Der Beitrag Germany Commits to Making B2B E-invoicing Mandatory erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>This progressive move toward e-invoicing not only demonstrates Germany’s commitment to leveraging technology for economic rejuvenation, but also positions German businesses at the forefront of digital financial practices.
What does the Growth Opportunities Act aim to achieve?
The act aims to provide tax relief measures to facilitate growth in an economy that has struggled in recent times, with Gross Domestic Product (GDP) having fallen by 0.3% in 2023. In short, by passing this act, the German government hopes to make the country’s economic landscape more efficient, transparent and resilient moving forward.
What changes will the Growth Opportunities Act bring?
A pivotal component of the Growth Opportunities Act is the introduction of a new e-invoicing mandate for domestic business-to-business (B2B) transactions. This development represents a drive to streamline financial operations and reduce the administrative overhead associated with traditional paper invoicing processes. Although debates within the Bundesrat in November 2023 suggested a potential postponement, which would have extended the timeline for adopting electronic invoicing until 2027 for receivers, the initial schedule set forth by the German Ministry of Finance (BMF) will proceed as planned.
What is the timeline?
The timeline for the phased implementation of the e-invoicing mandate is as follows:
- 1 January 2025: All German businesses must be able to receive and process electronic invoices
- 1 January 2027: German businesses with an annual turnover exceeding €800k must issue their invoices electronically for domestic B2B transactions
- 1 January 2028: All German businesses must issue invoices electronically for domestic B2B transactions
What are the technical requirements?
To ensure a seamless transition, electronic invoices must adhere to the EN 16931 standard. However, businesses retain the capacity to negotiate the Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) standards used, provided mutual agreement is reached between invoice issuers and recipients.
Whilst Germany will eventually need to comply with the digital reporting requirement (DRR), as outlined in the European Commission’s VAT in the Digital Age (VIDA) proposal, the mandate is specific to invoice exchange between supplier and buyer and does not include a Continuous Transaction Controls (CTC) / centralised model.
How ecosio can help
For organisations preparing to navigate this change, understanding the specifics of the mandate and beginning the transition early can significantly mitigate the challenges associated with adopting new technological frameworks. Thankfully ecosio’s e-invoicing experts are able to support you as Germany embarks on this journey toward digitalisation.
ecosio.invoicing makes meeting country-specific regulations easy. Our state-of-the-art Integration Hub acts as a single gateway to connect your business to customers, tax administrations and other government platforms all over the world; enhancing automation, driving down costs and helping you to achieve compliance.
Find out more
For more information on ecosio’s unique EDI solution, please contact us at edi@ecosio.com or talk to our Sales team.
Der Beitrag Germany Commits to Making B2B E-invoicing Mandatory erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Explore the Latest in German E-Invoicing: Mandatory Implementation in B2B Sector starting from 2025 erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Compared to other European countries, Germany has rather complicated rules when it comes to electronic invoicing. This is due to the fact that regulations differ between the country’s 16 different federal states.
Since 18 April 2019 it has been mandatory for central public bodies in Germany to be able to receive and process e-invoices. Subsequently, in April of 2020 it became mandatory across all German states for suppliers to the German public sector to be capable of sending electronic invoices.
Current status of changes to German
e-invoicing legislation
On 23 February 2024 the German legislature took a step towards boosting economic growth and reducing bureaucratic hurdles with the Growth Opportunities Act. The law was passed by the Bundestag and later approved by the Bundesrat on 22 March 2024.A central component of the Growth Opportunities Act is the introduction of a new e-invoicing obligation for domestic business transactions. This modernisation is intended to optimise financial processes and reduce the administrative burden of traditional paper invoicing processes.The staggered implementation of the e-invoicing obligation is as follows:
- January 2025: all German companies must be able to receive and process electronic invoices.
- January 2027: German companies with an annual turnover of more than €800,000 must issue their invoices electronically.
- January 2028: All German companies must issue their invoices electronically.
To ensure a smooth transition, electronic invoices must comply with the EN 16931 standard. However, companies can negotiate the EDI standards as long as the invoice issuer and recipient are in agreement. This transition to e-invoicing demonstrates Germany’s commitment to technological innovation and makes German companies leaders in digital finance practices, promoting a more efficient and transparent economy.
Who will be affected?
The changes will affect all B2B transactions involving a German supplier where the goods/services in question are taxable in Germany. Once B2B e-invoicing is mandatory, all parties involved in such transactions will need the ability to create, validate, send and receive electronic invoices.
Why are these changes being proposed?
The country’s coalition government wants to simplify e-invoicing in Germany and is therefore keen to introduce a country-wide approach. The aim is not only to help to fight VAT fraud, but also to streamline the process of creating, verifying and sending electronic invoices.
How does e-invoicing in Germany compare to other European countries?
Germany is not alone in moving towards mandatory B2B e-invoicing. In Italy, Poland and Romania, for example, similar requirements are already in place. Meanwhile, several other countries, such as France, Belgium and Hungary, have publicly announced their intention to introduce similar legislation. This shift has also been accelerated by the European Commission’s recent proposal to optimise and improve VAT processes across Europe. This proposal, known as ViDA (VAT in the Digital Age) aims to simplify cross-border transactions by creating a single digital market within which businesses require only one VAT ID. And while no concrete guidelines have yet been issued as a result of this initiative, it is expected that formats compliant with the EN 16931 standard will become mandatory by 2028.
What e-invoicing standard is used in Germany?
The XRechnung is the preferred standard for B2G e-invoicing in Germany. The XRechnung standard was developed to align the EU specification to the pre-existing requirements of the German public administration. Technically, XRechnung is a Core Invoice Usage Specification (CIUS) of the EN 16931. The specification is now in force and used by national, regional and local bodies. The two supported XML formats of XRechnung are (as with the EN 16931):
- UBL (Universal Business Language)
- CII (UN/CEFACT Cross Industry Invoice)
In addition, the Factur-X (ZUGFeRD) standard can also be used if preferred, as this also aligns with the European standard. ZUGFeRD is a French/German standard which is predominantly used for hybrid invoicing*. A ZUGFeRD 2.1 invoice using the profile EN 16931 is a valid XRechnung as well.
*A hybrid invoice joins two separate types of invoice – structured format (XML) and human-readable format (PDF). This allows for automation, while still allowing for easy manual processing where necessary. Only the XML part can be used for XRechnung, however.
Is there a central German e-invoicing platform?
The current update to the German Value Added Tax Act (UStG) for B2B invoices doesn’t mandate the use of any delivery infrastructure such as Peppol. In fact, it doesn’t mention anything regarding the exchange protocol to be used. Consequently, there is also no central German e-invoicing platform.
It is expected that such a solution will be introduced at a later stage, when Germany introduces the mandatory central reporting system (aka “Meldesystem”).
Achieving compliance – what’s required?
To be prepared for the upcoming changes, businesses must have the capacity to create, transmit and receive invoices in structured formats.
It is important to note that e-invoicing does not mean simply sending an invoice electronically. For example, sending a PDF invoice to a customer does not constitute e-invoicing, as in such a transaction there is still manual effort required to extract data from the invoice and log it in the relevant place (e.g. accounting software). E-invoicing involves the automated exchange of invoice data between business partners via a computer-readable language. As opposed to more traditional invoicing methods, with e-invoicing there’s no manual data input required, as the exchanged data appears directly in the recipient’s ERP system.
To ensure you are prepared for the upcoming changes in German e-invoicing legislation, you might want to ask yourself the following questions:
- Are you able to process data automatically?
- Do you have sufficient internal e-invoicing expertise to ensure you maintain compliance with e-invoicing requirements in Germany and all other relevant countries moving forward?
- Are you confident of your ability to stay up to date with relevant e-invoicing legislation changes and update your system accordingly?
- Are message exchanges with your partners free from media breaks?
If the answer to any of these is no, you will need to optimise your existing systems/processes. As improvements can take time to implement, it’s important to start planning as soon as possible.
In more extreme cases it may be necessary to upgrade to an entirely new ERP system. However, for most businesses problems such as outdated technology and/or in-house expertise can be solved by enlisting the help of an experienced e-invoicing solution provider such as ecosio.
How ecosio can help with German e-invoicing compliance
As a fully managed EDI service provider, ecosio aims to help customers achieve maximum automation with minimum effort.
Over the years we’ve helped hundreds of businesses to implement reliable and futureproof e-invoicing systems, and are experts when it comes to optimising B2B integration.
At ecosio we don’t just provide software, or access to our network… we take care of the entire e-invoicing process for you, from initial setup right through to ongoing operation.
To find out more about how we can help, visit our e-invoicing solutions page. Alternatively, if you have any questions why not contact us directly? We’re always happy to provide assistance, and look forward to helping you implement a successful e-invoicing solution.
Are you aware of our free XML/Peppol document validator?
To help those in need of a simple and easy way to validate formats and file types, from CII (Cross-Industry Invoice) to UBL, we’ve created a free online validator.
Der Beitrag Explore the Latest in German E-Invoicing: Mandatory Implementation in B2B Sector starting from 2025 erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag What is an E-invoice and How Does E-invoicing Work? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>In this article, we’ll take a look at the development and functionality of an e-invoice, as well as the challenges and benefits of e-invoicing for companies.
Definition of an electronic invoice
So, what is e-invoicing? Let’s start with the definition of the electronic invoice according to the EU Directive (Directive 2014/55/EU of the European Parliament and Council from the 16th of April 2014 on electronic invoicing for public contracts), which states that invoice recipients in public tenders are obliged to accept electronic invoices.
Definition of an e-invoice: an “electronic invoice” is an invoice issued, transmitted, and received in a structured electronic format that enables it to be automatically and electronically processed;
This EU Directive is solely concerned with organisations which provide services for public procurement and issue invoices as part of these projects or undertakings. The invoice recipients, who in this case are public companies, are obliged to accept electronic invoices. According to the same EU Directive, there is no obligation for the invoicing party to issue electronic invoices, however individual states are free to tighten up these regulations when specific scenarios call for it. We’ve provided a comprehensive summary about this and the situation in Austria in our article, “EU Directive adopted for electronic invoicing in public procurement.”
While the structuring of data records through e-invoicing sits at the heart of the EU Directive and provides for further central elements that an e-invoice should contain, the situation from a tax point of view looks somewhat different. In regard to tax law requirements, there are country-specific variations which must be observed in order for companies to be legally compliant when using e-invoices for business transactions.
From a tax law perspective, the implementation of e-invoices is not a specifically technical implementation or indeed tied to a specific format; rather what is important is that a correct invoice is created from which input tax (for example, VAT) can be deducted.
The following are, among others, the required criteria:
- Authenticity of origin, relating to the certainty of the service provider’s identity and the identity of the invoice issuer.
- Integrity of the content
- Legibility – readable by humans
We will return to these points a little later in relation to the requirements for e-invoicing. As is already evident from the definition of an e-invoice, there are numerous different criteria that need to be complied with due to different legal requirements. Because of this, companies need to consider a range of legal principles, as well as country-specific regulations, in order to be fully compliant when using e-invoices.
An introduction to e-invoicing
The beginning: paper invoices
Even today, many invoices are still sent as paper invoices. This is a questionable format to use due to its consumption of valuable resources and the costs incurred by both sender and receiver. Not only are there additional postage costs involved, processing invoices manually also brings about other costs, such as personnel and infrastructure expenses, which make the overall process considerably more expensive.
One step further: PDF invoices
After the paper invoice, comes the PDF invoice. PDF invoices have become increasingly popular since the discontinuation of the formerly mandatory electronic signature. This change means that PDF invoices can now be sent via e-mail or made available for download. Although in comparison to paper invoices, PDF invoices reduce the effort for the sender, due to the change in media, they do not significantly reduce the effort for the receiver. This is because PDF invoices can only be transferred to the recipient’s respective ERP/FIBU system manually or by using copy-paste, as the PDF format itself is unsuited to recreating machine-processable data. Formats which are better suited to this are XML and EDIFACT.
The e-invoice
Let’s look more closely at e-invoices and the significant changes that adopting this format brings about for those who use it.
What is an e-invoice in essence and what makes it different from the paper and PDF invoices which came before it?
In contrast to paper or PDF invoices, the e-invoice doesn’t require any manual input from users and instead enables a fully automated approach; e-invoices allow organisations to transfer invoicing information electronically, receive it automatically, and to have that information processed within the recipient’s own system.
Unlike other types of invoices, the e-invoice presents its contents in a structured and machine-processable format which enables automated processing. During sending, the e-invoice generates a machine-processable format which is sent directly to the IT system of the receiver. This occurs without any manual intervention from the receiver and from this point the invoice is ready to be processed further.
Comparison of invoicing methods
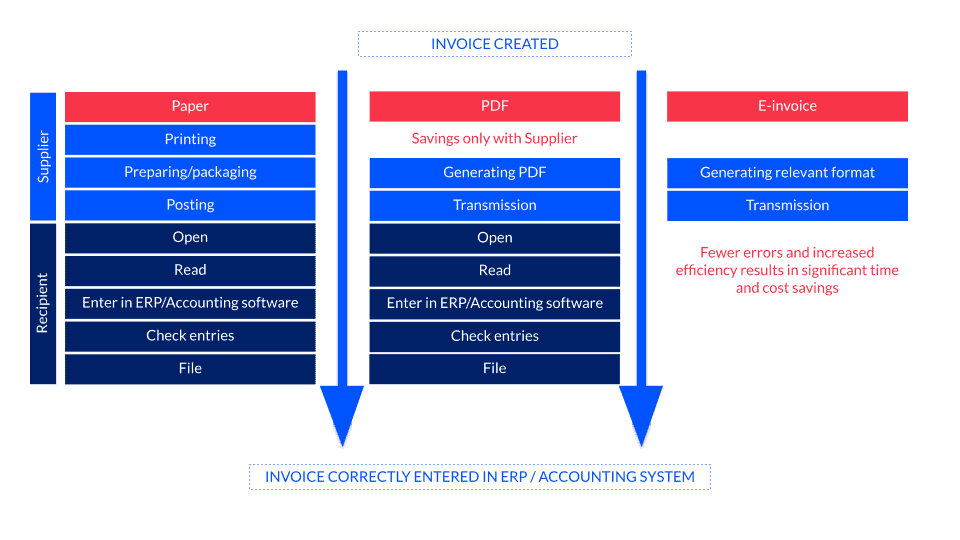
Using e-invoices / EDI invoices – challenges and requirements
Challenges in cross-border trading
Due to the country-specific formats and protocols which exist in relation to e-invoicing, there is a need for know-how and flexibility in cross-border trading, in particular relating to e-invoicing implementation. For many organisations, meeting the respective requirements needed to trade across borders can present something of a hurdle. It’s therefore important to evaluate if these challenges can be dealt with in-house, or whether it’s worth bringing in an external service provider with the necessary know-how to ensure a successful outcome.
In addition, the ViDA, issued by the European Commission, poses further cross-border trading challenges for companies.
VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA)
On December the 8th, 2022, the European Commission proposed a series of measures as part of ViDA (VAT in the Digital Age) to both modernise the value-added tax (VAT) system and make it more resilient against fraud. These measures were introduced in response to the loss of €93 billion in VAT in the EU in 2020. It is estimated that around a quarter of these losses can be attributed to VAT fraud in inter-community trade.
The European Commission has launched the “VAT in the Digital Age” initiative to improve the taxation of cross-border services and goods and adapt it to the challenges of the digital economy, in doing so closing loopholes and simplifying business procedures. The aim of the initiative is to ensure that businesses, in particular online retailers, make the correct VAT payments.
The following is an outline of the three main changes resulting from the ViDA:
- A new, real-time digital reporting system based on e-invoicing is to be introduced in 2028. In other words, e-invoicing is to become mandatory for all cross-border trading as of 2028.
- Updated regulations regarding VAT for the platform economy. Platforms for arranging passenger transport and short-term accommodation will be responsible for paying VAT to the tax authority, unless this is done by platform users themselves.
- Building on the existing “VAT One-Stop-Shop” model for online shopping businesses, VAT payments will be simplified for cross-border trade. Businesses will only need to register once for VAT purposes and will be able to fulfil all their VAT obligations through an online portal in a single language. This means that it will be sufficient for businesses to perform just one VAT registration when selling to consumers across the EU.
ViDA and electronic invoicing
ViDA aims to move towards real-time digital reporting based on electronic invoicing for companies that trade across EU borders. Key advantages arising from this include the reduction of administrative and compliance costs.
Compliance with the EU format is also addressed here. In cases where national e-registration systems are in use, they must support the EU format, which for electronic e-invoicing is EN16931. Business owners will need to bear in mind that the start of mandatory e-invoicing for cross-border trade has been set for 2028.
More information on ViDA (VAT in the Digital Age) can be found on the European Commission’s website under Taxation – Value added tax (VAT).
Ensuring the integrity of the invoice
As with previous invoicing formats, e-invoices are considered complete and unimpaired if the contents of the invoice have not been tampered with or altered in any way. However, this does not automatically mean that the invoice which has been issued contains the correct content.
Authenticity of the origin of an invoice
If the identity of the service provider or the invoice issuer can be guaranteed then the invoice fulfils the requirement for authenticity of origin. Authenticity can also be guaranteed through traceability.
Readability
The contents of each invoice should be fully legible and comprehensible. With e-invoicing, this can be facilitated through the use of the standardised messaging format.
Companies can choose to use one of a number of procedures to reliably meet the above criteria. However, as well as these requirements, there are, for example in Austria, the following additional e-invoice content requirements, which should also be taken into account:
- Name and address of the supplying company, or the company performing a specific service
- Name and address of the invoice recipient
- Quantity as well as description of the object of the invoice
- Date or time frame of services performed
- Invoice amount and tax rate
- Tax amount
- Date of issue
- Serial number
- VAT identification number (for invoices with an invoice amount of more than €10,000, the VAT identification number of the invoice recipient must be indicated)
In addition, depending on the type of enterprise, commercial law regulations also need to be observed:
- Legal status
- Registered office
- Company registration number
- Company accounts registrar
More information on this can be found in our blog article on the requirements of correct invoicing in Austria.
Furthermore, in Austria, additional content (such as the supplier number, order reference, etc.) must also be included, for example, when submitting an e-invoice to the federal government.
Archiving/Retention
It’s important to comply with retention periods for e-invoices. This applies above all to the tax office, which checks whether, for example, taxes have been paid correctly in Austria according to the Federal Tax Code. If the e-invoice has also been converted into another format, it must be clear from the retained file that no changes have been made to the document. For these reasons, it’s recommended to keep hold of both the original file and the converted file when possible.
Implementation of e-invoices
To ensure successful e-invoice processing and implementation, there are a number of additional aspects that need to be considered. Firstly, companies need to put in place workflows and systems for the creation and processing of e-invoices. Secondly, clarification regarding how e-invoices should be sent and received is needed. This clarification should pay close attention to country-specific regulations.
In addition to taking into account these requirements, there are also specific elements that the e-invoice itself must contain. The standard that specifies this was developed by the European Committee for Standardisation (CEN): EN 16931. Although this documentation provides useful recommendations for successful e-invoicing implementation, it only provides the fundamentals; each individual member state provides its own list of requirements, known as Core Invoice Usage Specifications (CIUS) to assist in the smooth implementation of e-invoices for businesses.
E-invoice standards and formatting
As we’ve seen, the CIUS only provides a basis for e-invoice implementation. Because of this, various versions of these have developed which has led to different e-invoice formats in different countries. This means that electronic invoicing can fall under different standards or specifications. In Austria, for example, the CIUS-AT-NAT was developed, while Germany has the XRechnung.
What exactly is regulated under EN 16931?
EN 16931 regulates core elements of electronic invoices, the requirements for which are syntax-neutral, i.e. prepared using plain or neutral language. However, the CEN does provide a list of permissible syntaxes (XML schemas) and we’ll provide concrete examples of those relating to the XRechnung in a later section of this article. What this regulation means for both sender and recipient is that for the e-invoice to be sent and received correctly both parties must be able to process the formats used.
How to send an e-invoice (using Germany as an example)
Different country requirements must also be taken into account when sending an e-invoice. In Germany, for example, there are two invoice receipt platforms (ZRE and OZG-RE) through which e-invoices can be transmitted to primary and secondary federal administration departments. For correct transmission, the sender must first determine which of these two platforms to use to send the e-invoice.
Various options can be used for the transmission of the e-invoice, with the type of transmission specified by each authority.
- E-mail & De-Mail (a German e-government communications service) with XML attachments
- Web entry
- Upload via an online form
- Fully automatic via Peppol
When invoices need to be sent frequently to federal government departments, it makes sense to use a fully automated transmission option via the Peppol protocol, which is supported by all authorities in Germany. In order to be able to transmit e-invoices via Peppol, a business will need a Peppol access point which can effectively communicate with the ERP system.
If the corresponding ERP system is already available in the company, it is worthwhile to convert an invoice in the respective ERP system into the necessary e-invoice format (e.g. XRechnung) automatically in order to transmit it immediately. To make this possible, there are fully automatic EDI solutions for the various ERP systems that can handle this conversion process. Through standardised import and export interfaces, the EDI systems can be integrated with the respective ERP system and therefore able to manage all electronic invoicing automatically.
When choosing the protocol, it is again important to consider which are prescribed by the country’s legislator.
How does e-invoicing work (using the example of XRechnung)?
Using XRechnung as an example, let’s now take a look at how e-invoicing works in practice.
As a mandatory e-invoicing standard in Germany, XRechnung affects all public institutions and authorities in Germany, as well as any companies that issue invoices to public administrators as clients. Suppliers, for example, must be able to create and send XRechnung invoices, while the authorities must be able to receive and process them.
Necessary steps:
- Clarify whether the company is legally required to create or receive the XRechnung (this varies from state to state).
- If so, implement the necessary e-invoicing standard in the company:
- Question current invoicing processes. How are outgoing and incoming invoices currently created and processed?
- If an ERP system is already in place, can it create or process electronic invoices?
Regarding the technical transfer of the XRechnung, according to the applicable standard, it must be transmittable or processed in one of the following two syntaxes:
a.) Universal Business Language (UBL)
b.) UN/CEFACT Cross Industry Invoice (CII)
Outgoing invoice – creating the XRechnung:
The relevant ERP system must create the invoice documents in the UBL or UN/CEFACT CII format. If this is not possible, the invoice must be converted to the required format. It is important that the conversion is automated and that the appropriate fields such as item description, identification numbers, units of measure, partner identification, etc. are maintained and can be converted accordingly. In addition, it is also essential that a receipt ID (called Routing ID in the XRechnung domain) is applied. Otherwise, the delivery of the document is at risk.
Incoming invoice – processing the XRechnung:
Before looking at importing an invoice via XRechnung, it is important to look at the workflow for approving and receiving invoices and to assess how well structured it is.The goal here is to convert XRechnung into a format that can be processed by the ERP system and to integrate the process seamlessly into that system. In addition to the format, the transmission channel (protocol) which receives the documents also plays an important role.
The various transmission options and the significance of the Peppol protocol are examined in detail in our white paper “Praxisleitfaden XRechnung und Peppol” (in German).
Verification of electronic invoices
As a general rule, companies should not send electronic invoices without prior verification. However, due to various legal regulations, there are differences in the criteria that need to be observed for successful invoice delivery. As mentioned above, most companies use an ERP system to map and automate processes. These systems can also export invoices in certain formats. However, these export formats are usually unable to meet the requirements for electronic invoices, making it necessary to convert or file them accordingly. Ideally, these conversions happen automatically, but this does not mean that the accuracy of the converted document is guaranteed. Various sources of error, for example, during input or directly during conversion, can lead to errors that need to be identified at an earlier stage. This is precisely where the verification of the e-invoice comes into play, so that these errors can be corrected earlier, long before the invoice is transmitted.
Verification can be performed in-house or by an external service provider. If a service provider is commissioned, it ensures that the e-invoice is transmitted to the relevant authority in accordance with the required standard.
Free online tool for validating Peppol and XML documents
Have you discovered our free online tool for validating Peppol and XML documents yet? It allows users to validate your documents according to EN 16931 (e.g. XRechnung), EHF, OIOUBL, A-NZ PEPPOL BIS3, CII Cross Industry Invoice, OpenPEPPOL formats, various UBL types, and many more.
Benefits of e-invoicing/EDI invoices
The use of electronic invoicing results in a number of advantages over traditional invoicing, although those benefits may vary slightly depending on several factors, such as the use of the transmission method. It should be noted that by cooperating with an external e-invoicing specialist, businesses can benefit from further advantages, depending on the specific services offered by the specialist in question.
Cost savings and efficiency gains in sending and receiving
Compared to sending and receiving paper invoices, electronic invoicing eliminates all costs associated with paper invoicing. The elimination of the manual paper process and automated invoicing process in the corresponding ERP/FIBU system also frees up the human resources involved in this workflow.
Reduction of material costs
The costs associated with paper, printers, postage, and more, are no longer a consideration.
Faster payment processes due to faster turnaround times
In contrast to paper invoicing, the time between sending and receiving an electronic invoice is significantly reduced. Once sent, the invoice reaches the recipient immediately. This significantly increases the probability of timely payments.
Minimising sources of error
By eliminating many manual processes thanks to automation, sources of error are significantly reduced.
Simplification of archiving
Archiving, which also plays an important role in invoicing due to the various retention periods required by law, is also simplified by e-invoicing. There is no need for a suitable room to store the paper invoices, nor is there any risk of invoices being lost in a fire. When invoices are archived digitally, they can be kept in electronic form and backups can be created.
Other advantages of using an external service provider in the context of e-invoicing include the following:
Technical compliance of e-invoices
External EDI service providers like ecosio ensure that e-invoices are fully compliant with e-invoicing requirements.
Cost savings through efficient and seamless automation
If an EDI service provider is contracted, then the automation of the invoicing process and the minimisation of manual processes is guaranteed, resulting in significant cost savings.
Flexible, scalable and future-proof
As experts in the field of electronic invoicing, EDI service providers make it possible to react quickly to changes in legal requirements, to scale invoicing processes if necessary, and make them future-proof.
User-friendliness
If the electronic invoicing process is integrated automatically into a company’s ERP system by the service provider, this enables companies to continue to work with familiar interfaces.
Zero hassle
Service providers such as ecosio further reduce complexity by enabling all invoicing processes to be handled via a single connection to the cloud. This means, regardless of the particular invoicing format or protocol, the stress and worry is taken out of the transmission and receipt of invoices.
The challenges of e-invoicing
E-invoicing, with its country-specific legal requirements and characteristics, not only poses challenges for companies when invoicing internationally, it also presents numerous hurdles when it comes to its technical implementation. Addressing this second challenge in particular will be of paramount importance for companies as having the correct technical integration is a necessary prerequisite for taking advantage of the many benefits e-invoices can bring about.
What this often means is that the switch to EDI invoices may initially involve increased costs to ensure its correct integration into a company’s system. However, over the long term these costs will turn into savings thanks to automation.
Getting the technical implementation right is an important first step in the successful implementation of electronic invoicing and companies need to be prepared to continuously adapt to both technical and legal requirements. This can be particularly challenging for internal IT departments. Depending on the availability of resources and internal expertise, company leaders must decide whether the e-invoicing requirements can be handled internally or whether an external service provider is actually the better choice.
If a company does choose to enlist the help of an external service provider, it’s important for them to consider how the necessary conversion will take place and which services are/aren’t included in the package they choose. For this reason, when choosing a suitable EDI service provider, it is crucial to take a close look at the services offered in order to successfully bring about the above-mentioned benefits of e-invoicing.
Country requirements
As we’ve already seen, there are numerous country-specific e-invoicing regulations which are especially relevant to organisations which operate on an international scale. In the list below, you’ll find some helpful articles that deal with how to implement and manage e-invoicing in different countries as well as related insights and an overview of that country’s specific e-invoicing requirements.
- E-invoicing in Belgium
- E-invoicing in Finland
- E-invoicing in France
- E-invoicing in Great Britain
- E-invoicing in Hungary
- E-invoicing in Italy
- E-invoicing in Norway
- E-invoicing in the Netherlands
- E-invoicing in Poland
- E-invoicing in Spain
- E-invoicing in Switzerland
- E-invoicing in Turkey
Summary
In summary, electronic invoices, also known as EDI invoices, e-invoices, and e-bills, are playing an increasingly important role in business transactions and accounting. Since the development and introduction of the EU Directive 2014/55/EU of the European Parliament and Council, e-invoices have gained even greater importance. While these legislative changes present challenges for many companies, they also bring about a number of sustainable benefits when implemented and managed correctly.
For companies, taking an honest look at existing capabilities and resources will be crucial to the correct implementation of e-invoices. If the question of whether e-invoicing can be handled internally without any worries cannot be answered with an unequivocal “yes”, it is worth consulting an external EDI service provider and expert in the field of electronic invoicing. This individual or team will not only take care of the complete automation of the invoicing process in conjunction with existing ERP systems, they will also know what to look out for in terms of different requirements and how to implement e-invoicing at the company in a manner that ensures long term sustainability.
If you are currently facing a similar decision, now is the time to get in touch. As a full-service provider in the field of electronic data exchange, at ecosio we are experts in electronic invoicing and its implementation. We are happy to advise you using our extensive knowledge and experience in the field.
Der Beitrag What is an E-invoice and How Does E-invoicing Work? erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Exchange of Electronic Invoices with the SAP eDocument Framework erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Before exploring the complexities of the SAP eDocument framework, let’s first consider the development of the e-invoice over recent years. In the past it was common practice to send paper invoices by post or fax. But since then, invoices have usually been created and transmitted digitally, for example as PDF documents that are sent by email. In the course of digitisation, the need for automation of existing processes is increasing. For this reason, and due to legal regulations, more companies are switching to e-invoices, which can be created, sent and processed automatically. Invoicing is carried out fully automatically using a structured exchange format (e.g. XML) between the IT systems of the participating companies – without any human interaction. This process not only saves time and money, but also reduces the likelihood of errors.
Governing institutions are increasingly focusing on e-invoices, which must be created in a certain processable format. This started primarily in Latin America to combat tax fraud. Since the use of the regulations has proven itself successful and authorities can thus act more effectively, European countries now also use similar guidelines.
The EU Directive 2014/55 / EU requires public authorities in Europe to receive and process electronic invoices. This resulted, for example, in the German CIUS (Core Invoice Usage Specification) XRechnung. The Italian Government went one step further on January 1st 2019 by obliging all companies in Italy to invoicing through the SDI system (Sistema di Interscambio). Likewise, there are already signs in Spain that the B2G e-Invoicing guidelines will be extended to the B2B sector.
E-Invoices in Use
Companies are therefore faced with the challenge of implementing various laws for sending and receiving invoices in IT systems. Depending on the country, different invoice formats are used and different transmission channels for e-Invoices are required. In particular, government institutions often rely on Web service-based approaches to transmit invoices – see, for example, the submission of ebInterface invoices in Austria or FatturaPA invoices in Italy.
Another challenge is the ongoing monitoring of e-invoice processes: were invoices created and converted correctly? Has the client received the invoice? Faulty invoices are a cause for complaint by the issuer and a well-used reason for non prompt payment.
When settling invoices through central governmental regulators (such as FatturaPA), the integrity check of invoices is already done by the authority. Invalid invoices will not be accepted and will not reach the recipient.
However, companies should focus primarily on their core business and therefore need a strategy that will allow them to work safely and efficiently for a long time, at the most up-to-date invoicing standards.
If an SAP system is used in the company as an ERP system, a component of this strategy can be the use of the SAP eDocument Framework in conjunction with the SAP Application Interface Framework (AIF). This framework is further discussed below.
SAP and e-invoicing: Overview of SAP Document Compliance
To enable SAP to better support its customers – especially in the area of e-invoicing – the eDocument Solution (also known as SAP Document Compliance) was developed for SAP ECC and SAP S/4HANA. This solution helps companies to meet the requirements of electronic invoicing in different countries.
How it works
With SAP Document Compliance, documents from logistics, sales and accounting can be converted into common e-invoice formats (e.g. XML files). In order to be able to respond to specific requirements of individual countries, the SAP Application Interface Framework (SAP AIF) can be used, which converts generated eDocuments into the required target format, such as the XRechnung for Germany or FatturaPA for Italy. In order to be able to map country-specific requirements in the AIF, “Packaged Solutions” must be imported. These build on the AIF and realise different country-specific requirements. In the case of FatturaPA, for example, these notes are to be entered separately in “Global AIF Settings & BC Sets” and “Italy-specific AIF Settings and BC Sets”.
To give the accounting system an overview of all eDocuments, SAP offers the eDocument Cockpit (EDOC_COCKPIT).
The benefit for you
As the first step in minimising the burden of issuing e-invoices, converting electronic invoices with SAP into popular formats provides a great relief for internal teams.
However…
After conversion the e-invoices must still be sent via a corresponding protocol or network (such as Peppol). In the case of government-mandated e-invoicing procedures such as FatturaPA in Italy, the exchange must also be carried out via a central service. This is not possible with the e-Document Solution alone.
In the next section we’ll look at the three available options for exchanging invoices with SAP Document Compliance…
Exchanging invoices with SAP Document Compliance – your three options
Option 1: Convert documents with SAP Document Compliance and AIF and send them via the SAP Cloud Platform
The SAP Application Interface Framework (AIF) is an SAP module for converting eDocuments into country-specific formats, such as the XRechnung. For the transmission of the created invoicing data the SAP Cloud Platform can be used, from which the invoices are forwarded to the receiver.
The SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) is a communication platform with which data from SAP ERP or S/4HANA can be exchanged with other systems. Web services are used to send and receive documents and messages to external systems. To use CPI, a subscription to the service is required.
Option 2: Convert documents with SAP Document Compliance and send them via an EDI service provider
Once e-invoices have been converted to the desired target format using the AIF, they can also be sent using a service provider.
To accomplish this, middleware is needed to link the customer’s SAP system with the service provider’s software. ecosio’s EPO connector is a perfect example of a lightweight middleware that performs this function. If another SAP middleware such as SAP PI or SAP PO is available, this can also be used for the “last mile” connection to the service provider. The following figure shows the principle used.
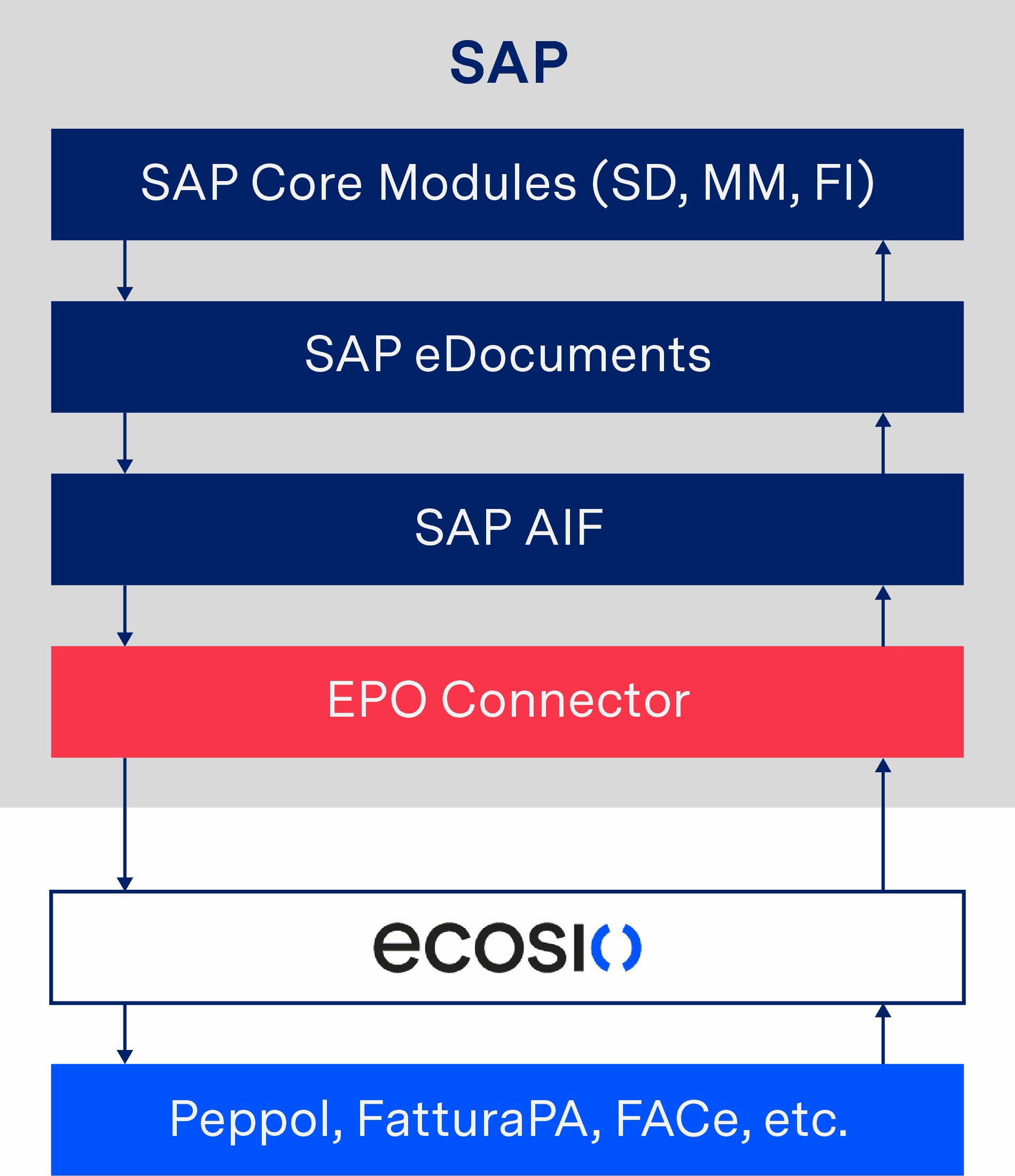
Conversion of an e-invoice via AIF and shipping via a service provider
As soon as an invoice arrives in the service provider’s system, the required data for the delivery of the invoice is extracted, enabling the e-invoice to be sent to the recipient. In the case of XRechnung, documents are delivered to the recipient’s Peppol access point, such as a German authority. Receiving data, such as an order via Peppol, is also possible in this way.
If only the AIF is used in conjunction with the EDOC_COCKPIT, the invoices are only stored on the application server and must be manually downloaded and sent from there. With a connection to the EPO Connector, however, the dispatch and receipt of the invoices as well as the transfer of the invoicing data to and from SAP takes place fully automatically and without manual interaction. This allows complete automation of the invoicing process.
But what if you are unable to convert documents with AIF? Although SAP AIF is part of SAP Business Suite / S/4HANA and standard in modern SAP releases, to use the “SAP Document Compliance, On-Premise Edition” you need a separate license. If this is the case for you, it may make sense to consider outsourcing the conversion of eDocument formats to a service provider. If the provider is already connected to SAP ERP, the required process can be implemented particularly quickly and easily. The following example shows an integration of SAP eDocument in conjunction with the EPO Connector.
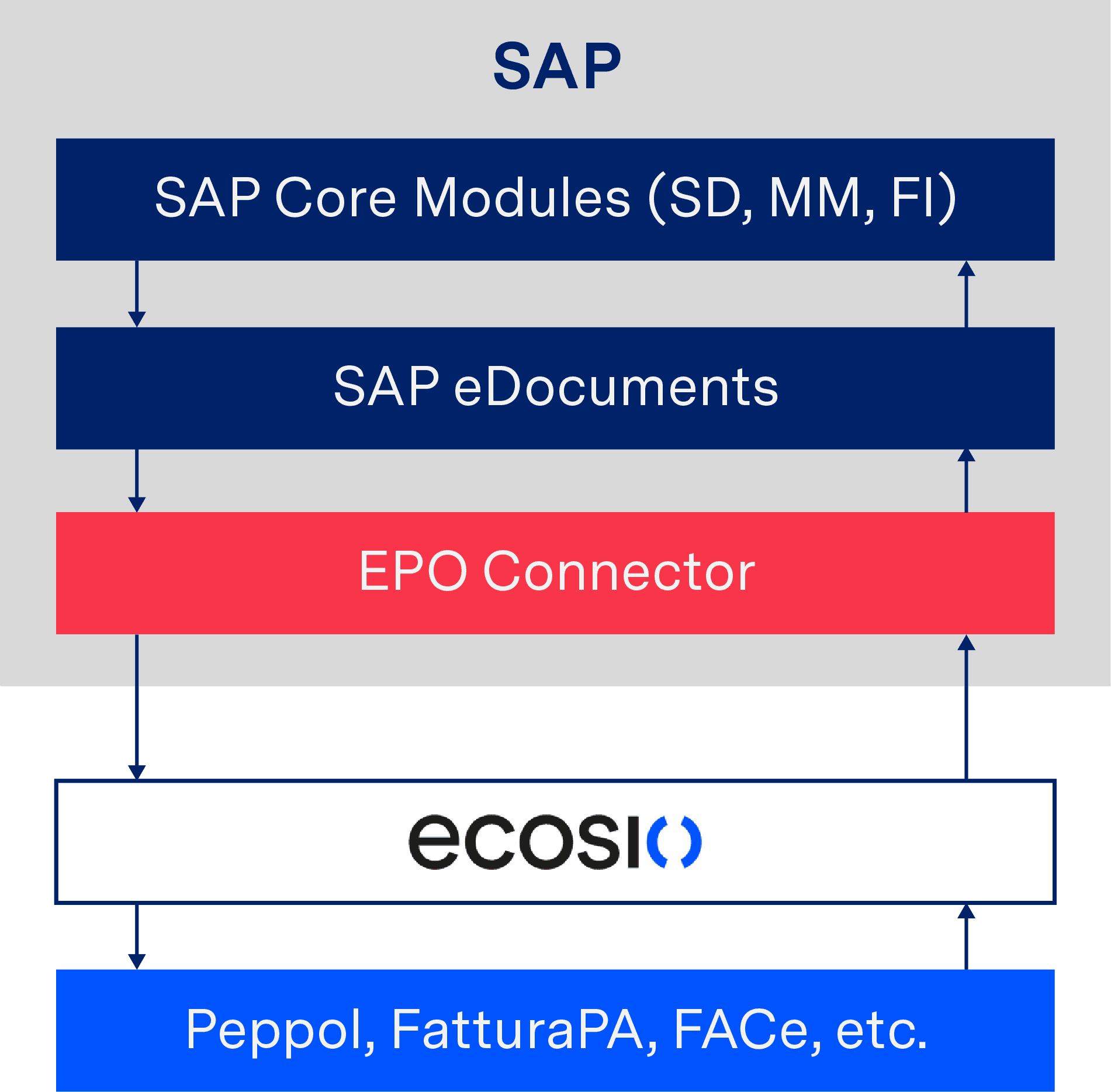
Conversion and sending of e-invoices with the help of a service provider
In this process, eDocuments are sent to the service provider via the EPO Connector, which then automatically determines the required invoice format and – if necessary – converts the document accordingly. It is then sent to the recipient as previously described.
Option 3: Use IDocs and a dedicated EDI service provider instead
The third and simplest option for internal teams involves bypassing the need to convert the documents internally (via Document Compliance) with a single connection to a fully managed service provider.
In such a solution, the provider is essentially a B2B network, creating and ensuring the success of all technical elements, such as conversion into all common and necessary formats, including e-invoicing requirements, as well as routing via various protocols, VANs and Peppol.
How this works
Let’s take the exchange of an invoice as an example using ecosio’s EPO connector…
Upon sending, the invoice data is transmitted directly from SAP ERP to the EPO Connector. The EPO middleware handles the conversion of the invoice into the required format and forwards the final document to your service provider. This takes care of the correct addressing and delivery of the e-invoice. The following figure shows the principle used.
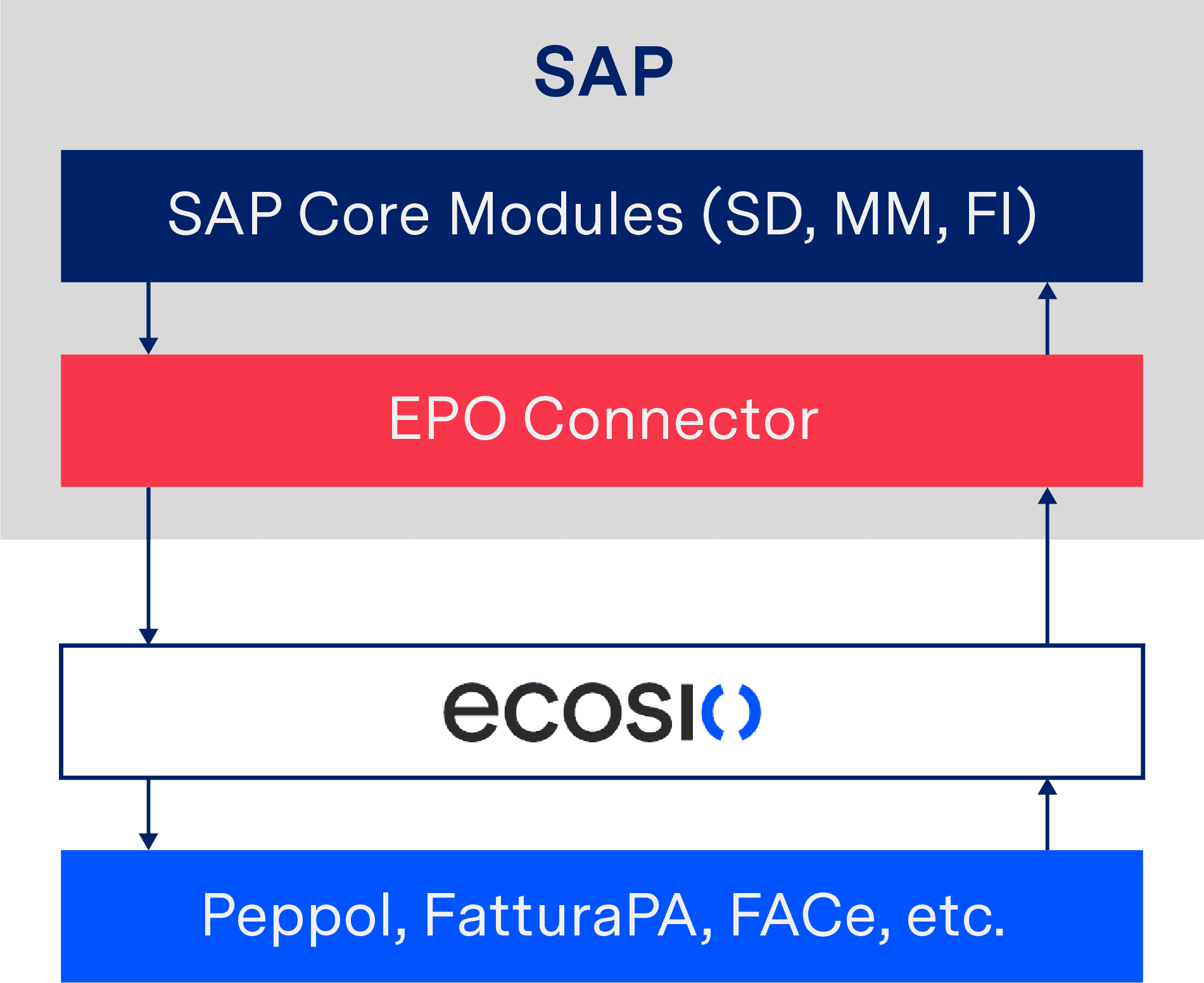
Conversion of an e-invoice via AIF and shipping via a service provider
The main advantage of this approach is the financial savings.
When using the AIF solution, many SAP notes must be imported. These in turn require a large number of further manual adjustments. For SAP consultants who work on a time and material basis, this can quickly become very expensive.
By contrast, using the EPO Connector in conjunction with ecosio eliminates expensive time and material costs, allowing you to work with predictable fixed costs. The final e-invoice solution is handed over “key in hand” and the exchange of electronic invoices can be fully automated.
The most efficient way to use fully managed EDI seamlessly in the familiar user interface of SAP systems is through integration via API (Application Programming Interface). This allows you to display the status of a sent message directly on the SAP IDoc or SAP document, for example, or to perform a full text search in all documents – for more information on what this means, see the following section.
The benefits of a fully managed EDI service provider
A fully managed service provider not only takes care of the conversion and transmission of e-invoices, but also the monitoring of ongoing processes. This way invoices that do not meet the required standard can be corrected immediately. In addition, converted invoices are validated before they are sent to ensure that the recipient has no reason to contest the invoice.
As e-invoicing is subject to constant change due to changing legal requirements, using a fully managed provider also provides peace of mind that your system will always be up to date. If new requirements are imposed by the legislator, these are implemented by the service provider and the company can make full use of the modified solution. There is no additional implementation effort for the company.
In short, fully managed EDI offers companies the possibility to use all EDI functions in their company without an expiration date – all while relieving internal teams.
Evaluating your options for document exchange with SAP
SAP document compliance undoubtedly offers a good basis for converting e-invoices into popular formats. Sending too can be effectively handled via SAP document compliance in combination with other SAP add-ons and extensive internal knowhow. However, handling EDI via a powerful single connection to a fully managed provider provides an easy-to-implement, future-proof and cost effective alternative for businesses without in-house expertise or simply looking to streamline the process.
To help you understand which option makes the most sense for you, we have identified 12 possible capabilities/funtionalities that you may desire from your SAP-EDI solution:
- EDI status visible on the SAP IDoc or SAP document (purchase order / invoice, etc.)
- Full text search across all documents
- Support for all standard EDI protocols
- Out-of-the-box routing to third party EDI networks (VANs)
- Out-of-the-box routing to Peppol
- Support for message conversion in EDI formats such as ANSI or EDIFACT
- Support for message split and merge
- Support for international e-invoicing requirements
- Automatic alerts when message failure occurs
- IDoc field conversions of ext./int. IDs in SAP
- EDI project coordination
- Ongoing support/monitoring/error resolution
For more information on these 12 points and to find out which solution offers what, download our white paper “EDI Integration in SAP: A Definitive Guide”. In it we expand on the specifics of these 12 functionalities and how they can benefit your business. We also compare the numerous options available to SAP users when it comes to EDI integration and how they differ in relation to these 12 factors.
Alternatively, if you have any other questions about EDI integration in SAP systems, or B2B data exchange more generally, please get in touch. We are always happy to help!
Are you aware of our free XML/Peppol document validator?
To help those in need of a simple and easy way to validate formats and file types, from CII (Cross-Industry Invoice) to UBL, we’ve created a free online validator. To try it out yourself!
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag Exchange of Electronic Invoices with the SAP eDocument Framework erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag Create and Process UBL Documents with Attachments in SAP erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>As of November 27th 2019, all federal agencies in Germany must be able to receive and process XRechnung. XRechnung is the German CIUS (Core Invoice Usage Specification), which originated from the EU standard EN 16931 . EN 16931 provides two types of XML schemas: Universal Business Language (UBL) and UN / CEFACT Cross Industry Invoice (CII). As a result, the ability to process CII and UBL documents is becoming increasingly important.
Companies that are contractors of public institutions must be able to create and send XRechnung. Furthermore, the billing format is also used in the B2B sector, which is why it makes sense for companies to make their ERP system fit for the creation, transmission, and receiving of XRechnung.
SAP ERP is one of the most popular ERP systems in the world but cannot create, convert or read documents out of the box according to the UBL standard. This means that without add-on modules, SAP ERP cannot work with the standard XRechnung and companies must look for suitable solutions.
Create UBL documents in SAP using the EPO connector
The SAP ERP system cannot generate XML files from the SD and FI modules that conform to the UBL specification. However, a solution can be created by using middleware in conjunction with a service provider. The EPO Connector happens to be a middleware solution that is integrated directly into the SAP system and helps connect further external products and services to the SAP. This means additional functions can be added to SAP cost effectively without having to intervene in the system itself.
In the following, we’ll look at how to use the EPO Connector to create UBL files with attachments, and also send and receive them.
Create and send XRechnung with attachments
Using the EPO Connector, e-Invoices can be created in UBL format from SD and FI documents. Since the middleware is written in ABAP and thus runs directly in SAP, no external tool is necessary, and the invoice workflow can be completely mapped in SAP. In addition, the EPO Connector can be used to integrate attachments into UBL that are directly embedded as Base64-encoded character strings in the document. For this purpose, UBL has its own attachment elements (cac: AdditionalDocumentReference):
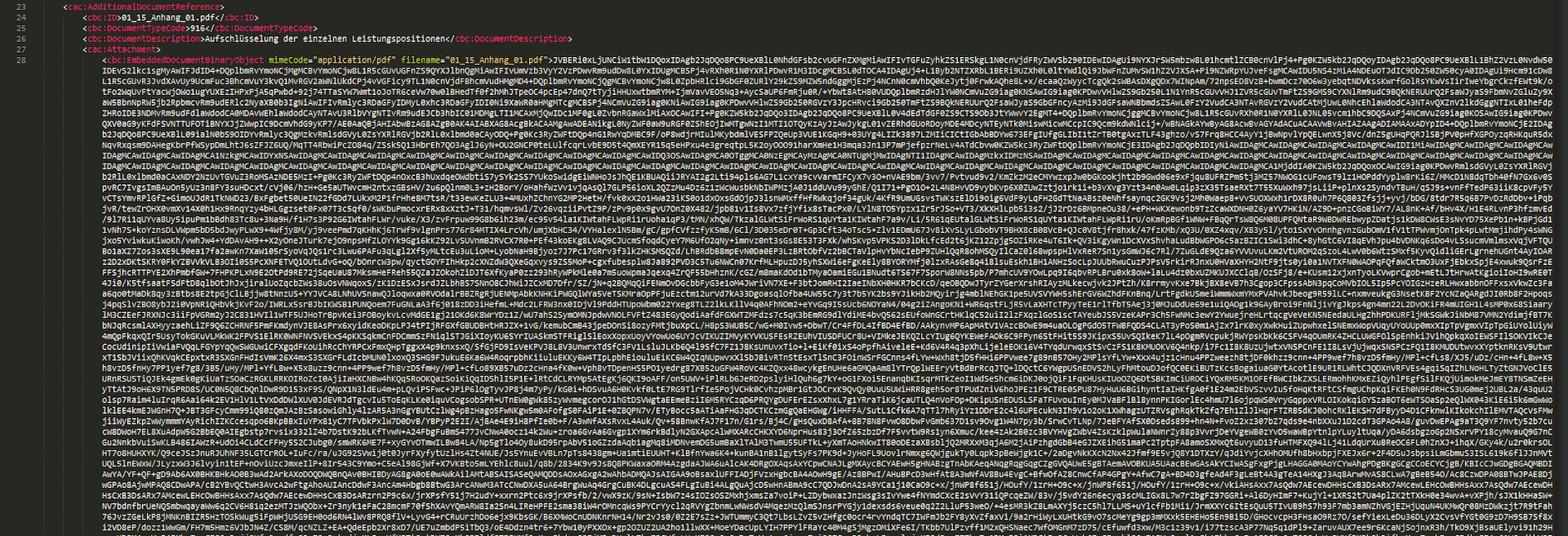
Extract of a Base64-encoded Attachment in UBL
The EPO Connector takes care of the correct coding and embedding of the desired attachments and creates the final UBL file according to the XRechnung specification. In order to be able to transmit the created e-Invoice to the recipient, a service provider such as ecosio can be connected to the middleware. ecosio reads out the sender and recipient ID as well as the document type and sends the invoice to the bill-to party via the required channel. This results in a consistent and seamless invoice delivery and invoice receipt process. Peppol (Pan-European Public Procurement Online), which was developed by the European Union to facilitate the exchange of data between companies and public authorities, must be used for the automatic sending of XRechnung. In this case, the service provider connects to the recipient’s Peppol access point, which receives the transmitted XRechnung and forwards them for processing.
Receive and process XRechnung with attachments
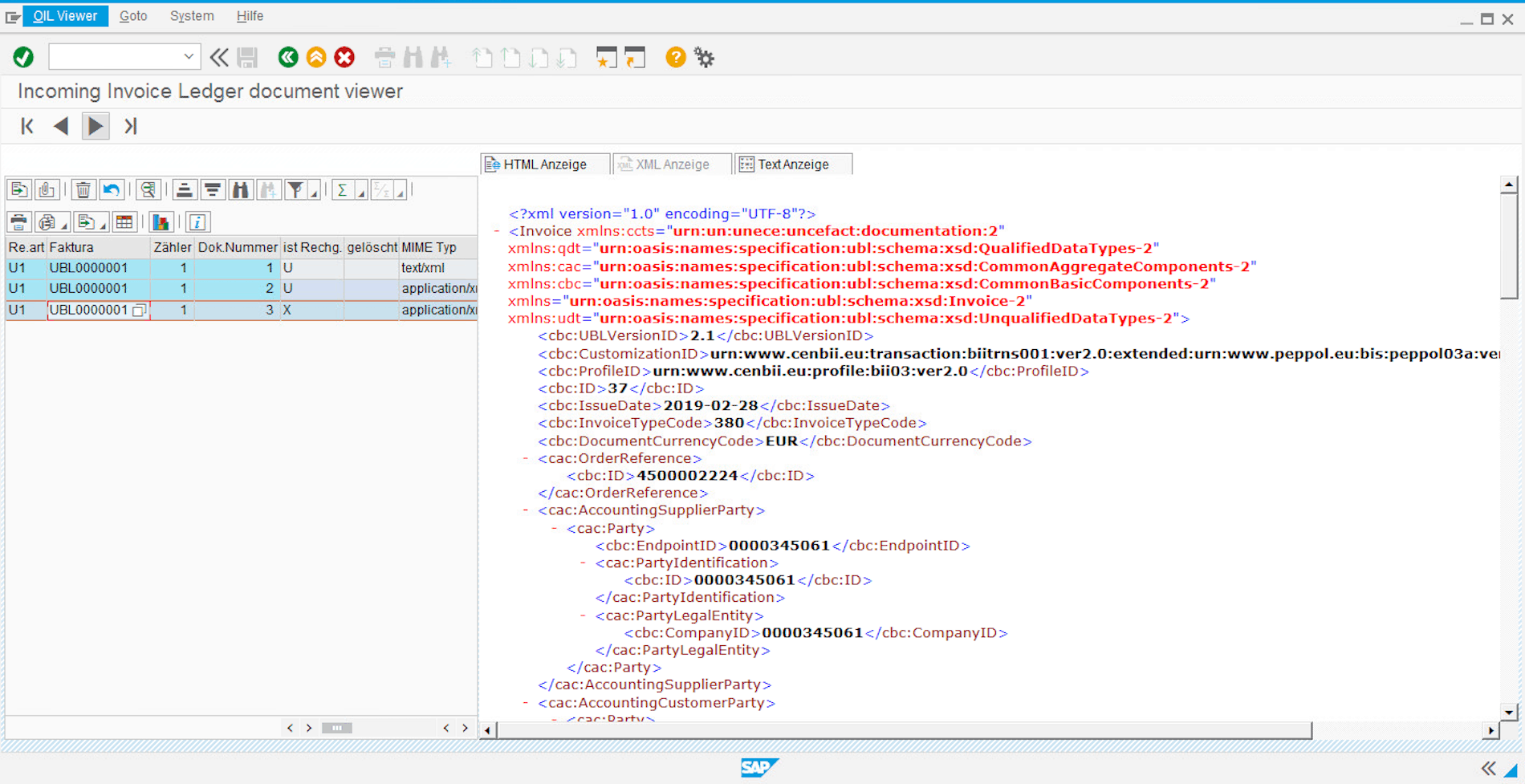
The invoice receipt process using the EPO Connector is like sending invoices. The EDI service provider receives invoices via the required protocols (e.g. Peppol) and transfers them to the EPO Connector, which controls the transfer of the documents to the SAP system of the company. Since SAP cannot work with the XML format UBL, the received documents must be converted to the required SAP format. The EPO Connector is responsible for the correct conversion and unpacks any attachments from the UBL.
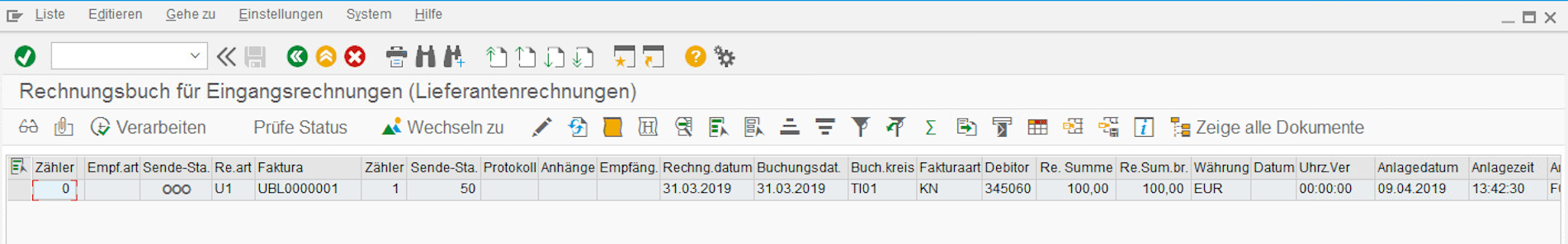
Invoice Book for Incoming Invoices Provided by the EPO Connector.
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
These attachments are appended to the final SAP document and can be viewed in the system as usual. The approval workflow can now be started in SAP and invoices released accordingly for payment.
© 2020. SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. Used with permission of SAP SE.
Transmission of UBL invoices by ecosio
Thanks to ecosio’s connection to the SAP system, documents can be sent in various structured formats via all common EDI protocols. In addition to the usual document exchange protocols such as X.400, AS2, SFTP, SMTP, OFTP2, as well as EDI networks such as GXS, INOVIS, etc., files can also be accessed via special platforms such as Peppol, FACe (Spain) or the Sistema di Interscambio (Italy).
This makes it quick and easy to send and receive UBL documents via the Peppol network.
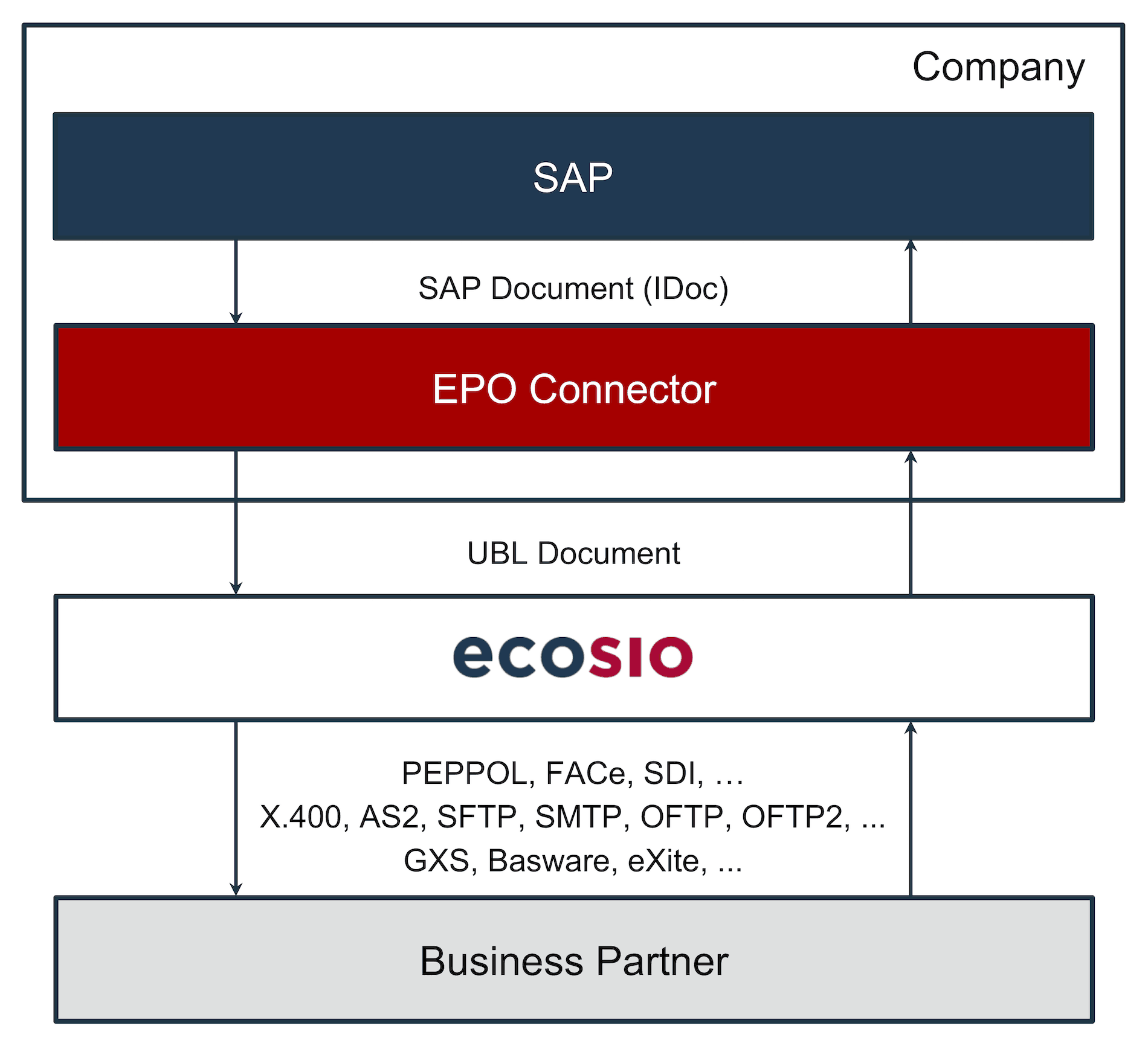
Conversion and Dispatch of UBL Documents with the EPO Connector and ecosio
Since ecosio allows the connection of any partner via different protocols, companies do not need to worry about expensive special programming in SAP. In conjunction with the EPO Connector, companies stay up to date with the technological requirements surrounding EDI and can focus on their core business.
Summary
The EPO Connector allows companies to convert invoices in SAP into XML format UBL and add attachments. Likewise, UBL documents can be received, converted into an SAP format and then edited. In conjunction with ecosio, the generated invoices can be sent via all standard exchange protocols. It is also possible to send and receive XRechnung via Peppol with ecosio.
Thus, companies are not dependent on expensive additional software for SAP but can pursue a long-term and cost-saving strategy to meet the ever-increasing requirements for e-Invoices.
Any questions?
Do you still have questions about UBL documents in SAP and how they can be created and sent? Feel free to contact us or check out our chat, we would love to help you!
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag Create and Process UBL Documents with Attachments in SAP erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag How to Validate an XRechnung Message erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Why XRechnung?
The XRechnung is the result of the implementation of the EU Directive 2014/55/EU, which states that contracting authorities in Europe must be able to receive and process e-invoices.
From this directive, the European Committee for Standardisation (CEN) developed EN 16931, which defines the basic components of an electronic invoice. Each member state can use this standard to create a refined guideline that addresses the specific needs of their administration. This is called Core Invoice Usage Specification (CIUS) and XRechnung is Germany’s version of this.
Did you know… ecosio offers a free tool which allows you to check your XML and Peppol messages for correctness and conformity with various formats such as XRechnung, OpenPEPPOL and more.
XRechnung: creation and transmission
For XRechnung implementation, there are two permitted syntaxes: UBL and UN/CEFACT Cross Industry Invoice (CII). This means that companies must transmit invoices in one of these two syntaxes and authorities must be able to accept and process them.
The Peppol (Pan-European Public Procurement Online) transmission protocol, which was developed to exchange data securely and reliably, is increasingly used for the mass transmission of invoices.
More details on the development, creation and transmission of XRechnung messages can be found in our article How to connect SAP to Peppol to allow the exchange of XRechnung.
Why should I validate XRechnung messages?
Most companies use an ERP system to map and automate processes. These systems normally export invoices in certain formats (e.g. IDoc in the case of SAP). However, this export format does not meet the requirements of XRechnung and must subsequently be converted into UBL or UN/CEFACT CII. This process is referred to as conversion, or mapping.
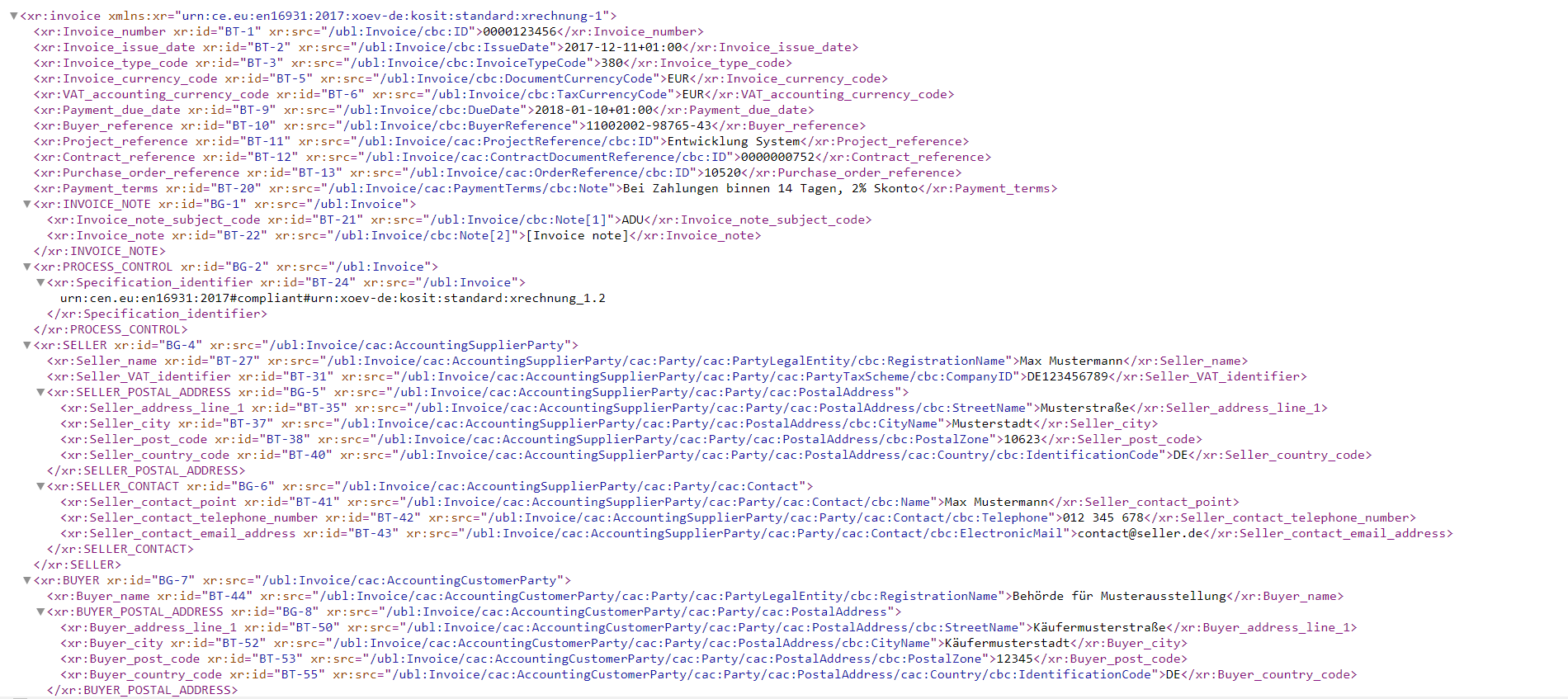
Section of an XRechnung in UBL (click to enlarge)
Ideally, this conversion is automated – but this alone can’t guarantee the document is correct.
There are two primary error sources:
- Mandatory fields are missing when the data is entered into the ERP system
- There is an error in the programme code during the conversion itself
By validating the document before it is transmitted, errors can be detected at an early stage. If, for example, obligatory data has not been entered, this must be communicated to the invoicing party. The biller then has the option of correcting the invoice and exporting it again.
As a general rule, invoices should only be sent if they are flawless and have been recognised as correct by a validation tool. Remember – an incorrect invoice is a reason to dispute the invoice!
How can I validate XRechnung messages?
In order to help you check that XRechnung messages are correct, we have developed a free online tool that can be used to validate a wide variety of Peppol or XML documents immediately.
Our tool can validate your XML documents according to all common specifications worldwide, from EN 16931 (e.g. XRechnung in Germany) to the A-NZ PEPPOL BIS3 for Australia and New Zealand, various UBL types, OpenPEPPOL formats, CII Cross Industry Invoice and many more – for different versions and document types.
If you would like to integrate this helpful tool directly into your own IT environment in the future, this is possible via a RESTful Web Service. For more information, please contact us.
Can I validate XRechnung automatically?
When you use an experienced e-invoicing service provider, such as ecosio, yes!
As well as handling conversion and transmission of XRechnung, a good service provider will also take care of document validation. The data exchange with the service provider works as follows…
The export file from the company’s ERP system is transmitted to the service provider, where the document is automatically converted into the XRechnung format.
Before the invoice is sent to the recipient, it is checked for accuracy, whereupon there are two possible scenarios:
- No errors occurred during validation and the creation of a valid XRechnung is thus confirmed. In this case, the invoice can be sent safely to the recipient.
- The validation was not successful and the e-invoice does not comply with the XRechnung standard. The incorrect invoice is not sent; instead a status message with a detailed error description is returned to the company’s ERP system. If, for example, data is missing, the invoicing party can then add it, export the document again and have it converted and validated by the service provider again.
Through this process, companies can ensure only invoices that comply with the standard are sent to clients. This way, companies can avoid invoice objections due to non-compliant XRechnungs.
Conclusion
Thanks to the software and tools provided by KoSIT, creating and transmitting XRechnung messages doesn’t have to be complicated. If a service provider is used, only invoices that comply with the standard will be transmitted to the authorities. Meanwhile, any errors detected are flagged in the company’s ERP system and can be corrected.
Want more information?
Still have questions about XRechnung messages or e-invoicing in general? Contact us or use our chat – we’re always happy to help!
SAP ERP® and SAP S/4HANA® are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag How to Validate an XRechnung Message erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>Der Beitrag How to connect SAP to Peppol to allow the exchange of XRechnung erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>XRechnung overview
Things are getting serious as of November 27th 2018 – all federal ministries and constitutional bodies In Germany must be able to accept electronic invoices according to the XRechnung standard. All the other federal organisations will follow up a year later, on November 27th 2019, and will also have to accept XRechnung. Suppliers, on the other hand, will still be able to send paper and PDF invoices.
Paper invoices will then completely disappear from November 27th 2020 in this sector – suppliers will henceforth have to generate all their invoices electronically in XRechnung format for the public bodies. Paper invoices will not be accepted anymore after that. Therefore, it is time for any supplier of a federal agency to deal with the topic of XRechnung.
But what exactly is an XRechnung?
The XRechnung was developed in Germany as part of the implementation of the EU directive 2014/55/EU. This EU directive dictates the creation of an individual European standard for the core elements of an electronic invoice. The public bodies of the EU-member states will have to accept electronic invoices which comply with this European standard. The EU directive has already become reality – the EU-member states already developed the standard: today it is known as the EU invoice standard EN 16931.
Since every EU member state will have specific requirements for electronic invoices, the need arose to develop so called Core Invoice Usage Specifications (CIUS). As a matter of fact, the XRechnung is a CIUS for Germany, even though it is not the only CIUS in Germany.
From a technical point of view, an XRechnung is an XML file, which complies with the XML schema according to the European standard EN 16931 and further restrictions dictated by the XRechnung. The European Standard EN 16931 provides two types of XML schemas: Universal Business Language (UBL) and UN/CEFACT Cross Industry Invoice (CII).
For SAP systems this represents the first challenge. SAP systems are unable to populate UBL or CII data on the SD side (Sales and Distribution) out of the box.
Learn how to unlock the potential of EDI with ERP integration
Why Peppol?
Further to define a uniform e-invoicing standard, the protocol to be used to send e-invoices to the authorities must also be determined. In theory one could use the whole spectrum of communication protocols, the same way they are being used for B2B transactions, such as SFTP, AS2, X400 etc. This would result in the authorities having to support all those protocols, including the disadvantages each one may represent.
In order to define a uniform standard, the legislator had to fall back on a rather popular standard in the B2G area within the EU: Peppol. Peppol is the acronym for Pan-European Public Procurement OnLine and was developed by the European Union. Its goal is to simplify the communication between suppliers and public bodies for e-procurement.
Technically, Peppol is the definition of a delivery infrastructure for electronic documents.
Peppol consists of:
- The Peppol e-delivery network
- The Peppol document specifications, which determine the structure of the electronic documents (Peppol Business Interoperability Specifications – BIS)
- A legal framework, which regulates the collaboration within this network (Peppol Transport Infrastructure Agreement)
In order to send and receive via Peppol, one must be equipped with a Peppol Access Point. Since it might prove quite costly from a technical and organisational point of view to create and register an Access Point, most companies will resort to a specialised service provider, through which one can reach the Peppol network.
Do you have any questions?
Do you have further questions about XRechnung or how to connect SAP to Peppol? Feel free to contact us, we would love to help you!
Are you aware of our free XML/Peppol document validator?
To help those in need of a simple and easy way to validate formats and file types, from CII (Cross-Industry Invoice) to UBL, we’ve created a free online validator.
SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE or its affiliates in Germany and in several other countries.
Der Beitrag How to connect SAP to Peppol to allow the exchange of XRechnung erschien zuerst auf ecosio.
]]>