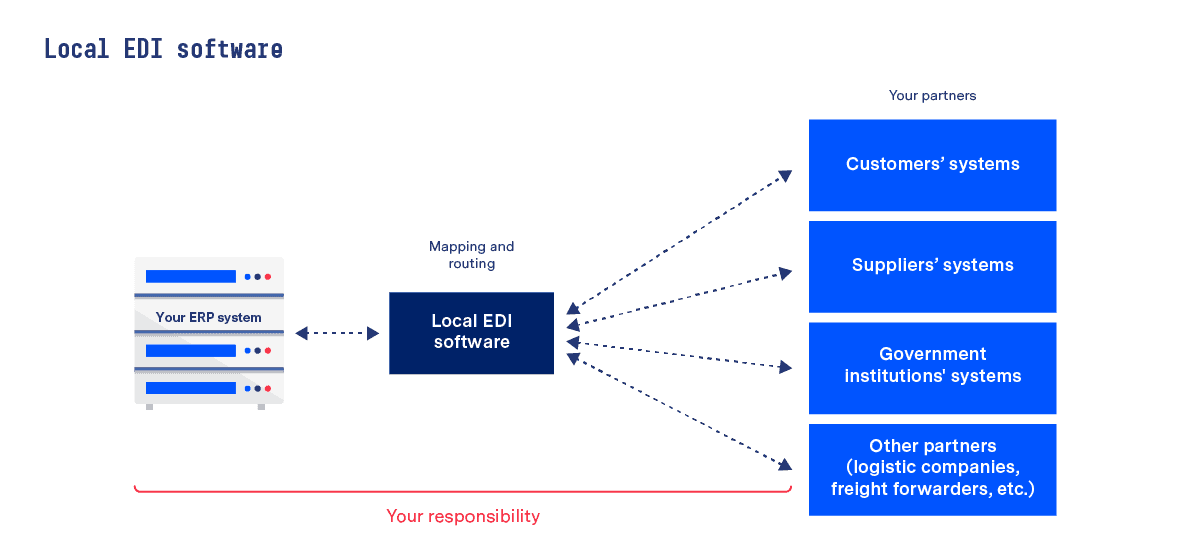
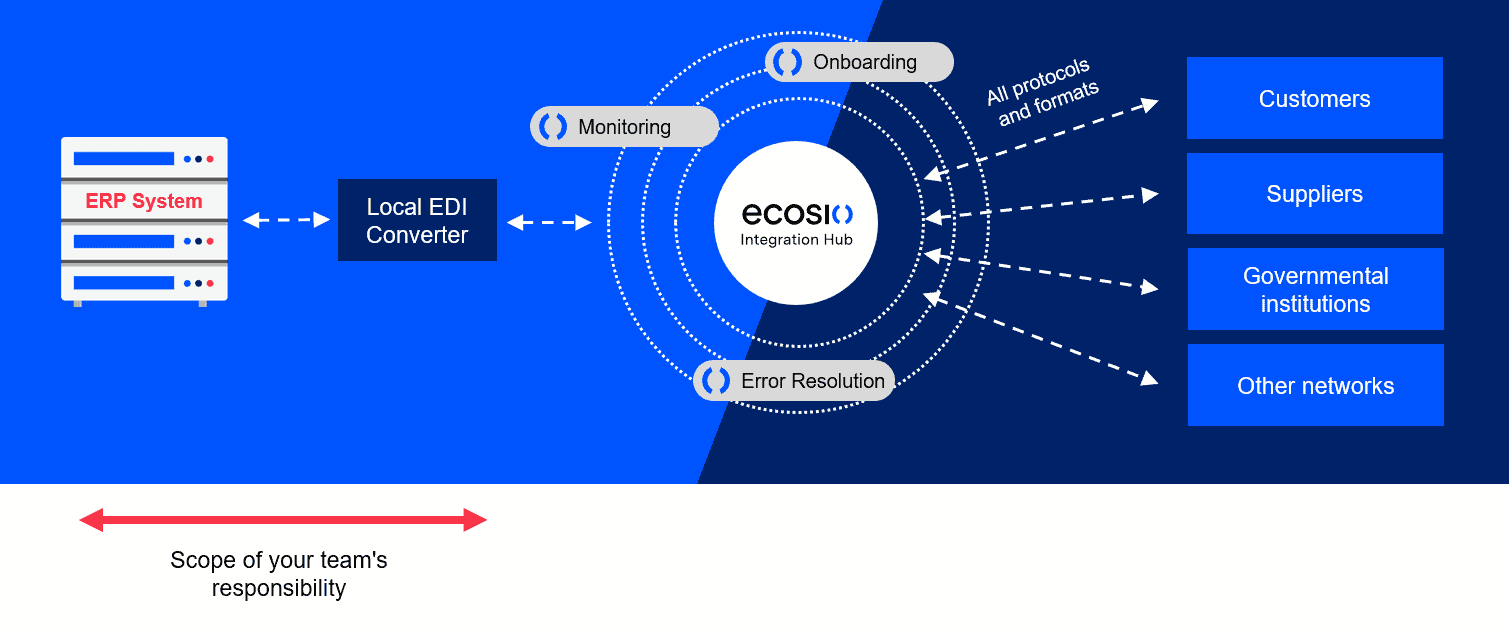
For companies with a substantial amount of EDI expertise and sufficient internal resources, using local EDI software can be a viable solution. Essentially this is an additional piece of software that enables your business to transform messages into whichever different structured formats are required and to route them to your business partners via different transmission protocols.
It is important to note that this approach requires all EDI tasks to be undertaken in-house, however. Setup, testing, onboarding, mapping, routing, monitoring, error resolution and updates – all of which take time, effort and technical knowledge – must all be handled by your business.
Typically such EDI software solutions are also not integrated into your ERP system directly, meaning that access to EDI information requires a separate login and is often limited to IT teams. Thus, there is no end-to-end message visibility directly in the ERP system (i.e. being able to see whether or not your messages have been received or where sending has failed).
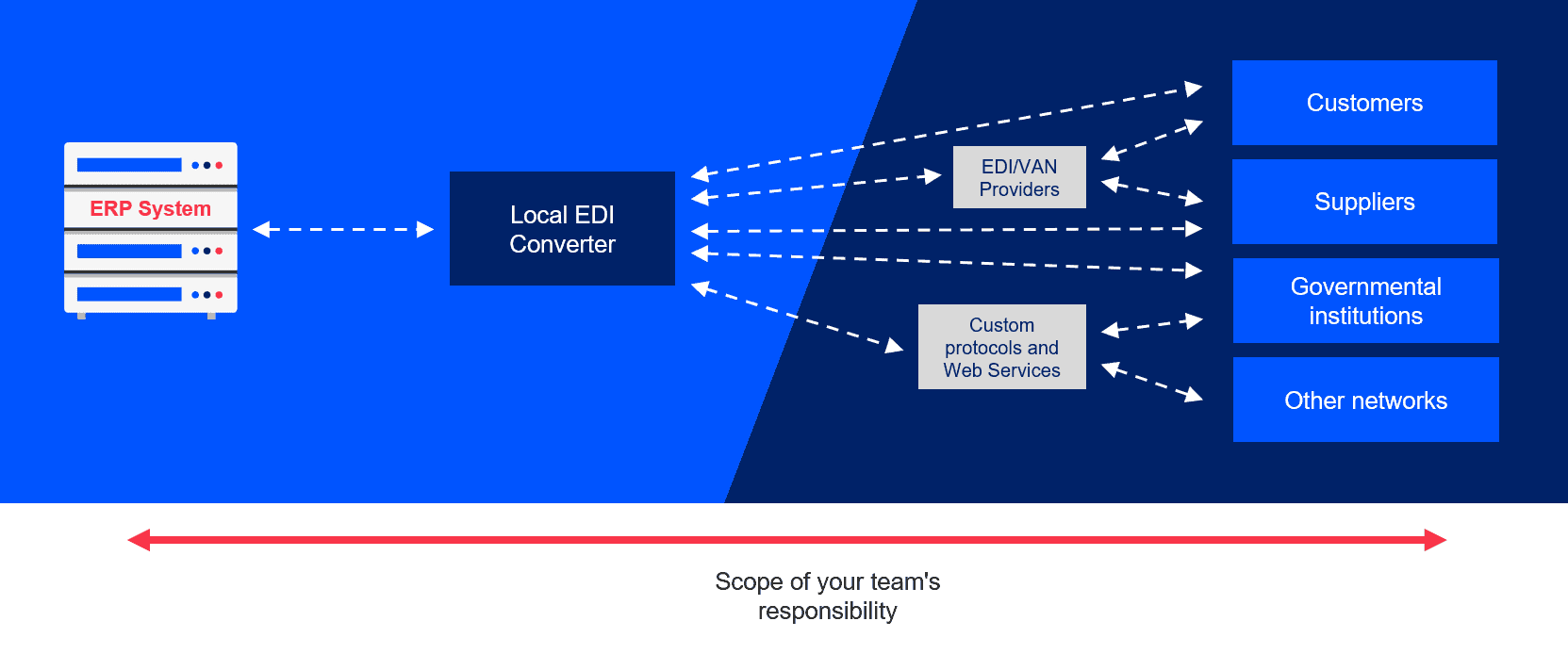
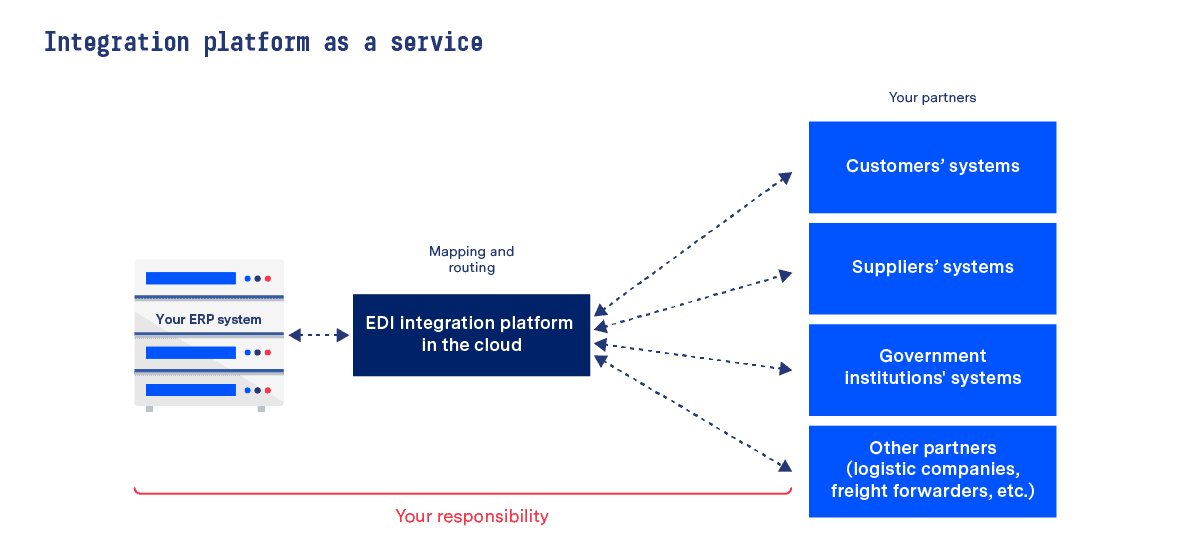
2) Use an integration platform as a service solution
Using an EDI integration platform as a service approach enables you to retain full control of all EDI aspects such as routing and mapping. Technically, the solution is similar to a local EDI converter, with the major difference being that an integration platform as a service solution offers the capabilities of an EDI converter in the cloud. As with using a local EDI converter, however, this solution still requires substantial internal input and expertise.
Similar to local converter approaches, internal teams need to balance partner onboarding and testing etc. with existing work. Likewise, while the platform may come with some out-of-the-box features, the ongoing operation and connection maintenance again falls to you alone.
The major advantage of an integration platform as a service solution compared to a local converter is the fact that the integration platform as a service solution is constantly updated. Thus, the underlying technology doesn’t age, as is the case with local converters if they aren’t regularly updated (which usually comes with a price tag).
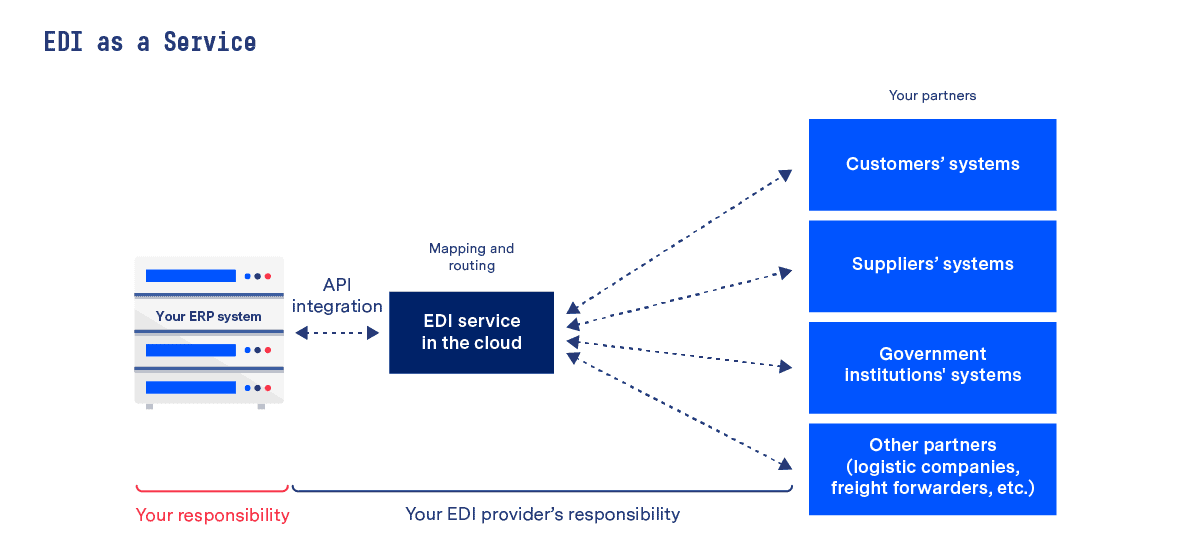
3) Use EDI as a Service
For businesses without extensive internal resources, opting for an EDI as a Service approach typically represents the most logical choice. In this option all of the EDI work is taken over by your provider via the cloud – from project management and technical setup right through to ongoing monitoring and support. Essentially EDI as a Service turns EDI from something that requires a lot of internal time, effort and expertise to something that simply works quietly in the background without you needing to worry about it.
Crucially, too, this option is also much more future-proof, as EDI as a Service solutions can respond quickly to any changes in your requirements – something that is tricky when some/all EDI tasks are handled in-house.
What benefits can efficient EDI integration offer my business?
By enabling you to exchange automated messages with your business partners and eliminate manual processes, EDI offers huge benefits to companies. For example, according to research conducted by GS1, the UK grocery sector saved over £650 million in one year alone through the use of EDI!
However, the extent of the benefits offered by EDI is dependent on which type of solution is opted for. For the purposes of this article we will look at the potential additional benefits for businesses that opt for an EDI as a Service model, as this offers the most advantages. With such a solution, in addition to experiencing the advantages of automated B2B message exchange, businesses can…
Save time
As well as reducing the time needed for partner onboardings through external project management and use of intelligent tooling, the best EDI integration solutions also shorten error resolution time by offering deep ERP integration and full-text search across all EDI messages. Additionally, in solutions where the majority of EDI tasks are handled externally, internal teams are able to focus more on core competencies.
Save money
EDI solutions that offer EDI on a pay-per-use basis can reduce total cost of ownership (TCO) of B2B processing. Similarly, being able to hand time-intensive EDI tasks such as partner onboarding to your provider can save you money. Plus, choosing a solution that is flexible and that can grow as your requirements change will ensure you continue to reap the benefits of EDI into the future, without encountering prohibitive “price cliffs”.
Reduce risk
While all EDI minimises the potential for human error, the best EDI solutions go further, offering round-the-clock monitoring of the technical infrastructure to ensure errors are detected and resolved as quickly as possible. Good EDI providers will also offer a redundant infrastructure to safeguard you from any severe data loss. EDI as a Service solutions will also proactively update your solution on a regular basis so it is always performing at optimum level.
Gain a competitive advantage
When all EDI tasks are undertaken by external experts businesses are able to focus on their core business. Meanwhile the ability to meet partner requirements faster and more accurately also boosts business relationships.
External management of EDI also allows companies to stay flexible in the long-run, as changes such as fulfilling country-specific e-invoicing requirements can be met easily whenever the need arises.
For more information on the benefits that EDI can deliver, why not download our printable, stat-filled infographic.
Interested in seeing how EDI integration could benefit you?
At ecosio we are experts in EDI integration and offer a solution that provides full EDI capability within your existing ERP system. What’s more, as we offer an EDI as a Service approach, there is virtually no work required from you to set up, test and monitor your solution.
If you would like to know more about how streamlined EDI integration with ecosio could transform your B2B processes and benefit your business, get in touch today. We are always happy to help!
Der Beitrag EDI integration: what is it and how can it help your business? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag How easy is handling EDI in-house? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>So how do you know if this approach is right for you? The key to answering this lies in asking the right questions and understanding what handling EDI in-house really involves.
Let’s start by looking at some crucial questions anyone considering handling EDI in-house should ask before making a decision…
Four key questions to ask
1 – Will managing EDI in-house actually save me money?
Ironically many CIOs invest in local EDI converter software (as opposed to a fully externally-managed EDI solution) in an attempt to save money. However, when the time and resource costs relating to document mapping, message monitoring, partner communication, update installation, error handling etc. are factored in, in-house solutions generally work out to be far more expensive than fully managed solutions.
2 – Does my IT team have the necessary know-how?
Unfortunately EDI expertise is rare. As a result, EDI tasks are often assigned to individuals for whom EDI is not their main area of expertise. What’s more these individuals also typically have to juggle EDI tasks with their other responsibilities. With time, such a situation can lead to a deterioration in efficiency.
3 – Can my team cope with the workload?
Even if your team IS very experienced in EDI, changing requirements can still result in workloads increasing rapidly, which reduces the speed of potential growth and multiplies the likelihood of errors occurring.
4 – Could staff be adding more value elsewhere?
By having to focus on time-intensive EDI tasks such as mapping and error resolution, internal teams are also prevented from focussing on more value-adding activities. Moreover, with internal solutions the responsibility for successful message exchange lies completely with the company in question.
What does handling EDI in-house actually involve?
In order to be able to answer some of the above questions, it is first necessary to understand exactly what is required of internal teams to operate an in-house system…
With an in-house solution, responsibility for the continued success and operation of EDI lies entirely with internal teams (as pictured below).
The main tasks
From a coarse-grained perspective, the main EDI tasks when handling EDI in-house are:
- Handling data correctly between the ERP system and the local EDI converter. In the case of SAP ERP systems for instance this means ensuring correct IDoc processing, both inbound and outbound.
- Setting up mappings between your in-house ERP format and your business partners’ formats.
- Operating the local EDI converter. EDI connections must be set up and maintained and the entire onboarding/maintenance communication with the various business partners and their EDI/VAN providers must be handled. Exchanged EDI data must also be monitored 24/7.
- Chasing and resolving errors with your business partners and their EDI or VAN providers.
Don’t forget redundancy!
Another key aspect of handling such business-critical and data-heavy IT processes in-house is safeguarding your business against system failure and data loss.
Worryingly most organisations handling EDI in-house neglect to invest in redundant servers to back up message exchange. By doing so businesses risk severe financial losses should total system failure occur, as such an event can impact an entire supply chain.
Of course, when managing EDI in-house, maintaining redundant servers does come with additional costs, however.
Have you considered fully managed EDI?
Because of the numerous complications associated with running EDI in-house, more and more businesses are turning to fully managed EDI, as it offers a simpler and more cost-effective solution.
Unlike in-house scenarios, with fully managed EDI the responsibility of internal teams is limited to the ERP system only. As shown in the image below (and in even more detail in our helpful infographic comparing EDI solution types), all other EDI tasks are taken over by the fully managed EDI service provider. From connecting partners and resolving errors, to keeping on track of new regulations and installing updates, your provider takes care of everything, leaving existing teams free to focus on more value adding activities.
Fully managed EDI also offers flexibility and scalability, as your solution can be extended and adapted as necessary if and when requirements change.
Although not offered by every provider, the best EDI solutions (such as ecosio’s) also offer deep integration in your ERP system via an API connection. This connection provides full visibility of all processes, directly in your ERP’s user interface.
For a detailed comparison of what different EDI providers actually offer, please see our helpful infographic on this subject…
Want to maintain your local converter?
As we have already touched on, some companies do have specialised internal teams that are capable of operating and maintaining large scale EDI solutions. Nevertheless, the management of the hundreds of different EDI connections via a local converter solution in such cases still remains a huge challenge. In such cases a fully managed EDI service provider can help by taking over all routing tasks – the mappings still remain on the side of the local EDI converter.
Want more information on what EDI solution suits your business best?
At ecosio we have handled EDI integrations for thousands of businesses across all industries and in a wide range of different ERP systems. As a result, we know exactly what works best when it comes to establishing reliable and future-proof EDI systems.
If you would like to discuss your particular situation with one of our EDI experts (with no obligation), get in touch today! We are more than happy to help you take the right next step.
Alternatively, check out our many helpful resources for more detailed information on everything from fully managed EDI to EDI integration in specific ERP systems.
Der Beitrag How easy is handling EDI in-house? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag An Introduction to the Four Main EDI Methods erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>To help you identify the best EDI method for your business, in this article we explore the four main approaches to conducting EDI – namely point-to-point connections, point-to-point connections using Platform-as-a-Service, unmanaged VANs and fully managed VANs.
1) Local point-to-point connections
These connections require a business to have a local EDI middleware on-premise. This software is often referred to as a local EDI converter. It is used to perform business document mappings between the ERP export/import format and the different formats of EDI partners and may also be used to establish individual connections with partners. As every connection is different there is limited scope for reuse of work, making this method highly time intensive. While mapping and connection templates can help to reduce the workload, all work eventually falls to in-house teams, including setup, monitoring, error resolution and updates. Thus, a highly skilled EDI team is a must to operate such a setup.
2) Point-to-point connections using Platform-as-a-Service
In essence the Platform-as-a-Service (or PaaS) method is exactly the same as local point-to-point connections using an EDI converter. The only difference is that this middleware software is now in the cloud. Some service offerings include pre-configured document mappings and connection assets, which must be tailored and configured to one’s needs. As with local point-to-point connections, every connection requires a great deal of effort, which will either fall to internal teams or require additional services to be purchased.
Common examples of this type of solution include PaaS cloud offerings from EDI converter vendors or the SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) solution.
Other examples of this kind include for instance MuleSoft or Microsoft Azure Logic Apps.
3) The traditional unmanaged VAN
In short, traditional unmanaged VANs offer businesses the opportunity to simplify message exchange processes by moving from the mesh model of point-to-point connections to the star model. Needing just a single connection to your internal system, a VAN acts as a post office, serving to deliver messages to EDI partners who are also connected to this network. However, whilst connection to an unmanaged VAN does simplify message sending, not all EDI partners connected to said VAN will have the same requirements when it comes to formats and document standards. As a result, work is still required to establish document mappings, before messages can be sent via the VAN.
The term “added value” originates from the fact that the network itself may provide additional “value” to its participants. Next to the fact that one may reach any participant in the network easily other added values include validation, message audits, monitoring, etc.
However, as we will explore, the extent of the “value” added differs greatly between different types of VAN.
With unmanaged VANs the value offered usually include only:
- A mailbox
- The ability to send via various protocols (e.g. AS2 and SFTP)
- The ability to trace messages up to the central network node, i.e., you will receive a technical acknowledgement such as an MDN in case of AS2, if the network node has received the message. However, no receipt about the delivery of the message to the final recipient is usually provided.
This is typically the extent of the value offered by these networks. Importantly, there is also a lot that they do not do that customers should be aware of. In particular…
- You have to do everything yourself! – Although less work is needed to send messages via a VAN than point-to-point, the work that remains (e.g. structuring and verifying messages) falls entirely to internal teams.
- There is no proactive support – Once connections are up and running, you and your partner alone are responsible for ensuring the connection is functioning correctly.
- No error alerts/notifications – When errors do occur it is easy for them to go unnoticed if suitable procedures are not put in place internally.
An easy way to think of an unmanaged VAN is like an email provider such as Gmail. Once you have an email mailbox you can send messages to anyone else with an email address. What you put in the email and how you manage your inbox is completely up to you, however. When you do experience problems it is also up to you to find the solutions – you will not be able to get hold of anyone at Google’s headquarters to assist, or even find a number to call. What’s more, unlike email, unfortunately unmanaged VANs are not free!
4) The full service managed EDI network (aka fully managed VAN)
Last, but by no means least, is using a fully managed VAN – or as we prefer to say, B2B Network in the Cloud. As you would expect, this EDI method offers all the benefits of an unmanaged VAN but with key additional advantages, including…
- All protocols and document formats are supported – Rather than offering transmission via a limited number of protocols, fully managed VANs (such as ecosio) can typically handle transmission via all common protocols and map messages between all formats (e.g. EDIFACT, ANSI ASC X12, XML, etc.).
- Proactive monitoring and support – Rather than leaving the operation of the solution to you, a fully managed VAN should offer round-the-clock message monitoring. In addition, providers may offer (as ecosio does) proactive error resolution, meaning that often nothing is needed from you to fix an error – it may even be fixed without you ever knowing there was an issue!
- Web EDI – A Web EDI solution allows you to benefit from automated message exchange with all partners, no matter their current capabilities. Access to the benefits of Web EDI is only possible with a fully managed VAN.
- Merge/split functionality – As some ERP systems aren’t able to receive multi-document messages, a fully managed VAN will split the message to enable receipt. Similarly, to cater to partners with particular requirements (e.g. those who request only one transmission a day), fully managed VANs can merge messages and send them via a batch message.
- API integration – Whilst not offered by all fully managed VANs, an API connection between your ERP system and VAN can ensure vastly improved data visibility. In addition to allowing for access to real-time data for both you and your partners, such a connection offers full message traceability – right up to the final recipient (rather than just the network, as is the case with unmanaged VANs). This makes it possible to pinpoint where an issue is and what needs to be done to resolve it.
- E-invoicing solution – A fully managed VAN should be able to handle all your e-invoicing needs, no matter how disparate and complex. ecosio, for example, was one of the first certified Peppol access points and can exchange invoices in compliance with all national regulations.
- Cross-VAN communication (VAN interconnect) – In order to simplify users’ EDI landscapes and minimise the number of connections internal teams need to worry about, fully managed VANs offer cross-VAN communication. In many cases (as we shall explore later) this can save clients money.
- Verification – Fully managed VANs are able to verify sent messages to ensure that they are formatted correctly before they are transmitted to the recipient. Ideally this should be done automatically, alerting the sender instantly if something is wrong so that it can be fixed and the amended version resent.
By offering such services, not only do these fully managed VANs grant internal teams much more time to focus on more value-adding tasks, they also ensure the client is less likely to experience issues (as EDI experts are naturally better at EDI matters than non-specialised in-house IT teams). Thus, clients not only save time, but money and stress too.
Unlike ecosio, not all so-called “managed” VANs offer the full range of services and features listed here. Consequently, it is important to examine what services providers using different EDI methods actually offer (see our infographic “How much internal work is required to operate different VAN solutions”).
Want to discover a better solution?
This article is a snippet from our white paper Everything You Need to Know About VANs. In this paper we explore the various issues associated with different types of VANs, the benefits of doing EDI via API and what steps you can take to improve your EDI landscape and minimise VAN costs (among other topics).
Download your copy of our white paper Everything You Need to Know About VANs and find out how you can optimise your processes.
Alternatively, if you have any questions about EDI methods or any related topic, feel free to get in touch. We are always happy to help!
Discover more about our updated product, ecosio.flow.
Der Beitrag An Introduction to the Four Main EDI Methods erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Five Reasons Handling VAN Connections In-house is Unwise erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>In this article we’ll explore five reasons why you should avoid conducting EDI in-house via an EDI converter if you need to route messages through VANs.
1) The need for EDI expertise and internal resources
Undoubtedly the main hurdle stopping businesses from attempting to manage EDI in-house is the complexity of EDI processes. Unfortunately, given the way in which EDI has developed over the decades and the myriad of formats and protocols available to businesses today, managing EDI requires significant technical expertise which is rare among in-house IT professionals. Further, even when a business does have sufficient EDI expertise, they may not have enough resources to cope with system setup and/or ongoing operation. Unless you are willing to invest in new staff members to cope with the additional workload, you risk overloading your IT team and increasing the likelihood of errors as a result.
2) Maintenance of various different servers
When handling EDI via an EDI converter it is often necessary to maintain various different servers. These are needed to enable the transmission of certain document formats over different protocols to various VANs and partners. For example (as pictured below) you might easily need to maintain an X.400 mailbox as well as both an AS2 and an SFTP server to be able to reach all your business partners. In such a scenario you also need to monitor and maintain the connections to and from these servers, including any interconnects to different VANs.
Further, as EDI enables the transmission of business-critical documents such as orders and invoices, it is imperative that total system failure is safeguarded against. The only way to do this properly is to maintain multiple redundant servers so that all message exchange and archived messages are backed up. However, as this involves investing even more on hardware etc. than the already significant amount required to maintain a single server, many businesses opt not to provide EDI systems in a redundant manner. In so doing, these businesses risk catastrophic financial consequences should total system failure occur.
3) Monitoring of connections and interconnections with different VANs etc.
There are many problems with having to juggle multiple VAN connections. In short, these issues concern the difficulty of message tracing, maintaining multiple VAN mailboxes and resolving errors (something made particularly hard by the fact there is often no clear point of contact). Unfortunately, these issues are unavoidable for companies that choose to handle EDI internally, as the only future-proof way to simplify messy EDI landscapes is to pass the management of VAN connections to an EDI solution provider such as ecosio.
4) High likelihood of errors occurring
Whereas fully managed VANs will have rigorous and reliable testing, onboarding and verification procedures in place, this is often not the case with in-house arrangements. As in-house teams often have a large and varied workload it is easy for oversights to occur during system setup which are hard to correct further down the line (neglecting to test for every possible iteration of an invoice, for example). Also, the more VANs that are being used, the higher the likelihood of errors occurring.
5) The cost!
Unsurprisingly conducting EDI in-house is not cheap. Not only does purchasing the necessary hardware and software require significant outlay (particularly if multiple servers are required), the time and staff costs are also considerable.
Want to solve your VAN connection headache?
This article is a snippet from our white paper Everything You Need to Know About VANs. In this paper we explore the different types of VANs, the benefits of doing EDI via API and the practical steps you can take to improve your EDI landscape and minimise VAN costs (among other topics).
Download your copy of our white paper Everything You Need to Know About VANs and find out how you can optimise your processes now!
Alternatively, if you have any questions about VANs or anything else EDI related, feel free to get in touch. We are always happy to help!
Der Beitrag Five Reasons Handling VAN Connections In-house is Unwise erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Alternative Solutions for EDI in SAP PI and SAP PO erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- Managing EDI with SAP PI or SAP PO internally yourself
- Installing a local EDI converter and connecting to SAP PI or SAP PO
- Outsourcing to a fully managed EDI service provider
We will show you which EDI functionalities you can implement in your company with the respective solution and which questions decision-makers can use to help themselves in choosing the right solution.
EDI and B2B integration with SAP PI or SAP PO – What do I need to know?
SAP Process Integration (SAP PI) is a comprehensive software component that enables data exchange between the SAP system and internal and external systems. SAP PI uses various Java-based routing and integration mechanisms as well as various adapters that can be used to implement transport protocols and format conversions.
SAP Process Orchestration (PO) is an SAP PI installation variant (with different license models) that has been enhanced to include functionality in the area of “business process modeling and implementation”. In addition to the classic SAP PI capabilities of message routing, mapping and connectivity, PO also includes parts of SAP Business Process Management and SAP Business Rules Management.
In terms of EDI, the core technical functionalities of SAP PI and SAP PO are:
- Connectivity
- Mapping
- Routing
Under Connectivity, SAP PI offers a range of adapters that can be used to convert various message transport protocols. These include many protocols that are required for electronic message exchange with external partners, such as AS2, X.400, OFTP2, SFTP, RESTful Web Services, and so on. Mappings can be used to implement translations between SAP internal formats (for example, IDoc) and external EDI formats such as EDIFACT, XML, ANSI ASC X.12, and so on. Mappings can be converted using a graphical editor, based on XSLT, or using a Java program. Routing controls message delivery to different recipients based on information in the message.
All three solutions presented in the same way are based on these core functionalities of SAP PI or SAP PO, but differ essentially in the following factors in EDI operation or in the following questions that the decision-maker can ask himself:
- How much internal EDI capacity (i.e. personnel & EDI expertise) can I use for mapping, routing, 24/7 monitoring, troubleshooting and maintenance of the connections? Do I want to manage EDI completely internally or do I want to relieve my internal teams and outsource EDI?
- Which technical requirements does my EDI solution have to meet? Which document types, protocols, formats and legal requirements regarding electronic invoicing (e.g. XRechnung in Germany or FatturaPA in Italy) do I need for my B2B network?
- What EDI capabilities does my B2B network require? Do I need access to Value Added Networks (VANs)? Do I want or need to connect to Peppol? Do I have suppliers without EDI capabilities that I still want to connect to automated message exchange (with Web EDI?)
- How flexible or scalable do I want to design my EDI solution? Can I rely on a rigid implementation in the long term or do I want to become more resilient and future-proof with regard to the technical requirements?
If you know the answer to all these questions for your company, you will be able to make the right choice for your business. Keeping the questions in mind, we will now look at the three technical approaches for an EDI implementation in SAP PI and SAP PO.
1. Managing EDI with SAP PI or SAP PO internally
SAP PI and SAP PO are extremely complex and extensive software components that allow for internal implementation of some EDI functionalities. According to the point-to-point principle, automated EDI connections to individual partners can be established by appropriately qualified personnel.
However, one of the main challenges during implementation is precisely the complexity of the software. One does not get the proverbial hammer and nail in the hand, but a very extensive toolset. For the independent configuration and the ongoing operation of EDI connections via SAP PI or SAP PO, highly qualified employees with corresponding EDI expertise are therefore required. If smooth EDI operation is to be guaranteed 24/7, these employees must be available on a continuing basis.
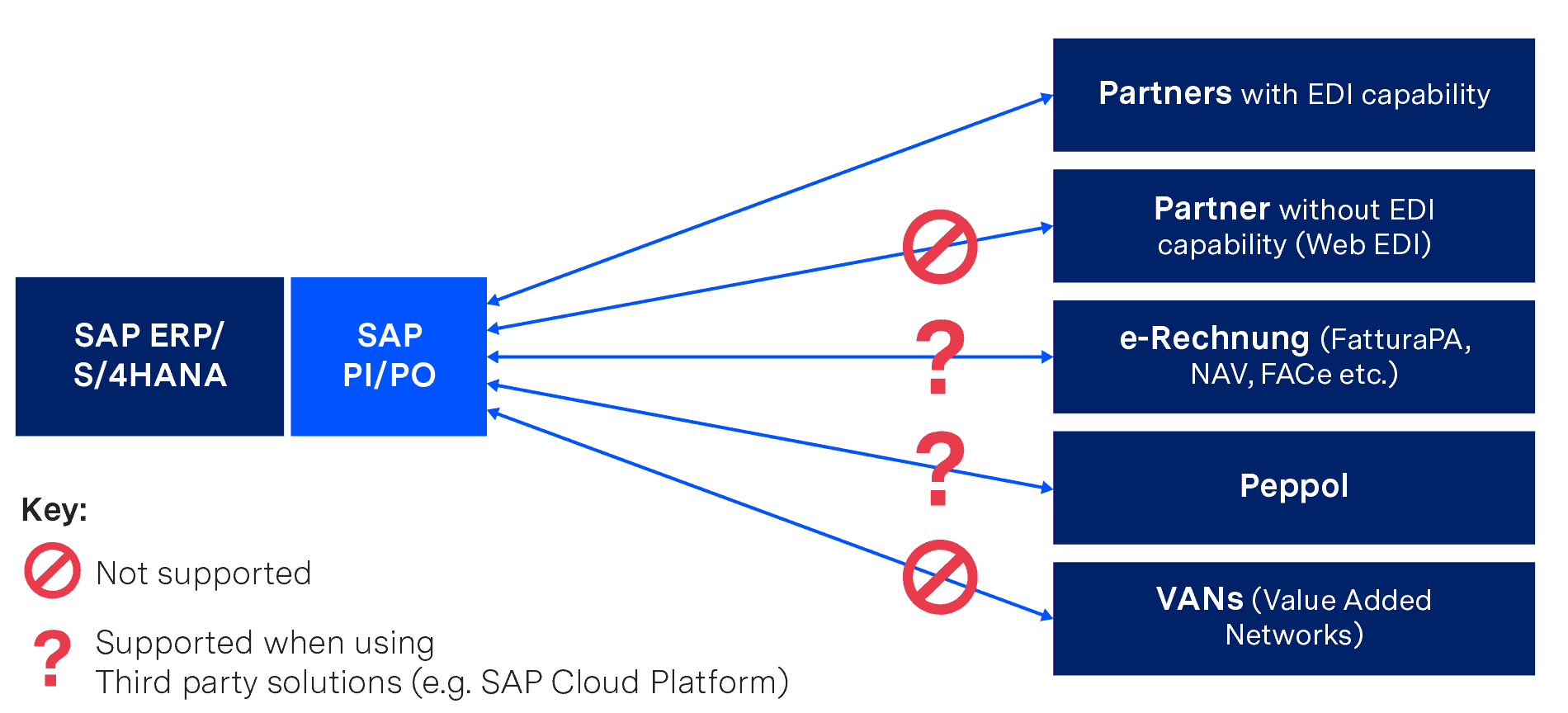
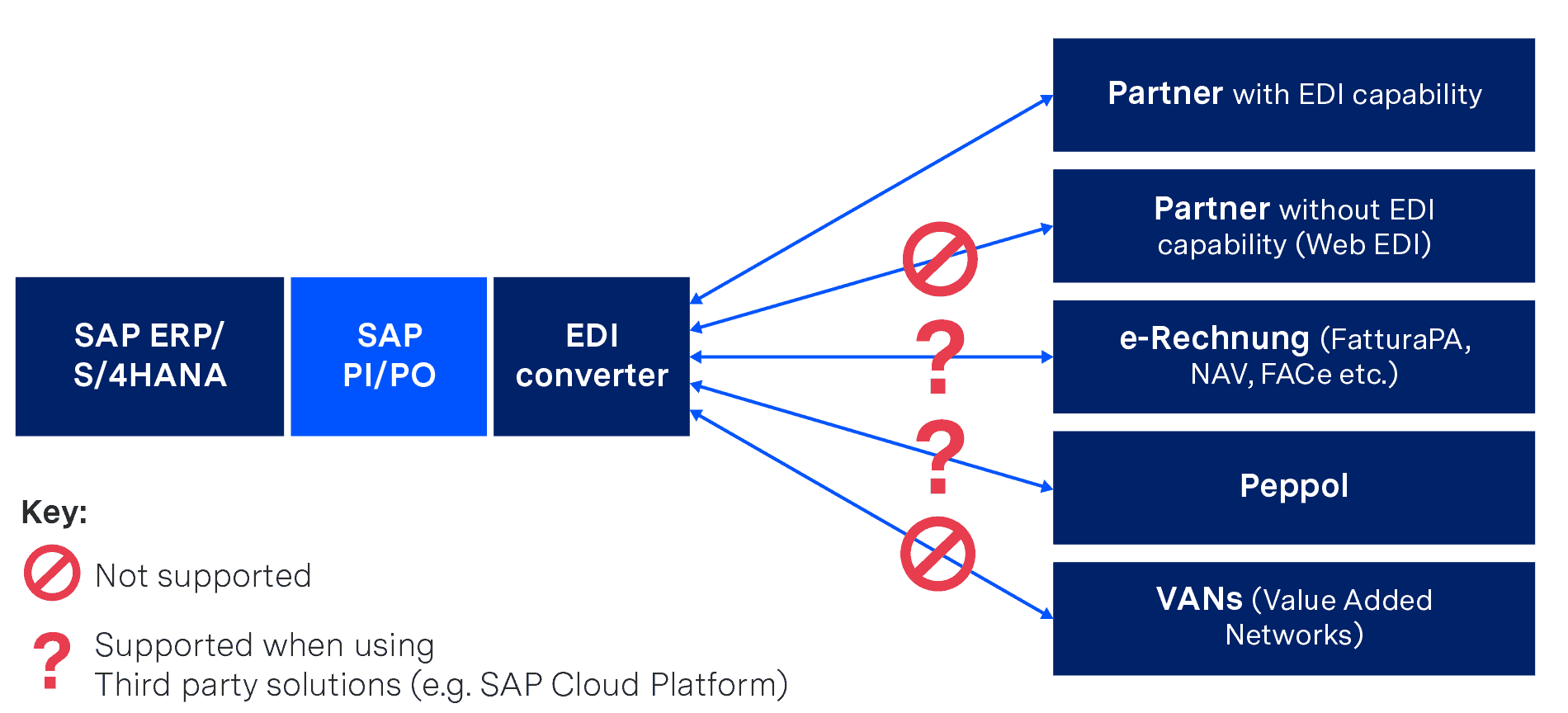
Furthermore, not all required EDI functionalities (current and future) may be supported or require the use of additional solutions, as shown in the graphic:
If you want to implement EDI internally purely with SAP PI or SAP PO, you will therefore have to do without some functions (or implement them as a third-party solution), but you will also need highly qualified personnel, EDI know-how and sufficient resources to cope with:
- Mapping and routing of all necessary connections
- Ongoing maintenance of the connection parameters and regular renewal of certificates
- Ongoing maintenance of mapping tables and industry internal practical knowledge about the implementation of special formats (e.g. VDA)
- Ongoing coordination with the B2B partners and procurement of all necessary information (especially in the onboarding process)
- 24/7 monitoring and troubleshooting
Incidentally, those who only want to work with SAP PI have to accept a major restriction – this only allows flat file formats via SFTP/SOAP/REST/HTTP protocols. If you want to use “classic” EDI formats (such as EDIFACT or ANSI ASC X12) and protocols (such as AS2 or X.400), you must have either a special package from a third-party manufacturer or the “B2B Add-on” from SAP – but this is only available with the SAP PO license (even if no other SAP PO functions are required).
The issue of X.400 costs should also be mentioned. If messages have to be transmitted to third-party networks that are subject to charges, these costs can be quite high. As an individual company, often only poor rates are available due to the relatively small amount of data being exchanged.
Internal implementation of EDI with SAP PI and SAP PO offers you a very high degree of functionality and flexibility. However, configuration, operation and maintenance also require the use of appropriate resources, which must be included in the total cost of ownership analysis. These costs must also be taken into account when using a local EDI converter, the option we present next…
2. Installing a local EDI converter and connecting to SAP PI or SAP PO
Another possibility is the acquisition and operation of a local EDI converter, which is connected to SAP PI or SAP PO. This is a software to be installed locally that converts documents from SAP internal IDoc format to partner format and vice versa.
Converter solutions are individually adaptable, but are potentially cost-intensive due to individually payable license costs for various functionalities, formats and upgrades in combination with long-term maintenance contracts. For example, support for protocols such as X.400 or services such as VAN connectivity must be purchased separately.
Local converter solutions must also be operated completely by internal teams, just as in the previous solution (implementing and operating EDI in SAP PI or SAP PO internally). This includes particularly time-consuming processes such as mapping, testing and 24/7 monitoring. This again requires appropriately trained employees.
SAP PI/PO with local EDI converter
It should also be considered that both the software itself and the individual mappings age. In other words, over time new releases of the converter will be published, which do not necessarily allow an upgrade from the existing version and mappings. This results in corresponding migration projects that have to be realised internally or with the help of an external consulting company.
3. Outsourcing to a fully managed EDI service provider
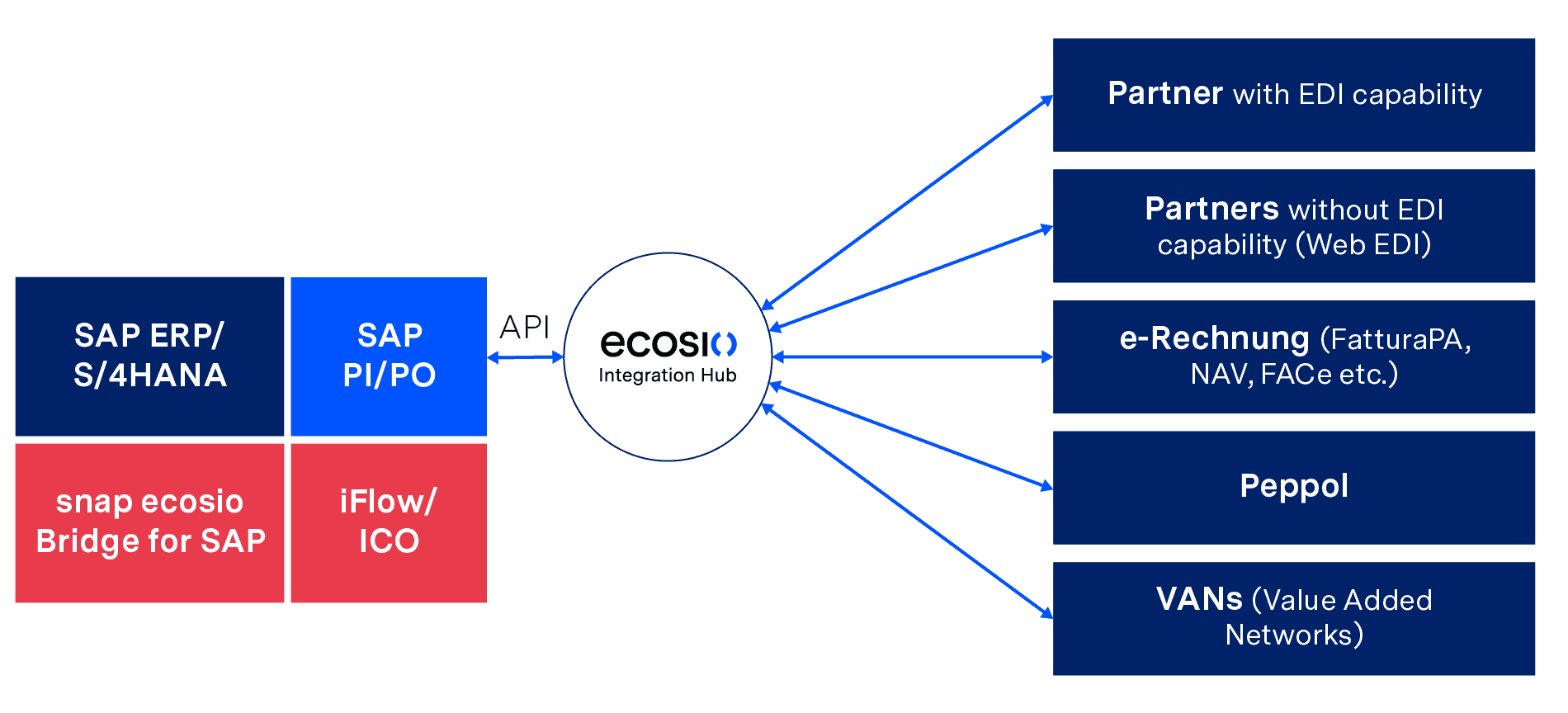
Fully managed EDI is a cloud-based EDI solution where a company is connected to a specialised EDI service provider via a single connection. This service provider then takes over all EDI functions and processes, depending on your company’s requirements.
If your company uses SAP PI or SAP PO, all you need for a successful connection to ecosio as your EDI service provider is the snap ecosio Bridge for SAP and its turnkey integration flows in SAP PI or SAP PO, which was especially created by SNAP Consulting.
Deep EDI Integration in SAP with snap ecosio Bridge for SAP and iFlow/ICO
In this solution the EDI service provider creates and ensures all technically desired EDI prerequisites, such as routing via various protocols, VANs and Peppol or conversion into all common and necessary formats, including legal requirements in the field of e-invoicing. Further, operation, 24/7 monitoring and partner onboarding (including partner communication) are also handled by the service provider.
The deep integration of the EDI functionalities into the SAP system also enables your business department to:
- Jump to the original EDI message for incoming messages, directly in SAP – without need for an extra login
- Jump to the generated EDI message for outgoing messages – again without extra login
- Track the EDI message status directly in SAP by changing the IDoc status of sent EDI messages to status 40 or 41 – depending on whether the recipient received the message or not
- Conduct a full text search of all messages and documents
- Benefit from automatic alerts/notification if messages are incorrect or could not be delivered
Updates, the ongoing certification of protocols and new SAP versions (such as SAP S/4HANA) are easily adopted and supported. Fully managed EDI offers companies the possibility to use all EDI functions without an expiration date – providing maximum EDI efficiency with minimum internal effort.
Summary
You now know the three possible technical approaches for implementing EDI on the basis of SAP PI or SAP PO and which criteria and questions you should use to select the most suitable one for your company. Essentially, you need to assess how much capacity you have internally to cope with implementing and operating an EDI solution.
Independent EDI implementation or the use of a local EDI converter enables a company to send and receive EDI messages, but requires a high level of internal effort, and highly qualified personnel. In addition, some functionalities may have to be purchased externally.
Outsourcing to a fully managed EDI service provider offers you all the EDI functionalities available with SAP PI and SAP PO but in a flexible and freely scalable way. The entire effort, from mapping and routing to monitoring and troubleshooting, is taken over by the EDI service provider, relieving internal teams.
Want more information?
Discover more about our updated product, ecosio.flow.
Do you still have questions about SAP PI data exchange or EDI with an SAP ERP system? Feel free to contact us, we would love to help you!
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag Alternative Solutions for EDI in SAP PI and SAP PO erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Managed vs fully managed EDI – What’s the difference? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- Managed EDI often requires significant internal effort, with limited onboarding, monitoring, and support services despite the “managed” label
- Fully managed EDI handles all technical tasks, including partner onboarding, message tracking, error resolution, and ongoing system updates
- The key benefits of fully managed EDI include saved time and cost, reduced operational risk, and faster partner onboarding through expert-led support
- For scalable, low-maintenance B2B integration, fully managed EDI offers a futureproof approach, especially for businesses with limited internal resources
With such a large number of EDI solution providers out there, all of whom offer slightly different products and services, assessing the value of different packages can be a long and complex process. From where the solution will be hosted, to what functionality is included in your package, there are a multitude of factors to consider when selecting the best EDI solution for your business.
One of the most important decisions that businesses must make at this crucial point is the extent to which they want their provider to manage their EDI solution (from set-up and operation to monitoring and error resolution). Unfortunately, however, the term ‘managed EDI’ is used to mean different things by different providers and is therefore frequently misunderstood by those selecting a solution. In turn, this can lead to huge expense further down the line as in-house teams struggle to run their new system efficiently in conjunction with the unexpectedly minimal support offered by their provider.
In order to help you to avoid experiencing such a situation, in this article we’ll examine the full breadth of what providers mean when they talk about ‘managed EDI’, looking in detail at the areas where some providers’ supposed management is often lacking.
First, though, let’s briefly recap the basics of electronic data interchange…
The basics of EDI
Electronic data interchange offers businesses a means of exchanging key business documents with partners automatically – i.e. with minimal human intervention. The data from commonly exchanged documents such as invoices, order confirmations and delivery notes are translated into computer-readable formats and sent to business partners via standardised EDI protocols.
This method of exchanging data removes the need for manual data input/extraction, thereby minimising errors and improving the speed, cost and efficiency of B2B document exchange. A good EDI system also offers businesses flexibility and scalability, as automated processes require less internal work than manual ones.
In short, EDI allows your business to operate more smoothly as connections with partners are streamlined and reliable.
Common issues with existing EDI solutions
Despite the compelling benefits of EDI, many EDI systems sadly fall short of offering users the full potential of the technology. This is due to a number of issues with commonly implemented solutions…
1) They require too much in-house effort/expertise
This is undoubtedly the most common issue encountered by EDI users. In addition to expertise being necessary to set up an EDI solution, ongoing operation also requires effort (e.g. monitoring message exchange and resolving errors). Unfortunately, such tasks are often not considered when selecting a solution, however. As a result, many businesses end up with a solution that requires substantial in-house expertise/resources.
While this may be fine for those businesses who have extensive in-house EDI expertise, for those that don’t it stops employees from focussing on more value-adding tasks. Similarly, even if your team is able to cope with current requirements, handling EDI in-house limits scalability. Further, handling EDI in-house can also lead to an reliance on individual employees, which can lead to issues come illness or departure.
2) They offer poor support
Another key frustration for those with substandard EDI solutions is the difficulty of getting hold of someone to help you when issues arise (e.g. if a message is stuck somewhere and has not reached your partner for some reason). Given the significance of the documents being exchanged via EDI and the pace of modern supply chains, this can have a significant knock-on effect on revenue and business relationships.
3) They may inhibit your business’s flexibility through “price cliffs” or limited technical scope
While all EDI solutions should enable you to exchange automated messages with your partners, different providers offer very different packages. In particular, some solutions may be extremely rigid in terms of the technical capabilities offered, meaning you may not be able to adapt your solution as needs change (e.g. should you want to send messages via a new protocol or introduce a Web EDI platform for smaller partners). Likewise, the flexibility of your system may be limited thanks to a solution’s pricing structure, with some providers charging extortionate amounts for even minor changes to solution functionality.
The three main cloud-based solution types
Cloud-based solutions generally fall into one of the following three categories: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS).
1) IaaS
IaaS relieves users of the need to purchase the physical equipment (e.g. servers). IaaS solutions may also provide operating system, disk storage and messaging resources. By opting for an IaaS system rather than an in-house solution, businesses avoid the considerable upfront costs associated with on-premise setup and remove the dangers associated with a single point of failure system.
Although an IaaS model offers customers substantial control, users are also responsible for installing and running their own software systems and must conduct all necessary maintenance/upgrades themselves.
2) PaaS
PaaS models provide a framework for in-house developers, on which they can build custom applications as required. PaaS systems do not allow for the direct use of software via the internet, but instead provide access to a platform where the necessary software applications can be created.
3) SaaS
SaaS offers access to cloud-based software. This removes the need for applications to be built or for software to be downloaded and installed on every machine. This solution model is highly scalable and is much faster to set up than IaaS and PaaS, which both require substantial internal effort.
Managed platform or a managed EDI service?
Of these three cloud-based models, SaaS is the only one which does not require considerable internal work, with the EDI partner instead providing all the necessary IT elements for a successful EDI solution. As a result, IaaS and PaaS are referred to as managed platforms, while an SaaS solution is generally referred to as a managed service model.
However, as we shall explore, not all SaaS EDI solutions are born equal. As anyone familiar with EDI will know, there is much more to successful EDI than simply setting up the basic functionality. While many SaaS EDI solutions are described as ‘managed’, this often refers purely to the fact that they provide the elements necessary for EDI to be conducted via the cloud; significantly it does not necessarily mean that they offer any help when it comes to the key EDI areas where businesses experience the most issues, such as partner onboarding or message monitoring. Those solutions that offer valuable assistance regarding the setup, operation and maintenance of EDI systems in order to lighten the load on internal teams are more accurately referred to as fully managed EDI solutions.
While they may sound similar (and both differ from on-premise solutions), managed and fully managed EDI solutions are very different and should not be confused.
What is fully managed EDI?
A fully managed / full service EDI solution, such as that offered by ecosio, is one in which the EDI provider handles all EDI tasks, from technical setup and message testing etc. right through to ongoing operational tasks such as message monitoring and error handling. It is for this reason that full service EDI providers are known as fully managed EDI providers – they manage everything for you! Just how much of the work required to set up and run a successful EDI solution is handled by a fully managed EDI provider compared to other providers can be seen in our helpful infographic on this subject here.
Fully managed EDI solutions also typically offer much better support and more flexibility than other EDI solutions, and may even be able to offer better data transparency too. Crucially these qualities allow businesses to avoid the common issues listed above.
The table below illustrates the considerable differences between the three types of solution over the life cycle of an EDI project:
The three key areas where managed EDI differs from fully managed EDI
While, as the table above clearly illustrates, there are many ways in which managed and fully managed EDI solutions differ in terms of what the provider is able to do, there are three main differences that it is worth exploring in more detail…
1) Partner onboarding
Partner onboarding is arguably the area where there is the biggest disparity between fully managed EDI solutions and those that claim to offer managed EDI. As those who have onboarded EDI partners before will know, the process can take a frustratingly long time if a proactive approach is not taken.
…with ‘managed EDI’ solutions
Unfortunately, it is common for ‘managed’ solution providers to complete only the basic initial mapping and pass the responsibility for testing the connection to their customer. In this scenario, the purchaser of the EDI solution has to chase their partners for whatever data or documents are required. As well as being a time-consuming exercise, when issues are discovered that require mapping to be adjusted, the solution purchaser then has to act as a middleman between their partner and their EDI solution provider. In turn, this further increases the time of the project and the likelihood of errors and oversights occurring.
It is important during this phase to test all possible message exchanges, including all variations of a document (e.g. invoices with and without VAT). However, as many supply chain organisations are unaware of what thorough testing involves, their testing is often far from comprehensive. Having received no help during the testing phase from their ‘managed’ solution provider, businesses in this situation are then likely to experience many errors following go-live. Depending on the number of partners and exchanges involved, this can be extremely expensive to fix!
…with fully managed EDI solutions
With a fully managed EDI solution such as ecosio’s, virtually all of the internal effort is removed. These solutions will provide businesses with a dedicated integration engineer whose job it is to chase down information from partners and ensure that testing is conducted as thoroughly as possible, preventing issues further down the line. Not only does this have a dramatic impact on the time in which partner onboardings can be completed, as EDI integration engineers have a wealth of testing experience, clients can be sure that their connections will be extremely reliable before going live.
For a comprehensive rundown of the steps involved in supplier EDI onboarding, read our article “Supplier EDI Onboarding – The Seven Key Steps” on this.
2) Message monitoring
While establishing connections may be the most technical aspect of implementing an EDI solution, effort is also required to ensure the solution is operating correctly from day to day.
…with ‘managed EDI’ solutions
With the average ‘managed’ EDI solution day-to-day message monitoring is handled exclusively by the client. This involves regular checking to ensure no messages are stuck and that there are no errors with incoming or outgoing documents.
…with fully managed EDI solutions
With a fully managed EDI solution the pressure of checking message statuses and delivery / error notifications is removed. Instead, your provider will oversee the smooth running of the system, which should include setting up automated alerts and flags for different occurrences.
Further, providers offering a comprehensive service may also be able to offer clients a depth of data visibility simply not possible in less complete solutions. For example, as it is directly integrated into clients’ systems via API, ecosio cloud-based EDI solution (our Integration Hub) provides users with unparallelled data visibility, allowing users to see information on every stage of message exchange. What’s more, this information is all visible within their existing ERP user interface!
3) Support + error handling
No matter how much care is taken during system setup to avoid errors, the nebulous nature of EDI standards, formats and protocols is such that they are inevitable from time to time. With this in mind, and given the hugely detrimental impact errors can have on profits and partner relationships, it is important to have reliable processes in place to deal with errors when they occur. This includes not only error identification, but also resolution.
…with ‘managed EDI’ solutions
With most ‘managed’ EDI services, the provider’s error handling is reactive at best. Generally the responsibility for identifying errors lies solely with the solution purchaser. It is then the purchaser’s responsibility to notify their provider of the issue and chase until it has been resolved.
As the level of support offered by ‘managed’ solution providers varies, however, this can be a frustrating process. Despite the business critical nature of EDI, customers often find it difficult to get through to someone with sufficient knowledge of the situation to help them resolve the issue. In some cases the ‘support’ offered by providers is simply a generic support email address, with customers left in the dark as to when they can expect to hear back.
…with fully managed EDI solutions
With fully managed solutions error handling and support is proactive, not reactive. A good solution should be able to spot errors quickly and instantly start the process of resolving them. Ideally this process should be so smooth that errors can be resolved before they are even noticed by anyone else.
For example, if an incoming order fails, there is no need for the client to spot this and notify their provider. Instead, as they are responsible for monitoring message flow, the provider should spot this and contact the sender directly to ensure the necessary amendments are made to enable the message to be sent successfully. Nothing is required from the client!
When it comes to support, fully managed solutions also offer far higher quality. Clients should have a dedicated integration engineer who they can contact who understands their business and knows their partners, and is therefore well positioned to resolve any issues quickly.
The benefits of fully managed EDI
From a business perspective, the most compelling benefits of fully managed EDI can be usefully condensed into four categories…
1) Fully managed EDI saves you time
While all EDI is capable of saving users time through minimising manual processes and increasing data accuracy, fully managed EDI enables businesses to multiply these savings further by…
- Allowing internal teams to focus on core competencies, as all EDI tasks are handled by your solution provider
- Reducing time required for partner onboardings through external project management and use of intelligent tooling such as automated testing
- Shortening error resolution time through deep ERP integration and full-text search across all EDI messages, which enables delivery errors to be spotted quickly
- Freeing up internal teams from EDI onboarding and support tasks, allowing them to concentrate on more value-adding activities
2) Fully managed EDI saves you money
Arguably the clearest and most convincing benefit of fully managed EDI is its capacity to save businesses money. Fully managed / full service EDI enables users to…
- Reduce the total cost of ownership (TCO) of B2B processing, as EDI is offered as a scalable service on a pay-per-use-basis
- Experience flexible, cost-efficient growth, as new features and connection types can be added in modular fashion without prohibitive “price cliffs”
- Minimise cost-intensive manual tasks by getting EDI connections to a working state faster, since onboarding tasks are handled by specialised external teams
Note: While on-premise and partially managed EDI solutions may initially appear cheaper, when CAPEX, OPEX and other indirect costs are all taken into account, fully managed / full service EDI almost always offers superior value.
3) Fully managed EDI reduces your operational risk
In addition to helping businesses save money, fully managed / full service EDI providers such as ecosio also serve to reduce risk by…
- Ensuring the highest possible level of availability through the operation of multiple redundant servers
- Ensuring your solution is always cutting-edge through regular, automatic installation of software/security updates
- Making sure your solution’s success isn’t dependent on individuals, as message exchange is overseen by dedicated experts
- Detecting potential message delivery errors and resolving them as quickly as possible thanks to continuous monitoring
As a result, businesses that opt for a fully managed EDI solution need not worry about issues such as damaged partner relationships, fines, deterioration of solution efficiency or catastrophic data loss. Fully managed EDI ensures that no matter what, your electronic processes stay up and running.
4) Fully managed EDI increases your competitive advantage
As well as making life easier for internal teams, fully managed / full service EDI also places businesses using such solutions at a distinct advantage compared to their partners. This is due to the fact that fully managed EDI helps you…
- Focus on your core business while supporting EDI tasks are taken care of by a specialised service provider
- Stay competitive in the long-run, as fully managed solutions can easily be adapted to suit changing requirements (e.g. introducing a Web EDI platform or fulfilling country-specific e-invoice requirements)
- Boost business relationships, as partners’ EDI requirements can be met faster and more accurately
What’s more, fully managed EDI also boosts the attractiveness of the business in question to prospective partners, with benefits such as fast onboarding and round-the-clock message monitoring/error resolution, likely to be particularly appealing.
Why fully managed EDI is the future of B2B integration
Given the benefits of fully managed EDI it’s no wonder that more and more businesses are adopting this approach. In fact, fully managed EDI is set to become the new norm in the coming years.
Far from being replaced by new technologies such as API (as has been wrongly predicted by many over the years), EDI is now more crucial than ever to business processes. While large industry players demand ever more detailed data from suppliers, many businesses are also looking to extend B2B message exchange automation across as much of their supply chain as possible, with Web EDI platforms now allowing even the smallest suppliers to send documents via EDI. In many countries, too, the use of EDI – particularly e-invoicing – is now being actively encouraged and even mandated by governments. Meanwhile the Covid-19 crisis prompted many businesses to step up B2B integration efforts in order to improve supply chain sustainability.
As the scope and popularity of EDI has grown, however, so has the effort and expertise required to set up and operate a successful EDI solution. As a result, while handling EDI in-house may still be possible for those businesses with a wealth of internal EDI expertise, for most organisations a full service approach via the cloud offers a more logical and futureproof solution.
Just as we no longer have to think about how our phone calls are connected to the person on the other end (thanks to our network providers sorting this for us), so modern businesses are recognising that they no longer have to concern themselves with the technical intricacies of EDI document formats and protocols. By offering businesses security, flexibility and (perhaps most notably) the freedom to focus on what they do best, full service EDI is undoubtedly the future of B2B integration.
For more info on what the future of EDI might hold, see our article on the five top trends in EDI here. Alternatively, a more detailed exploration of how EDI is likely to evolve in the coming years can be found here.
Conclusion
As you should now recognise, managed and fully managed EDI are by no means the same. Whilst not all managed solutions offer the same exact services and some offer more than others, none can compete with fully managed solutions in terms of the extent to which they relieve pressure on internal teams.
Unfortunately, as providers often veil the limited nature of the service they provide, many businesses find themselves stuck in contracts they can’t get out of with solutions that require more resources and expertise to maintain than are available. Given that EDI contracts are usually fairly long, this commonly results in either the business in question having to pay over the odds for additional support from their provider or external consultants, or struggling to handle complicated processes in-house.
To avoid these situations it is extremely important to select a provider whose services fit your requirements. With a better understanding of the differences between managed and fully managed EDI, hopefully you are now more aware of what questions to ask prospective providers to establish the extent of their offering and make the right choice.
Looking to experience the benefits of EDI with minimal internal effort?
Efficient EDI is essential for ambitious supply chain organisations. However, integrating, running and maintaining a successful solution takes time and expertise. As these are commodities that few supply chain organisations have at their disposal, at ecosio we offer a fully managed service.
Over the years we’ve connected thousands of companies and understand exactly what effective EDI involves. With a single connection to our powerful Integration Hub, our partners benefit from unparallelled end-to-end data visibility. Meanwhile, our experienced integration engineers and EDI experts oversee every connection so you don’t have to.
In short, we take care of all your EDI needs, from mapping and testing to message monitoring and error resolution… and everything in between, leaving you to concentrate on whatever it is your business does best.
Discover more about our updated product, ecosio.flow.
For more information, contact us today!
Der Beitrag Managed vs fully managed EDI – What’s the difference? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Achieving NetSuite EDI Integration erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>In this article we will attempt to help you answer that question, looking at the potential benefits of EDI integration, the advantages and drawbacks of different integration methods, and what exactly EDI NetSuite integration via a managed EDI service provider involves.
What is electronic data exchange (EDI)?
For any organisation exchanging a high number of business documents, electronic data interchange (EDI) offers an efficient way to streamline the process. Today’s supply chains are more complex than ever, with partners requiring frequently used documents such as invoices and delivery notes to be delivered in different formats, at different times and over different communication protocols. As a result, the use of EDI is becoming increasingly widespread as more and more businesses require an automated method of managing this exchange and ensuring data is sent and received in the correct form.
EDI with NetSuite
Thankfully, such has been the advancement in software in recent years that even small businesses can now benefit from EDI. This is particularly significant as many large retailers require suppliers to have EDI capability before they can become trading partners. As NetSuite does not offer inbuilt EDI capability, however, Oracle users must look to external EDI providers to achieve an effective solution.
Given the wealth of different solutions available, selecting the right provider can be a confusing exercise, particularly for supply chain managers and IT decision-makers unfamiliar with EDI. Further, even those who have a good understanding of EDI may be under intense time pressure to find a solution to their business’s current EDI issues. As a result, many organisations regrettably invest in sub-standard, ill-suited or short-term solutions.
As we shall explore, with the right solution and approach, effective EDI integration in Oracle NetSuite can bring a host of benefits and set your business up well for the future. Plus, handled correctly, integration itself needn’t be the headache-inducing process many predict.
What are the benefits of EDI NetSuite integration?
- Speak the same language as your partners – Once you have successfully integrated an EDI solution into NetSuite, your system will automatically send and receive messages in the correct format and over the appropriate protocol without the need for manual intervention and keying of business documents (e.g. orders).
- Error reduction – By automating key data processes, potentially costly manual errors will be eliminated, resulting in reliable data exchange and a streamlined supply chain.
“What NetSuite EDI integration options do I have”?
Businesses looking to achieve an effective EDI solution in NetSuite have two options:
1) In-house NetSuite EDI integration
If you have sufficient resources and internal EDI expertise it may be possible to attempt EDI integration via an integration platform – also often referred to as middleware, comprehensive integration system (CIS) or integration platform as a service (iPaaS).
This approach will give you full control of the integration and will mean your EDI user interface is consistent with your business’s other ERP elements. However, it does come with several drawbacks:
- Speed – Understandably, when it comes to the time needed to complete the implementation, internal teams will never be able to compete with experienced external teams who are used to implementing NetSuite EDI solutions – particularly when you factor in that internal teams will also be juggling existing responsibilities.
- In-house knowledge and resources – Given the complexity of integration, it is extremely important that you have sufficient in-house expertise and resources before attempting NetSuite EDI integration internally. If the process is handled incorrectly, thanks to the business-critical nature of the data exchanged via EDI, the consequences can be disastrous.
- Testing – Thorough testing is key if you are to ensure your new EDI solution is secure, efficient and reliable. Unfortunately, testing takes time, as it is important to test all relevant business cases. For example, rather than just testing standard invoice transmission, it is important to test all invoice variations, such as those with surcharges, allowances, and including and excluding tax etc. Understandably, in-house teams are unlikely to have a thorough EDI testing procedure set up. Unfortunately, this lack of experience can result in the testing phase not being completed to a sufficient standard, in turn leading to potentially costly issues further down the line.
- Monitoring / updates – Once NetSuite EDI integration has been completed in-house via an integration platform there is still a considerable amount of effort required to maintain an efficient EDI system, from continual monitoring of message status, to implementing updates and ensuring compliance with e-invoicing regulations (among other responsibilities). In short, due to the business critical nature of the processes and information involved, thorough monitoring of your EDI solution is essential.
2) NetSuite EDI integration via a managed EDI service provider
For businesses keen to ensure data integrity but lacking extensive in-house EDI knowledge and resources, the more sensible option may be to opt for integration via a managed EDI service provider, or VAN. These providers are extremely familiar with integration projects and should be able to ensure a swift and secure connection in partnership with your ERP customiser.
The key benefits offered by NetSuite EDI integration via a VAN are:
- No need for in-house expertise during or after integration! – As already mentioned, the resources needed to handle EDI internally are by no means insignificant. By integrating a managed EDI solution into NetSuite you will remove the need for in-house expertise and relieve pressure on internal teams.
- Time and cost saving – Perhaps the most compelling reason to integrate a managed EDI solution into NetSuite is the time and money it can save your business by hugely reducing the in-house effort required to maintain data processes and allowing you to reallocate internal resources.
Some managed EDI providers may also offer additional services and benefits, such as:
- Improved visibility via a deep API-NetSuite connection – A deep NetSuite EDI connection (such as that offered via ecosio’s cloud-based EDI solution – our Integration Hub) offers the ability to view message statuses directly in your ERP’s user interface, meaning there is no need to navigate to, or become familiar with a new system.
- A future-facing approach – To experience the full benefits of an efficient managed EDI service it is important to select a provider who is able to future-proof your business’s data processes. In order to achieve this, the best managed solutions will include 24/7 monitoring and support in combination with implementation of ongoing updates. Sadly this is not a priority for many providers, whose customers then suffer following important EDI developments (many providers do not offer access to Peppol for example).
- Batch message processing – Batch processing involves combining multiple documents in a single EDI message for increased efficiency, much like sending multiple letters to the same address in one envelope. Unfortunately, batch processing (inbound as well as outbound) is not supported by most standard ERP system interfaces. Integration of a managed solution (such as ecosio’s EDI solution) that offers a deep ERP-EDI connection will enable this useful functionality.
How to integrate managed EDI with Oracle NetSuite
Integration of an external, managed EDI solution into NetSuite can happen in one of two ways; via a connector or directly. You will require an ERP customiser for both approaches.
1) Integrating EDI solution into NetSuite via a connector:
The easiest way to integrate an EDI solution into NetSuite is to do so via an ERP customiser offering a tailored connector. The benefit of using a connector is principally the speed with which the connection can be completed. Once a customiser has developed a connector between NetSuite and your chosen EDI solution, the steps required to integrate the same solution into future customers’ NetSuite systems are greatly reduced. Think of it like a builder turning up at a job with all the necessary tools and equipment as opposed to one who first has to assess the situation and go out and buy the required materials.
Thanks to the minimal adaptations required when using a connector to integrate a managed EDI solution in NetSuite, this approach also has the benefit of low initial costs and reduced mapping costs.
In 2018 ecosio developed a NetSuite-EDI connector in partnership with ERP customisers and Oracle integration experts CW Global Partners.
Utilising a modern REST-API, this unique connector integrates ecosio’s EDI solution directly into NetSuite via a single standardised transmission channel and a unified document format. The result is seamless integration of the complete scope of ecosio’s API and an ERP environment that is 100% EDI optimised.
Following integration via this connector, NetSuite users will benefit from:
- Accurate delivery/fetching of messages – Once the connection with the ecosio cloud-based EDI solution (our Integration Hub) has been established, the receiver can set up regular requests to check if new messages have arrived. Alternatively, new messages can be transferred proactively from the Integration Hub to the recipient.
- End-to-end message monitoring – Thanks to the depth of the connection, there is no need to log into an independent EDI monitor. Users will instead receive feedback directly into their NetSuite user interface that their partner has acknowledged the message.
- Full-text search – Messages can be searched by content. For example, if required, a user could locate a document by searching by document number, interchange reference or protocol ID (OFTP2 or AS2 Message-IDs).
- Error handling – NetSuite EDI integration via a connector will ensure the user has access to valuable information if and when errors occur. In addition to being able to see why the transmission failed, users can also identify where the error occurred and what needs to be fixed.
2) Direct NetSuite EDI integration
The second method for implementing a managed EDI solution in NetSuite is via direct integration. This process works as follows:
- NetSuite will expose an HTTP endpoint for the EDI provider to push inbound messages to your ERP.
- Your chosen EDI provider will expose an HTTP endpoint for NetSuite to push outbound messages to them.
- Content is transferred in a JSON format and the required fields need to be defined from scratch between EDI system and NetSuite for every new project.
While just as valid an approach as integration via a connector, direct NetSuite EDI integration differs in several ways. In particular, the last bullet point above represents a key disparity. Unlike when using a connector – where import/export formats (including the information/fields that are transferred) are ready to implement – each of these elements needs to be defined from scratch during direct integration. More generally, the amount of work required to set up a direct NetSuite EDI connection means that it will undoubtedly cost more and take longer than integration via a connector. Further, functionality after implementation will also be different, as customers opting for direct integration will not benefit from error-handling, end-to-end monitoring or full-text search capabilities.
Key differences at a glance
NetSuite EDI connection via connector
- Only minor adaptations required before the interface is ready to use
- Minimal initial costs and mapping costs
- Tried and tested method
- End-to-end monitoring
- Error handling
- Full-text search
NetSuite EDI connection via direct integration
- Higher implementation costs
- Longer implementation time / more complicated setup
- EDI functionality limited to sending and receiving messages (no end-to-end monitoring)
- No error handling capability
- No full-text search
How ecosio can help
At ecosio we have done, are happy to do, both direct and connector-enabled NetSuite EDI integration. By integrating our unique API as a native feature in NetSuite, in addition to experiencing all the benefits of a regular managed EDI solution, you will benefit from:
- 24/7 support and monitoring
- Implementation of ongoing updates
- Excellent customer service
- Ability to view business-critical data in your existing user interface
- One contact person – one EDI partner – one interface
To find out more about our solution or if you have any questions about NetSuite EDI integration please contact us. We’re happy to help!
Der Beitrag Achieving NetSuite EDI Integration erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag SAP Business Connector (SAP BC) – Replacement Alternatives erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>The SAP Business Connector is a separate software component that is installed and managed independently of the SAP system. By using RFCs (Remote Function Calls), functions can be called in another system, which enables communication with SAP and non-SAP systems. Both synchronous communication (sRFC) and asynchronous communication (tRFC and qRFC) are supported. As part of the data communication with external systems, the Business Connector is also able to convert between different formats. For example, an SAP-internal format can be converted into the customer or supplier external format (e.g. EDIFACT).
The following graphic illustrates this process in a simplified way:
Document Exchange with the Help of the SAP Business Connector
For example, companies can exchange IDocs and XML files with business partners using the HTTP(S), FTP, or E-mail (SMTP / POP3 / IMAP) communication protocols. However modern protocols, which are increasingly used in the field of electronic data interchange (EDI), such as AS2, OFTP2 or Peppol are not supported.
Any company with a valid SAP license can operate the Business Connector for free, which contributes to a widespread use of the software. However, with the end of the maintenance of the SAP Business Connector approaching at the end of 2020, companies must find a successor. Otherwise, smooth data exchange with customers and suppliers cannot be guaranteed.
Alternatives to the SAP Business Connector
Before deciding to replace the SAP Business Connector, a company must first clarify whether a local solution should be installed again or to it set to a managed solution.
Alternative 1: Install a local solution
A local solution is installed and operated similar to the Business Connector. This involves purchasing a software that is installed in the company alongside the SAP system. This solution performs data mapping between SAP documents and third-party formats as well as routing through the required channels. Companies must make sure that the new system supports all required formats and protocols of the business partners.
As a further local alternative, an SAP add-on can be installed, which takes over the conversion into different file formats. The difference to the previous solution is that the add-on runs directly in the SAP system and not in an external instance. Therefore, a routing software must be purchased additionally to this solution, so that documents can be sent and received.
The biggest disadvantage of a local solution is the associated cost. Companies must expect high initial and maintenance costs in order to always be able to operate the software with a state-of-the-art technology. To ensure the functionality and security of the system, regular updates must be made. Depending on the software which was selected, these updates may be subject to an additional charge.
The ongoing maintenance of the document mappings, the maintenance of the EDI connections (certificate exchange, parameter change, etc.) and the ongoing monitoring must also be included in the cost analysis.
Alternative 2: Change to a Managed Solution
A resource-saving alternative to the SAP Business Connector is to hire a service provider, such as ecosio, who offers a Managed EDI solution.
In this variation, the company’s SAP system is connected to the service provider’s external software solution, eliminating the need to install software in the in-house IT environment. For example, the ecosio.MessagingHub, which handles the data exchange, can be connected to the company’s system via a connector.
The service provider takes care of the conversion of the documents into the required formats, for example UBL for the standard XRechnung. The data is then sent via the required protocols, such as Peppol, AS2, X.400 etc.
The entire workflow is constantly monitored, thus preventing the transmission of faulty documents to business partners.
In addition, the service provider can also receive documents from partners and convert them into an SAP format. With the help of the service provider, the functionality of the SAP ERP system is extended so that all types of EDI traffic can be handled with customers and suppliers.
The EDI workflow between a company and its EDI partners is shown in the following diagram:
EDI Workflow with an EPO Connector and ecosio.MessagingHub
Businesses can use this to ensure that all processes in the EDI workflow are constantly monitored and that EDI traffic is maintained without disruption. Furthermore, the service provider keeps the systems up to date, which means there are no unpredictable costs for updates.
Due to the large number of supported file formats and transmission protocols, all EDI-specific requirements can be met. If, for example, a company gets a new business partner who demands a new file format, the data exchange can start without having to program extra software extensions – the service provider supports all common formats and protocols.
Summary
Due to expiring support for the SAP Business Connector, companies should look for a suitable replacement as soon as possible. Instead of buying a local converter again, an EDI service provider can be assigned to take care of the conversion and the transfer of documents between companies and their suppliers and partners. The big advantage of this solution is that companies do not face unplanned costs for updates. Also, it guarantees that the system is always state-of-the-art and therefore fit for the future.
Any questions?
Do you still have questions about the SAP Business Connector and its alternatives? Feel free to contact us, we would love to help you!
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag SAP Business Connector (SAP BC) – Replacement Alternatives erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>