Der Beitrag ecosio to Host SAP/EDI Workshop at UKISUG Connect 2021 erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>What is UKISUG Connect?
UKISUG stands for the UK and Ireland SAP User Group. UKISUG Connect is this group’s large annual conference. At the conference SAP customers, consultants, employees and partners from across the UK & Ireland come together to discuss relevant topics, listen to expert talks and collaborate.
About UKISUG Connect 2021
This year’s event will welcome over 500 SAP customers, 200 SAP experts and 70 exhibitors. Delegates will be able to choose from 80+ sessions across the conference’s three days, as well as enjoy the many opportunities to network. The full schedule can be found here.
At this year’s event ecosio will be exhibiting and will therefore be available throughout the conference to answer any SAP or EDI-related questions.
At the 2021 event ecosio will also be running a workshop, entitled “Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and e-Invoicing with SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA – Technical Foundations and Best Practices”.
What ecosio’s workshop will cover
In ecosio’s workshop SAP expert Philipp Liegl will explore how a cost-effective, efficient and sustainable EDI solution can be implemented in SAP systems, detailing several positive steps you can take to ensure your SAP/EDI project is a success – no matter what the target SAP system is or whether it’s yours or a client’s.
Thanks to the number of different SAP systems and EDI integration options out there, identifying which solution makes the most sense for your specific situation can be difficult. Available solutions are numerous, including local EDI converters, SAP PI/PO, SAP Integration Suite with its Cloud Integration component, and fully managed solutions from external service providers. This session will help you identify which of these represents the best option.
Attendees will discover how to access full EDI functionality via their SAP system’s existing user interface and turn their SAP into their own EDI control centre with a seamlessly integrated and customisable solution. They will also learn what the different options for EDI and e-invoicing integration in SAP are, how to reduce the strain on in-house resources and the secrets to long term EDI success.
Interested in attending?
Registration for the event is still open and tickets can be purchased here.
We look forward to seeing you there!
Der Beitrag ecosio to Host SAP/EDI Workshop at UKISUG Connect 2021 erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag SAP® EDI Project Roles – A Breakdown erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Given the many different SAP systems available and the myriad ways in which EDI capability can be achieved, however, it can be difficult to know exactly how to go about integrating a new solution. To help, in this article we provide an overview of the different roles involved in a successful SAP EDI project and which tasks are handled by each role.
For the purposes of this article we will look specifically at the roles required to integrate fully managed EDI, as this constitutes the most comprehensive EDI solution available to SAP users – and crucially requires the least internal effort from you. In this approach to EDI integration in SAP, the roles and responsibilities are typically spread across four key players: your EDI provider (ecosio in this example), your business, your SAP consultancy and your partners (e.g. customers/suppliers/relevant governmental agencies)…
Your EDI Provider (ecosio)
Thanks to ecosio’s fully managed approach, it is ecosio, rather than your internal team, that handles the vast majority of EDI tasks (click here for a more detailed breakdown of the amount of internal effort required to setup and operate different EDI solutions).
ecosio’s team of EDI and SAP experts manages the EDI SAP integration process from setup and testing to maintenance and error handling. This way you are able to experience all the benefits of EDI with none of the hassle.
A key part of the success of the ecosio approach is the nature of the two roles involved…
1) Integration Engineer

Every ecosio customer is assigned a dedicated Integration Engineer. This ecosio Integration Engineer is your very own EDI hero and acts as a single point of contact for all things EDI.
As well as being an expert in EDI protocols and formats, they also understand the underlying IDoc structure and the correct data representation. More importantly, they know your company, are familiar with your needs and are easy to get hold of. Contrary to many other EDI support personnel, our Integration Engineers really care about every EDI message exchanged!
Their key responsibilities include (but are not limited to)…
- Managing the SAP EDI integration/migration process end-to-end
- Liaising directly with relevant parties so you don’t have to
- Handling industry-specific EDI issues within SAP
- Proactively identifying and resolving errors to ensure ongoing success
Main contacts: Your internal project manager, the ecosio Onboarding and Operations team, your SAP consultancy project manager, your partners’ EDI contact people
2) Onboarding and Operations Team

Working alongside and supporting your Integration Engineer is ecosio’s Onboarding and Operations team. The job of this team is to provide your ecosio Integration Engineer with support in regard to onboarding, document mappings, connection testing and any other EDI tasks whenever needed. Significantly, there is no need for your organisation to liaise with this team directly, as everything is handled via your Integration Engineer.
Main contacts: ecosio Integration Engineer, SAP consultancy project manager, your partners’ EDI contact people
Your Business
With ecosio’s fully managed EDI solution, there are three different EDI roles that must be filled by individuals in your business:
1) Project Manager
The first and most important role is that of the project manager. They are essential as they understand your business and what you want to achieve better than anyone.
Their responsibilities include…
- Developing the project strategy in line with your ecosio Integration Engineer
- Ensuring your project stays on time and on budget
- Collecting feedback from internal users
- Communicating regularly with your ecosio Integration Engineer and alerting them to any issues or changes in strategy (e.g. a change in the agreed order of partner onboarding)
Main contacts: ecosio Integration Engineer, key users, business users
2) Key Users

These users have the most comprehensive understanding of SAP/EDI. They are responsible for providing feedback during the mapping/testing phase and checking that messages are coming through as desired. They should also alert the project manager if any issues or opportunities for optimisation are spotted. Key users may also be used to help train business users.
Main contacts: Internal project manager, business users
3) Business Users

A business user is simply an employee who uses the final product. Their responsibilities are limited to using the product correctly and alerting the project manager should they spot any issues.
Main contacts: Internal project manager, key users
SAP Consultancy
When it comes to your SAP consultancy, there are four related roles:
1) Project Manager

The SAP consultancy project manager oversees all work done in relation to your project by that organisation. Their main task is to liaise with the ecosio Integration Engineer and pass any relevant information on to colleagues to ensure any SAP ERP issues are resolved as fast as possible. Their focus should be keeping your SAP system working and ensuring your project stays on time and on budget.
Main contacts: ecosio Integration Engineer, SD/MM/FI consultant, ABAP programmer, SAP basis administrator
2) SD/MM/FI Consultant

The SD/MM/FI consultant manages the necessary adjustments to your SAP system to enable seamless integration of your new EDI solution. This involves testing and carrying out acceptance. SD/MM/FI consultants are experts when it comes to SAP problem solving.
Main contacts: SAP consultancy project manager, ABAP programmer
3) ABAP Programmer
The ABAP programmer’s role is to realise custom code when the normal SAP means aren’t sufficient. Effectively, they step in when the SD/MM/FI consultant is unable to fix an issue.
Main contacts: SAP consultancy project manager, SD/MM/FI consultant
4) SAP Basis Administrator
The SAP basis administrator is like the SAP mechanic. They oversee SAP system operation and fix any issues relating to memory / processor use, network, etc.
Main contact: SAP consultancy project manager
Your Partners (Customers / Suppliers / Governmental Agencies)
For other partners, there is only one relevant EDI project role:
EDI Contact Person

This individual acts as the sole contact point for your ecosio Integration Engineer, who will liaise with them directly during onboarding to get them connected. Your ecosio Integration Engineer may also need to contact them post go-live to fix any subsequent message exchange issues.
Main contact: ecosio Integration Engineer
About ecosio and Connections That Work
At ecosio we are experts in providing EDI Connections That Work and have helped hundreds of businesses to experience the benefits of automated document exchange in SAP®.
Our expert Integration Engineers and Onboarding and Operations team takes care of everything from setup and testing to maintenance and error handling. With our solution virtually zero internal effort is required for you to experience successful EDI in SAP®.
To find out how you can experience streamlined, future-proof EDI in your SAP system, get in touch today. We are always happy to answer any questions you may have!
Want this information as a handy one-page infographic?
To help you visualise SAP EDI project roles, we’ve condensed the information in this article into a helpful, printable infographic.
Der Beitrag SAP® EDI Project Roles – A Breakdown erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag How do I implement EDI with SAP Integration Suite®? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- Implementing EDI with SAP Integration Suite® needs strong internal EDI skills and resources for mapping, routing, and 24/7 monitoring
- Managing EDI includes handling integration flows, certificates, mapping tables, and legal compliance like XRechnung or FatturaPA
- Outsourcing EDI to a managed service like ecosio makes the process simpler by providing one connection that covers onboarding, mapping, and monitoring
- Managed EDI reduces internal effort and gives access to a broad EDI network with full SAP integration and message tracking
In this article we show you how companies can best implement electronic data interchange (EDI) to automate message exchange across supply chains using SAP Integration Suite® (previously known as SAP Cloud Platform Integration).
In short are basically two possibilities:
- Managing EDI internally with SAP Integration Suite®
- Outsourcing to a specialised fully managed EDI service provider
We also present a number of questions that decision-makers and IT managers can ask themselves to find the right solution.
EDI and B2B integration with SAP Integration Suite® – what decision do I need to make?
The SAP Integration Suite® itself is a Platform-as-a-Service solution that includes a comprehensive range of services for the in-house development, integration and operation of cloud services or cloud applications. At the same time, individual extensions of cloud and on-premise landscapes can be carried out.
Thor’s SAP hammer…
One of these services is SAP Integration Suite®, which was designed to integrate cloud or on-premise applications into SAP systems. SAP Integration Suite® is an extremely comprehensive and powerful tool from the cloud that allows you to create EDI functions (and much more) in-house and is very popular in companies with large supply chains. In essence it is similar to SAP PI or SAP PO, but unlike these is designed to be used locally.
…can be quite difficult!
However, this tool must be used properly. The big challenge in implementing EDI in SAP Integration Suite® is the high degree of effort and EDI expertise required from the in-house teams that implement the connections individually for each B2B partner.
Therefore, the key question for decision makers implementing EDI in companies with SAP Integration Suite® is:
- How much internal EDI capacity can I use? Do I want to manage EDI completely internally or do I want to relieve my internal teams by outsourcing EDI?
Further potentially useful questions include:
- What EDI capabilities does my B2B network require? Do I need access to Value Added Networks (VANs)? Does I need to connect to Peppol? Do I want automated message exchange with those suppliers without EDI capability (via Web EDI)?
- How flexible do I want my EDI solution to be? Can I rely on a rigid implementation in the long run or do I want to make my EDI solution resilient and future-proof?
- Which technical requirements must my EDI solution fulfil now and in the future? Which formats, protocols, document types and legal regulations in electronic invoicing (e.g. XRechnung in Germany or FatturaPA in Italy) do I need for my B2B network?
Let us now look at the two options in detail:
1) Manage EDI internally with SAP Integration Suite®
In principle, many necessary EDI tasks can be implemented via SAP Integration Suite® with correspondingly high internal capacities and previous EDI knowledge. These include:
- Mapping and routing of all existing and new connections
- Ongoing maintenance of the connection parameters and regular renewal of all certificates
- Ongoing maintenance of mapping tables and industry internal practical knowledge about the implementation of special formats (e.g. VDA)
- Ongoing coordination with B2B partners and procurement of all necessary information (especially during onboarding)
- 24/7 monitoring and troubleshooting
These processes require a great deal of internal EDI know-how and corresponding industry knowledge, especially when problems or errors occur in message transmission, as protocols and formats can vary greatly across different industries, regions and business areas.
Potential problem areas must be considered:
- E-invoice compliance: this can be partially implemented with pre-defined integration flows. However, it is important to ensure that no necessary updates are missed, so that the legal requirements are always met.
- Maintenance of various integration scenarios: this must be done on an ongoing basis, including regular monitoring of integration flows and temporary data as well as the management of security artefacts such as digital certificates.
- No access to message payload. Only available if payload trace is enabled. This can only be activated for ten minutes per iFlow and then automatically deactivates again. This makes real-time monitoring of connections difficult.
It should also be mentioned that additional services may have to be purchased, such as OFTP2 connectivity. If Value Added Networks (VANs) or X.400 are used, companies that manage EDI themselves are also stuck paying a high cost per message. By contrast, EDI service providers can provide lower costs by exploiting economies of scale thanks to high message volumes.
2. Outsourcing to a fully managed EDI service provider
Fully managed EDI is a cloud-based EDI solution where a company is connected to a specialised EDI service provider via a single connection. This service provider then takes over all EDI functions and processes, depending on your company’s requirements.
All the above points are taken care of by an experienced team. The time-consuming coordination of information and technical changes during partner connections is also handled by a dedicated project manager – in turn speeding up the process hugely. Meanwhile, troubleshooting is a fixed component of the 24/7 monitoring and support and is carried out proactively.
This means:
- Internal teams are completely relieved of EDI tasks (especially during operation)
- A single connection provides companies with the complete “EDI package” without the need for EDI expertise
- Companies purchase bespoke, fully functional EDI that is turnkey ready
The technical implementation of the connection between ecosio and SAP Integration Suite® takes place via HTTPS using the ecosio API. This enables a seamless integration of EDI functions into the SAP system using SAP Integration Suite® and ecosio, which retains complete data transparency within the company – including full text search and message status tracking.
This means, for example, that the exact delivery status of a sent EDI message, right up to the final recipient, can be viewed directly in the SAP system as IDoc status. This gives specialist departments security and confidence in the EDI solution as well as the possibility to view failed messages and the exact reasons for rejection directly in the familiar SAP GUI at any time.
Summary: EDI with SAP Integration Suite®
You now know the two possibilities for EDI implementation with SAP Integration Suite®: handle it yourself or outsource it. SAP Cloud Platform is a comprehensive Platform-as-a-Service solution that can provide a good foundation for experienced developers and EDI experts – as long as your company has appropriate resources and expertise and potential future changes and extensions to your EDI landscape are anticipated and planned for in advance.
Partnership with a fully managed EDI service provider enables companies to fully manage and operate all EDI functions without the need for internal EDI effort and expertise, flexibly scalable and monitored 24/7 during operation.
Do you still have questions about EDI and SAP Integration Suite®?
Do you still have questions about SAP Integration Suite® or electronic data exchange with an SAP® ERP or SAP S/4HANA® system? Get in touch with us – we will be happy to help you.
Discover more about our updated product, ecosio.flow.
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag How do I implement EDI with SAP Integration Suite®? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag IDocs in SAP S/4HANA: The Differences to SAP ECC 6.0 erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- IDocs remain the standard format for data exchange in SAP S/4HANA, continuing from SAP ECC 6.0, with most integrations still based on IDocs
- The IDoc structure has been updated in S/4HANA, including corrections to segment descriptions and the addition of new elements like SGT_RCAT, HANDOVERLOC, and MATNR_LONG
- The INVOIC02 IDoc has 37 differences compared to its ECC 6.0 version, with 33 being descriptive corrections and 4 adding new elements
- The changes aim to improve handling of S/4HANA, with new fields supporting enhanced data precision and extended material numbers
SAP ECC 6.0 has officially ended. Until 2027, maintenance of the third version of SAP SE, which was introduced in 1993 (!) as R/3, will continue unchanged and without additional fees. Between 2027 and 2030 only core applications of Business Suite 7 are to be maintained, but at additional cost. The fourth and current version SAP S/4HANA has already been guaranteed maintenance until at least 2040. Now is therefore a good time to get serious about the update from an EDI perspective as well. In this article we cover what you need to know concerning IDocs in S/4HANA.
IDoc: the SAP standard format and its changes under S/4HANA
…or rather, from the IDoc perspective. IDocs are the standard format in SAP when it comes to exporting or importing data and this will not change quickly in S/4HANA. This means that most SAP integrations and implementations of automated message exchange will also continue to be based on IDocs.
The update to S/4HANA changes the structure of the IDoc format. Some descriptions of individual segments have been corrected (mainly upper/lower case), other elements have been added. However, IDoc is known to use a lot of rather short abbreviations for the available elements, so without documentation and the XML tree from the XML schema it is not immediately clear which are new and which have changed. The XML schema of an IDoc can be easily exported using transaction WE60 – and of course also to S/4HANA.
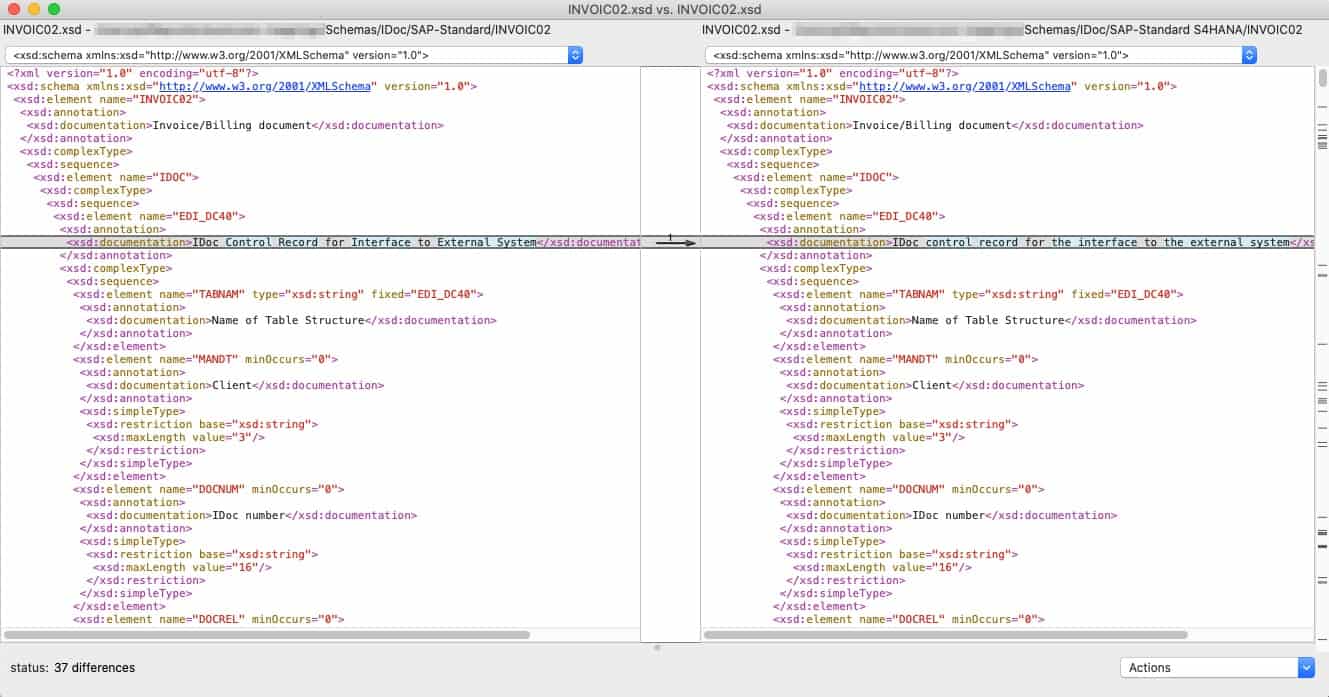
Below we’ll examine an example to illustrate the changes more clearly. We use the IDoc basic type INVOIC02 IDoc, which represents the de facto standard export of all invoices under SAP (this is particularly interesting as XRechnung will soon have to be generated from IDoc in Germany).
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
IDocs in S/4HANA – the differences in detail
In total, there are currently 37 differences between an INVOIC02 IDoc in S/4HANA and SAP ERP ECC 6.0.
The first 33 differences are merely corrections to the description of the segments (mainly case-sensitive). The other four differences are more interesting:
1) E1EDP01 – general data document item
The IDoc segment E1EDP01 receives some new elements. Their names and documentation are as follows:
"SGT_RCAT" Requirement Segment
"SGT_SCAT" Stock Segment
"HANDOVERLOC" Location for a physical handover of goods
"MATNR_LONG" Material Number
"REQ_SEG_LONG" Requirement Segment
"STK_SEG_LONG" Stock Segment
"EXPECTED_VALUE" Currency amount for BAPIS (with 9 decimal places)
"LIMIT_AMOUNT" Currency amount for BAPIS (with 9 decimal places)
2) E1EDP02 – document item reference data
There are also three new elements in segment E1EDP02:
"RMA" Order Acknowledgment Number
"REASON" Order Reason (Reason for the Business Transaction)
"RSNTXT" Description
3) E1EDP19 – document item object data
A longer material number can now be specified for the object data:
"IDTNR_LONG" up to 40-digit material number
4) Generic IDoc type extension
A new element in the generic IDoc type extension has also been added:
"E1IDOCENHANCEMENT"
You can use this element to specify generic key/value pairs in the IDoc XML file. However, the length of the character strings in the value elements is limited to 970 characters.
The changes in the IDoc structure are therefore manageable, and should be recognised as useful improvements for the best possible handling of S/4HANA.
Want more information on IDocs and EDI under S/4HANA?
For more details about the changes in SAP from ERP ECC 6.0 to S/4HANA and what a seamless EDI/ERP integration into your company’s SAP system involves, please contact us.
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag IDocs in SAP S/4HANA: The Differences to SAP ECC 6.0 erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Migration to SAP S/4HANA – 5 key considerations erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- Migrating to SAP S/4HANA is a complex, full ERP implementation, not a simple upgrade, so early planning is essential
- Archiving unused custom code and rethinking EDI integration can significantly streamline migration and reduce long-term effort
- Cloud-based, managed EDI solutions offer flexibility, 24/7 monitoring and reduced internal workload, especially important for S/4HANA Cloud setups
- Choosing the right EDI partner ensures long-term scalability, smooth onboarding, proactive support, and compatibility with SAP Cloud PI
While 2025 may signal many things to different people, for those working in IT for supply chain organisations currently using SAP systems, it is synonymous with one key deadline. 2025 is, of course, the deadline set by SAP for businesses to migrate to their new and improved system S/4HANA, after which supposedly they will no longer provide support for older systems. Whilst this may seem a generous deadline, as we shall explore in this article, transitioning to S/4HANA is by no means a simple process. In addition to the time-consuming exercise of migration itself, for those considering the move to S/4HANA the next few years offers a unique opportunity to refresh and update other key business processes, such as electronic data interchange (EDI), to ensure their businesses are in the best possible position when 2025 comes around.
In this article we’ll look at five key questions that anyone who is likely to be involved in coordinating a migration to S/4HANA should consider before proceeding.
1 – What iteration of S/4HANA is a good fit for your organisation?
Undoubtedly S/4HANA represents an exciting advance in ERP software and comes with considerable advantages. Key benefits include:
- Simplicity – The SAP Business Suite data model has been hugely simplified following the impact of the SAP HANA in-memory platform. Specifically, SAP has been able to remove (or reduce the number of) several table types from the data model. As a result, in addition to a significant reduction in your database’s memory footprint, your new system should also run faster.
- Ease of Use – Thanks largely to the above simplification, S/4HANA users also benefit from an improved user experience. S/4HANA makes heavy use of SAP’s new and improved user interface based on SAP Fiori apps.
- Future-proof solution – Another key benefit of transitioning to S/4HANA is the improved approach towards updates. Whereas previously new functionalities had to be manually switched on by in-house teams, with the S/4HANA cloud systems, updates will be implemented quarterly, removing the possibility of updates being delayed due to lack of in-house resources.
There are four basic options for businesses considering migration to SAP S/4HANA: self-hosted and on-premise, hosted by a hosting partner, private managed cloud and cloud ERP. The following Figure gives an overview of the different options.
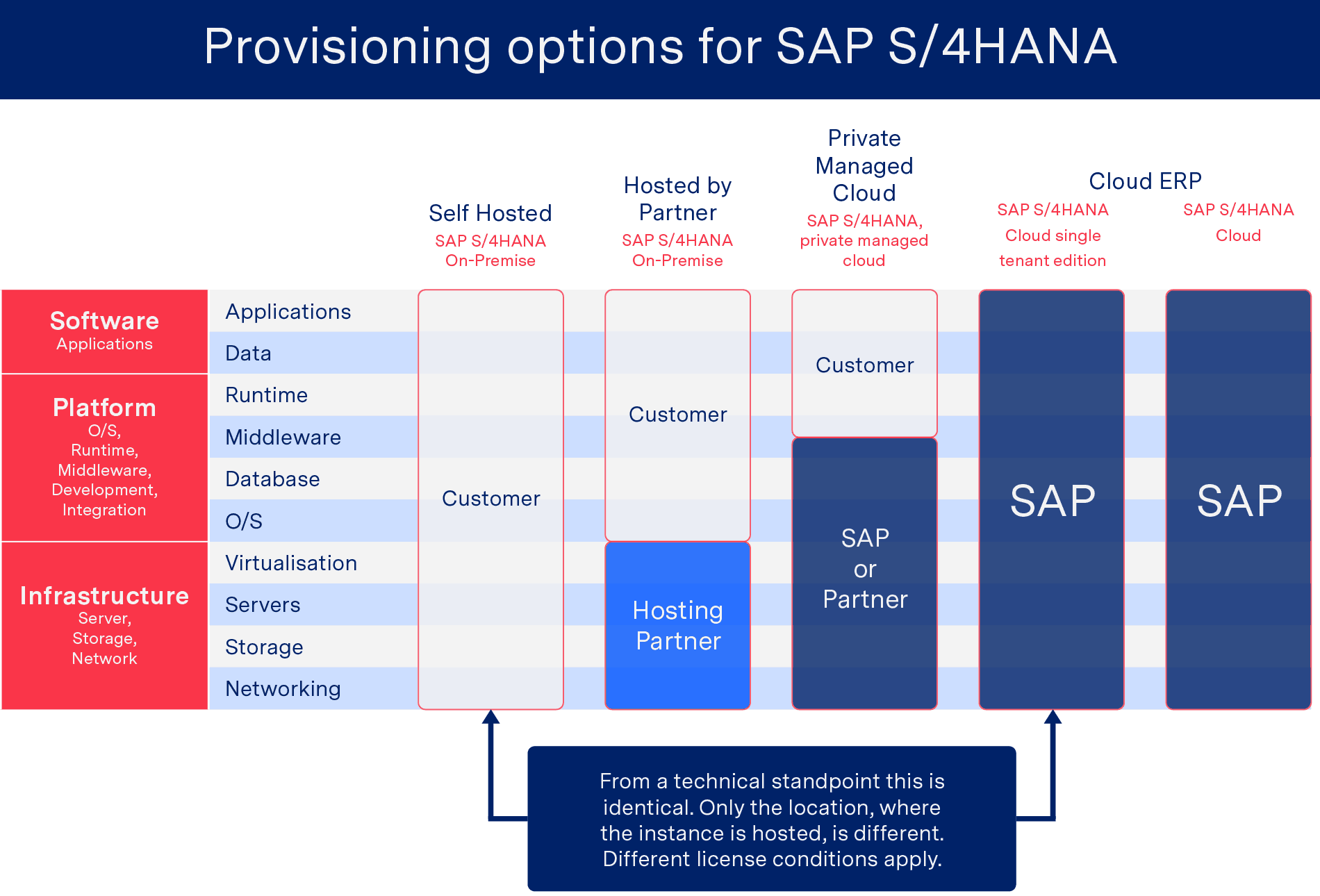
Migration to SAP S/4HANA – SAP Provisioning Platforms
The Cloud ERP solution is available in two different versions. The single tenant solution is hosted by SAP for a single tenant (= company), also allowing for company-specific code and system extensions. The SAP S/4HANA Cloud is a classic cloud-based software solution, where multiple different companies share the same SAP instance. The multi-tenant solution allows for less company-specific customisations than the Single Tenant Cloud edition. If a company seeks to implement custom adaptations or extensions to third party software solutions for the multi-tenant edition, they can be achieved through the SAP Cloud Platform.
It is important to remember, however, that every business is different and the most effective system for your company is unlikely to be any of the above ‘out-of-the-box’ solutions. Increasingly forward facing businesses are transitioning to so-called ‘postmodern’ ERP systems (those in which more suitable or tailored system packages from independent providers are integrated with standard ERP elements) in order to achieve the most efficient solution for them. Whilst postmodern ERP arrangements can prove complicated to set up and integration can, if handled poorly, jeopardise data integrity, intelligent integration of solutions better suited to your business’s needs (such as managed EDI) will produce a flexible and future-proof ERP environment.
Regardless of what system you are currently using or what version of S/4HANA you are looking to move to, the switch to S/4HANA is less of an upgrade and more of a full ERP implementation project. As migration is likely to be extremely heavy on in-house time and resources, it makes sense to consider what an optimum ERP landscape would look like for your business in advance of progressing with implementation. After all, if you are going to invest a huge amount of effort into the transition to S/4HANA, you may as well aim to finish with a system as closely tailored to your organisation’s needs as possible!
2 – “When should I start the migration process?”
According to SAP, moving from traditional SAP systems to SAP S/4HANA should take between 12 and 18 months. However, according to research from Gartner, companies that have already started the process have reported that migration to SAP S/4HANA can take far longer, with key steps potentially taking as long as the entire migration reportedly should.
“Migration” vastly underestimates the level and scope of transformation involved in adopting SAP S/4HANA. This is not a straightforward movement of your existing data and processes from one location to another. It’s more like you’re trying to relocate from the house you’ve lived in for the past 20 years to a more modern city apartment.
Wolfgang Platz – Founder & Chief Strategy Officer, Tricentis
With the above in mind, assuming you have identified the best ERP solution for you moving forward, it makes sense to start the migration process as early as possible. In addition to ensuring you have enough time to complete the transition to S/4HANA, starting the process earlier may save your business money, as implementation costs are likely to rise as the 2025 deadline approaches.
3 – Have you archived legacy data in preparation for migration to SAP S/4HANA?
Given the size of the task facing in-house IT teams, identifying effective methods of speeding up the migration process may prove crucial. With this in mind, perhaps the most worthwhile preparatory step a business can take in advance of transitioning is to archive legacy ERP custom code. Studies have shown that the majority of ABAP code is customer-specific code, a large proportion of which generally remains unused after being created. Migration to SAP S/4HANA offers a good opportunity to give your ERP system a spring clean. By completing this exercise in advance of migration you will benefit from a reduced migration volume and thus reduced financial and time costs. It really is a win-win!
4 – Should I move to a cloud-based EDI approach or will older EDI systems still be compatible?
With such a large-scale transition involving changing the source of EDI data (i.e. your ERP system) there will always be risks. Given the scope of the work involved in migration to SAP S/4HANA your EDI solution will inevitably be affected at some stage during the process. With this in mind it makes sense to use this as an opportunity to transition to a future-proof EDI solution. Moreover, thanks to the modern features of S/4HANA some older EDI solutions may simply not be compatible.
As explored in detail in our white paper in which we compare the benefits of on-premise and cloud-based EDI solutions, cloud-based EDI offers numerous advantages, such as flexibility, scalability and predictable pricing.
Significantly, while (as illustrated in the above diagram) the SAP S/4HANA multi-tenant cloud option offers only limited customisation, it is still possible for users with this system to integrate an external EDI solution into their ERP landscape. This means all users of S/4HANA have the opportunity to benefit from more efficient EDI in addition to the new features of S/4HANA, regardless of what system they opt for.
5 – Which cloud-based EDI approach shall I choose?
Thanks to the number of cloud-based EDI providers out there, selecting the right EDI partner can be a complicated process unless you know what to look for. Yet, much like deciding to upgrade your ERP to S/4HANA, selecting the right EDI solution for your business constitutes an important step towards future-proofing your organisation.
On the face of it, the most obvious candidate for a cloud-based EDI platform for businesses looking to move to S/4HANA is the SAP Cloud Platform Integration (or SAP Cloud PI for short). However, significantly SAP Cloud PI is an entirely unmanaged solution, meaning that everything is dependent on your in-house resources. Whilst this could potentially be a viable solution for businesses that have a wealth of in-house EDI expertise, for companies looking to optimise business data processes and streamline in-house resources a managed, cloud-based EDI solution represents a far more attractive option.
As we’ve already touched on, one of the common criticisms levelled at postmodern ERP setups is that the improved flexibility they offer comes at the price of additional complexity. However, when it comes to implementing a managed EDI solution with S/4HANA, whether your business opts for on-premise, private cloud or multi-tenant cloud, the end result will be a significant reduction in user complexity and required internal effort.
When considering potential managed EDI providers, make sure to consider the following:
- Are they compliant with SAP Cloud PI? – If you opt for either S/4HANA’s private cloud or multi-tenant cloud system, you will need to select an EDI provider (such as ecosio) that is compliant with SAP Cloud PI and can connect to your new ERP system. Unlike on-premise S/4HANA systems, where EDI connections can be set up via any channel (API, EPO Connector, SAP PI/PO, Business Connector, Local Converter etc.), with cloud-based S/4HANA systems, EDI integration must happen via SAP Cloud PI.
For businesses running both on-premise and cloud systems, SAP Cloud PI can be used as a gateway to connect all systems to the EDI provider. - Do they offer 24/7 monitoring? – Undoubtedly the biggest benefit of choosing a managed EDI service is that it should relieve you of the responsibility of monitoring incoming and outgoing data. Choosing a provider that offers effective, round-the-clock monitoring will mean you will no longer have to check that messages have been sent and received, that certificates have been renewed, or that the correct e-invoicing protocols are being followed.
- How comprehensive is their support? – Unfortunately, the level of support offered by EDI solution providers often leaves a lot to be desired. Asking about the specifics surrounding the support you can expect may help you avoid frustrating and potentially costly situations when you experience issues further down the line.
- How simple is partner onboarding? – The key here is to select a provider who will manage the onboarding process from start to finish. With a dedicated project manager partner onboarding becomes a simple and streamlined process. Choosing a provider who offers Web EDI is also essential if you want to connect to partners that don’t have EDI systems.
- Do they implement ongoing updates? – It makes sense that in order to future-proof your business you should select an EDI provider that is committed to implementing ongoing updates. For example, not every managed EDI provider provides access to Peppol, which can be disastrous when it comes to e-invoicing.
- Do they have “price cliffs”? – Again the key here is to think of your future needs as well as your current requirements. Many contracts include steep price rises (or “price cliffs”) if your EDI usage passes a certain point which can prove very costly.
Summary
In short, while 2025 may seem a long way off still, as we have covered, the journey to S/4HANA is a long one, and should ideally not be started without the necessary research and provisions. Given the scale of the task facing teams responsible for coordinating a migration to S/4HANA, it makes sense for decision-makers to use this time to consider what their ideal ERP would look like and upgrade or outsource other processes as necessary. Hopefully those who consider the above questions and make the effort to identify and implement the best solutions for them will ensure that 2025 starts to look less like a dark cloud on the horizon and more like the dawn of a new, more efficient era for their business.
Find out more
For more information about ecosio’s managed B2B integration solution and how it could help your business.
Alternatively, if you have questions about EDI and S/4HANA please contact us or use our chat – we are happy to help!
Discover more about our updated product, ecosio.flow.
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag Migration to SAP S/4HANA – 5 key considerations erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag An Overview of the Most Important SAP Modules erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>The SAP Business Suite is SAP’s core product. It consists of several solutions, which can be purchased either together or separately.
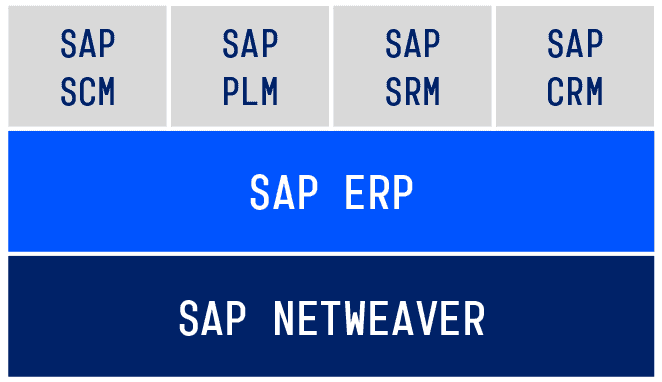
Structure of the SAP Business Suite
The technical foundation is SAP NetWeaver, on which all other modules and components are based. SAP ERP is the central component and offers functions for the following fields:
Logistics (SAP ERP Operations and SAP ERP Corporate Services)
- Real estate management (component RE)
- Production planning & control (component PP)
- Warehouse management (component WM)
- Customer service (component CS)
- Plant maintenance (component EAM/PM)
- Environment, health & safety (component EH&S)
- Logistics execution (component LE)
- Quality management (component QM)
- Sales & distribution (component SD)
- Materials management (component MM)
Accounting (SAP ERP Financials)
- Treasury (component TR)
- Project system (component PS)
- Controlling (component CO)
- Financial accounting (component FI)
- Enterprise controlling (component EC/SEM)
- Financial supply chain management (component FSCM)
Human Resources (SAP ERP Human Capital Management)
- Organisation management (component OM)
- Travel management (component TM)
- Recruitment (component RC)
- Personnel time management (component PT)
- Personnel planning and development (component PD)
- Personnel administration (component PA)
- Payroll (component PY)
- Personnel events (component PE)
The advanced modules can be found in the top layer of the SAP Business Suite. They are intertwined with SAP ERP and offer additional functions. Let’s first look at SAP ERP before looking at the single modules.
Logistics – SAP ERP SC
The SAP ERP SC (Supply Chain) maps the processes of a company’s entire logistics chain and is therefore very extensive. It consists of several components.
The SAP component MM (Materials Management) supports the purchasing of goods and services. It includes functions such as the processing of requisitions, inventory management and the maintenance of material master data.
The component PP (Production Planning & control) is used for sales and production planning, as well as an assembly process.
SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) covers the processes of selling goods or services of a company. It also provides solutions for foreign trade and customs clearance.
Finally, SAP CS (Customer Service) provides the most important functions for customer service, such as the processing of customer service orders.
Accounting – SAP ERP FI
The SAP ERP Financials covers internal and external financial accounting, corporate governance, treasury and receivables management.
Financial accounting and business transactions, among other things, are documented in order to produce the yearly balance sheet and the profit/loss account can be prepared (GuV).
The SAP component CO (Controlling) supports the internal accounting of a company. It allows the collection of economically important information based on cost, performance and investment calculation.
SAP ERP Financials is also responsible for other important tasks, e.g. the creation and planning of financial resources (Treasury), as well as the securing of liquidity through receivables management.
Human Resources – SAP ERP HCM
SAP ERP HCM (Human Capital Management) helps companies manage processes concerning their employees. Each employee is saved with a so-called infotype record. This record contains all important information about the employee, as well as their job title within the company. SAP ERP HCM can also record an employee’s working hours and create their payrolls. The entire course of training and further education for employees is also covered.
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
Special modules in detail
Now let’s look at the top layer of the SAP Enterprise Suite: the SAP modules. These partly overlap with the functions from SAP ERP. However, these modules offer a wider range of functions to address a business’s more specific needs.
Supply Chain Management – SAP SCM
SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM) offers advanced logistics functions from SAP ERP. SAP SCM is suitable for the entire supply chain: from the supplier to the customer. The SAP SCM functions include warehouse management, transportation management, supply chain planning and optimisation, and RFID processes (Radio Frequency Identification).
Product Lifecycle Management – SAP PLM
SAP Product Lifecycle Management (SAP PLM) represents the lifecycle of a product beginning with an idea through the production, and later to customer service. This module is very popular in the manufacturing sector, as it simplifies the internal and external communication through the exchange of information, plans, instructions, etc…
Supplier Relationship Management – SAP SRM
Businesses who work with many different suppliers can optimise their relationships with them using the Supplier Relationship Management (SAP SRM). Suppliers are more closely involved in the purchasing processes, which helps plan and manage the relationships in a more efficient way.
SAP Customer Relationship Management – SAP CRM
SAP Customer Relationship Management (SAP CRM) is responsible for the active customer relationship management and supports the communication between different departments and the customer. The customer information is given to the marketing department, sales and service, which in return allows them to fill the needs of the customer and react accordingly. Various analytic functions offer a deeper insight into customer behaviour and enable the development of efficient marketing strategies.
Special industry solutions
In response to the needs of different industries, SAP offers customised solutions in addition to the standard solutions. For this purpose, special functions are added on to enhance the standard processes of the respective industry. There are now over 20 industry solutions, including:
- Process industry (e.g. SAP for Oil and Gas)
- Service provider (e.g. SAP for Retail)
- Manufacturing industry (e.g. SAP for Automotive)
- Administration and finance services (e.g. SAP for healthcare or Banking)
Extensions to an SAP system
Thanks to the NetWeaver Stack, an SAP system is very flexible when it comes to the implementation of company-specific requirements and the integration from third party software. Therefore, almost all SAP modules can be provided with extensions, as long as they are programmed with ABAP.
If a specific functionality is needed, it is possible to implement the systems of third-party providers, such as an EDI provider, into the SAP ERP system.
Summary
SAP ERP already offers an extensive amount of basic functions for businesses of different industries. Depending on the requests, new modules can be added. This gives businesses the possibility to optimise control and have an overview in the logistics, accounting and human resource areas.
Questions?
Do you still have questions about SAP or implementing EDI into your ERP system? Feel free to contact us, we would love to help you!
Alternatively, you can find lots of relevant SAP content in our resource centre.
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag An Overview of the Most Important SAP Modules erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag What SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA version are you using? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>- Open SAP GUI → “Status” → zoom into SAP System data to check your installed version
- SAP ERP 6.0 (Business Suite 7) versions are shown via SAP_BASIS and SAP_APPL values
- SAP S/4HANA versions use a YYMM format (e.g. 1909 = September 2019), visible via the S4CORE component
- Knowing your version is key for EDI integration and upgrade planning
How to find your SAP version number
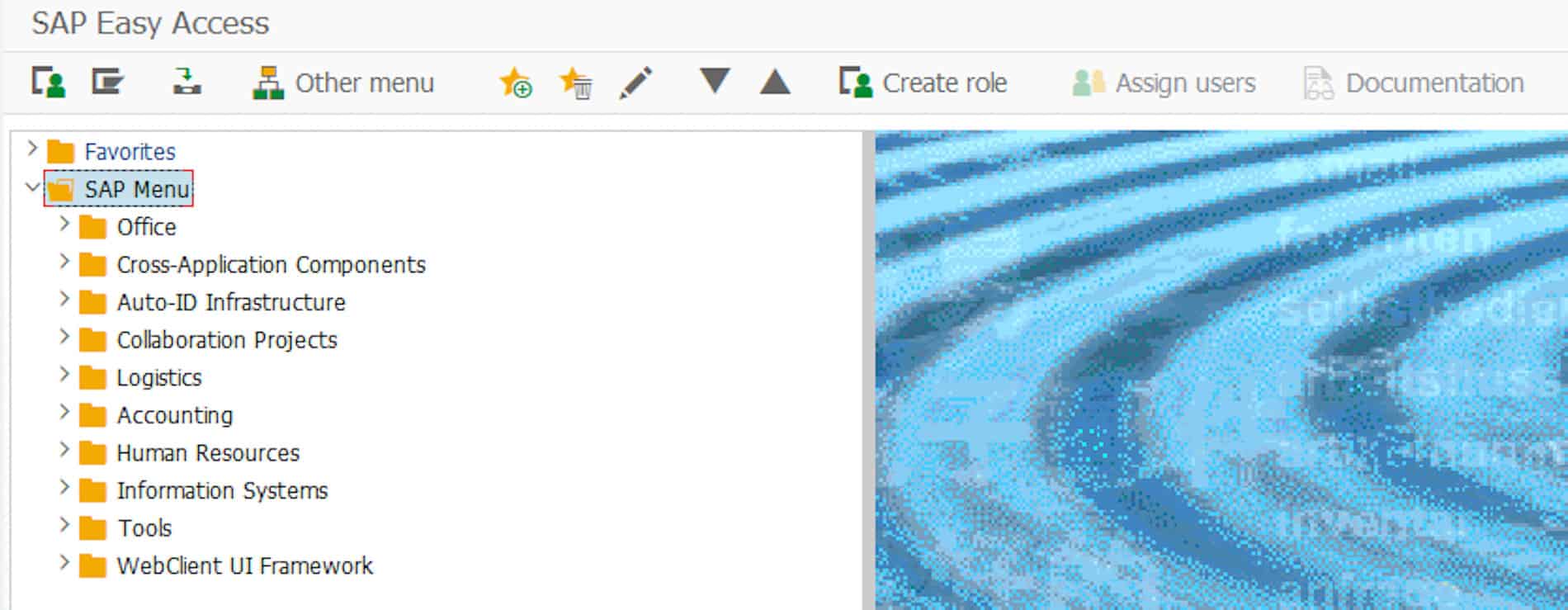
To find out which SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA system you are using, open the SAP GUI and select “Status” in the menu.

SAP Menu
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
Then click on the zoom button in the SAP System data section.
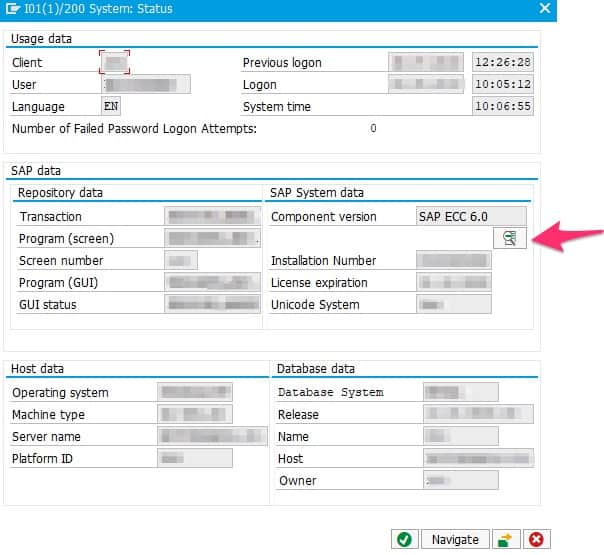
SAP Details
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
Depending on the SAP version and depending on whether you run SAP Business Suite 7 or SAP S/4HANA, details may be shown in different ways.
SAP Business Suite 7
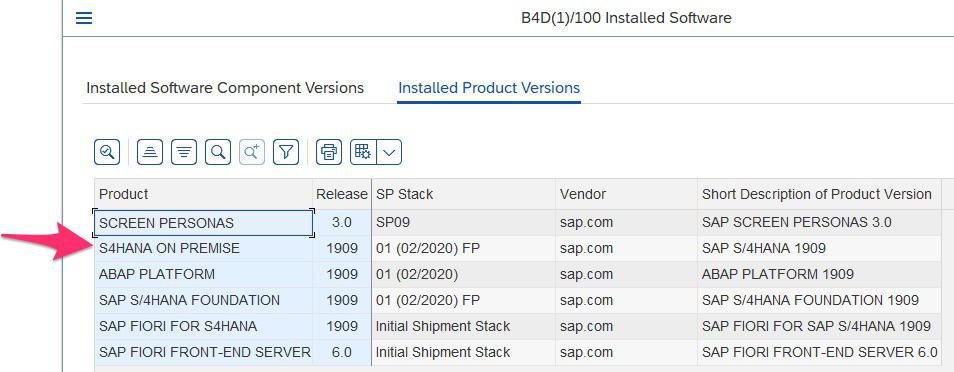
SAP ERP 6.0 is the central core component of SAP Business Suite 7 and the predecessor of SAP S/4HANA. Over the years new capabilities have been added to SAP ERP 6.0, which are called Enhancement Packages (or EHP in short). The latest EHP is EHP 8.0, which was released in 2016. The following screenshot has been taken from SAP Business Suite 7. The Installed Product Versions tab gives an overview of the currently used product versions.
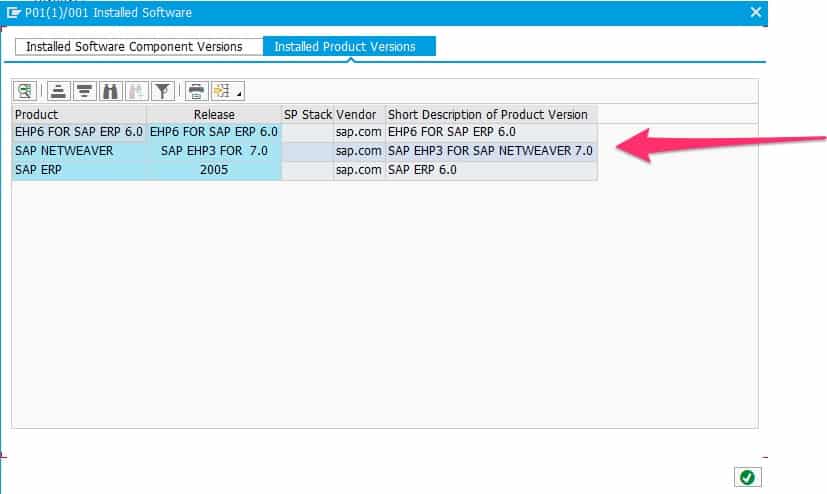
SAP product versions
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
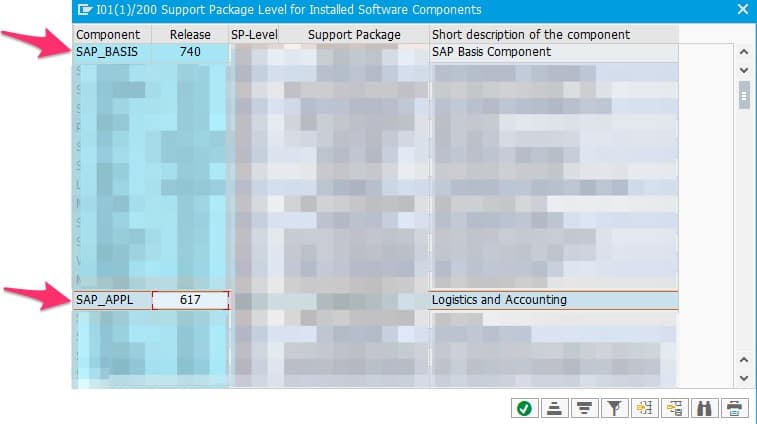
Where no tab exists, the version may be obtained by inspection of the two SAP_BASIS and SAP_APPL types. SAP_BASIS indicates the version of the underlying NetWeaver server and SAP_APPL the version of the used SAP ERP 6.0 component.
SAP product details
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
A SAP_BASIS type 740 indicates a SAP NetWeaver Server Version 7.4, SAP_BASIS 750 would indicate SAP NetWeaver Server Version 7.5 and SAP_BASIS 702 would indicate SAP NetWeaver 7.0 with Enhancement Package 2. Thus, the first two digits of SAP_BASIS indicate the SAP NetWeaver version and the last digit the NetWeaver enhancement package (if applicable).
A SAP_APPL type 617 indicates a SAP ERP 6.0 with EHP7. A middle digit 1 indicates that the system is enabled for HANA databases. A SAP_APPL 605 indicates a SAP ERP 6.0 with EHP 5. Since the middle digit is 0, the system is not enabled for HANA.
SAP S/4HANA
SAP S/4HANA is short for SAP Business Suite 4 HANA and is the newest ERP system of SAP. In SAP S/4HANA versions are named after the year and the month they were released (YYMM). Users of Microsoft Windows will find that naming convention quite familiar, as the same concept is used there.
Thus, an SAP S/4HANA system version 1909 indicates the release date of September 2019.
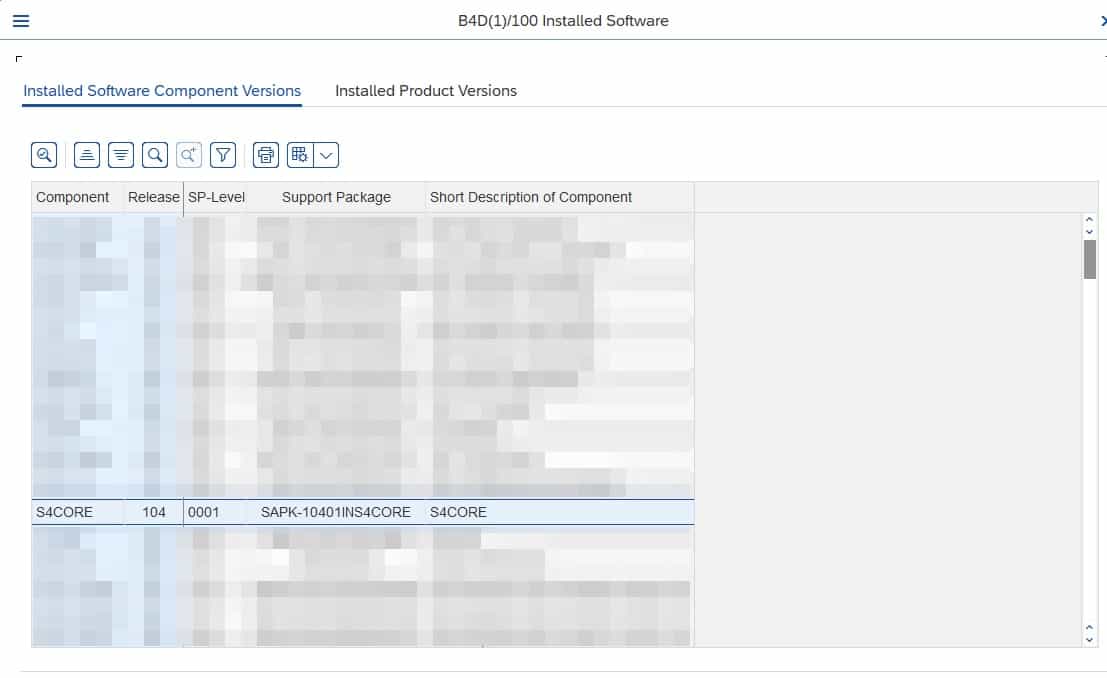
S/4HANA systems have a dedicated component called S4CORE (common questions regarding this component can be found in the SAP Community). The S4CORE version also indicates the used S/4HANA version.
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
S4CORE 102 means you are running an SAP S/4HANA 1709, S4CORE 103 means 1809, S4CORE 104 means 1909, etc.
Any questions about SAP ERP?
Got any questions about SAP and electronic data interchange (EDI)? Please contact us – we look forward to assisting you! You can also chat directly with one of our experts online.
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag What SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA version are you using? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>